![]() 21 Jan 2025
21 Jan 2025

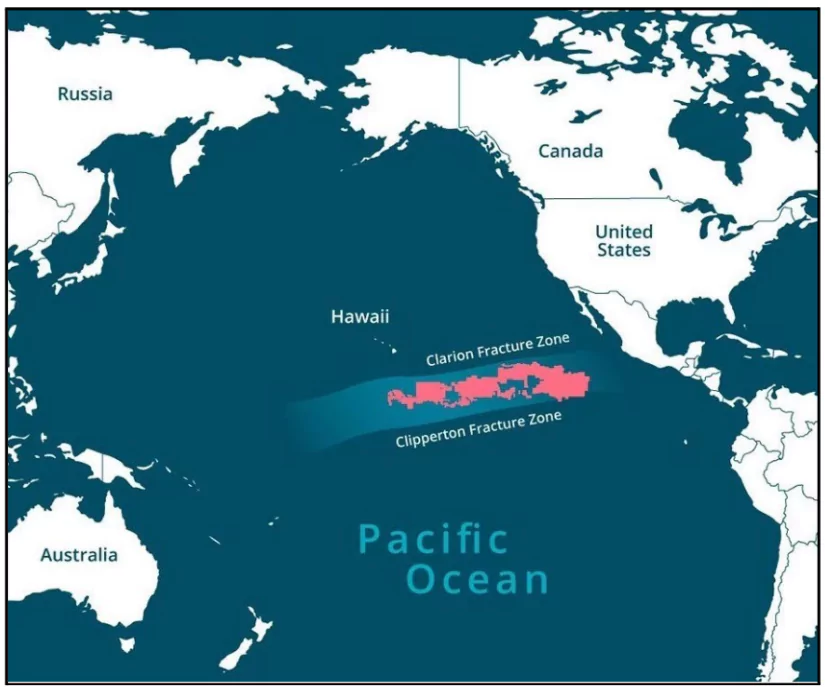
The recent discovery of “dark oxygen” production in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone has challenged conventional understanding that oxygen generation is solely tied to photosynthesis, which requires sunlight.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>