Context
Recently, archaeologists from Kerala University unearthed a 5,200-year old Harappan settlement at Padta Bet, around 1.5 km away, near Juna Khatiya, an Early Harappan necropolis, in Kutch district, Gujarat.
| A necropolis is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name derives from Ancient Greek, meaning “city of the dead“. |
Archaeological excavation reveals 5,200-year-old Harappan Civilization Settlement in Kachchh, Gujarat
- Archaeobotanical samples too have been collected from the site for further identification of plant exploitation and to understand agricultural practices.
- Few years ago, archeologists had unearthed a mass burial site with 500 graves on the outskirts of Khatiya village in Gujarat’s Kutch district.
Crucial Insights of the Recent Excavation On Harappan Settlement
- Discovered: Archaeologists discovered the presence of the skeleton, along with pottery artefacts, animal bones, semi-precious stone beads made of carnelian and agate, terracotta spindle whorls, copper, lithic tools, cores and debitage, grinding stones and hammer stones.
| Important Discovered Items |
Significance |
- Pottery Artefacts and the Animal Bones
|
- The pottery artefacts and the animal bones are representing cattle, sheep or goat and shell fragments.
- An Occupation Indicator: It points to possible animal domestication as well as shellfish exploitation.
- These are an indication of the occupation of the Harappan people.
|
|
|
- Unidentified Pottery Tradition: Ceramic artefacts could be from one of the unidentified pottery traditions of the Harappans, involving large storage jars to small bowls and dishes.
|
-
- Different Localities: Within the four-hectare area of Padta Bet, the researchers identified two localities:
- Locality 1: Artefacts dating back to the Mature Harappan era (2600 BC to 1900 BC) and Late Harappan era (1900 BC to 1700 BC).
- Locality 2: Artefacts from the Early Harappan era (3,200 BC to 2,600 BC), Mature Harappan era and Late Harappan era.
Given Hypothesis:
- Demographic Change on Different Localities: The population may have grown in the area, thus spreading out from Locality 2 to Locality 1 or that the inhabitants selected different areas to stay at different points of time.
- Impact of Unstable Nature: While the habitation site appears to have only a few structures, the researchers said it is possible that much of the structural remains were eroded due to the unstable nature of the landscape.
|
- Culture Formation and Evolution: Researchers believe that a network of such small Harappan settlements around the necropolis “might have played a significant role in the cultural formation of Early Harappan and subsequent occupations in this arid area.”
- Change in Burial Process: While Juna Khatiya was a burial ground from the Early Harappan phase, the skeleton at Padta Bet possibly indicates a change in burial practice over time.
- It is an intentional burial and it is possible that the skeletal remains (excavated at Padta Bet) are from the Late Harappan era or there might be a practice to bury within the habitational limits.
- There is no burial from the Late Harappan era at Juna Khatiya.
- Significance: The latest find supports the theory that the graveyard site may have served as a common facility for a cluster of several such smaller settlements.
About the Harappan Civilization
- It is one of the oldest in the world and has thrived along the banks of river Indus from around 5,000 BC to 1,000 BC.
- Classification: While the 2,500-year-long period from 5,000 BC to 2,600 BC is known as the ‘pre-urban’ Harappan phase, between 2,600 BC and 1,900 BC is the ‘urban’ Harappan phase. From there on, the civilisation declines and 1,900 BC to 1,000 BC is considered the ‘post-urban’ Harappan period.
Few Important Harappan Civilization Sites in Kutch, Gujarat
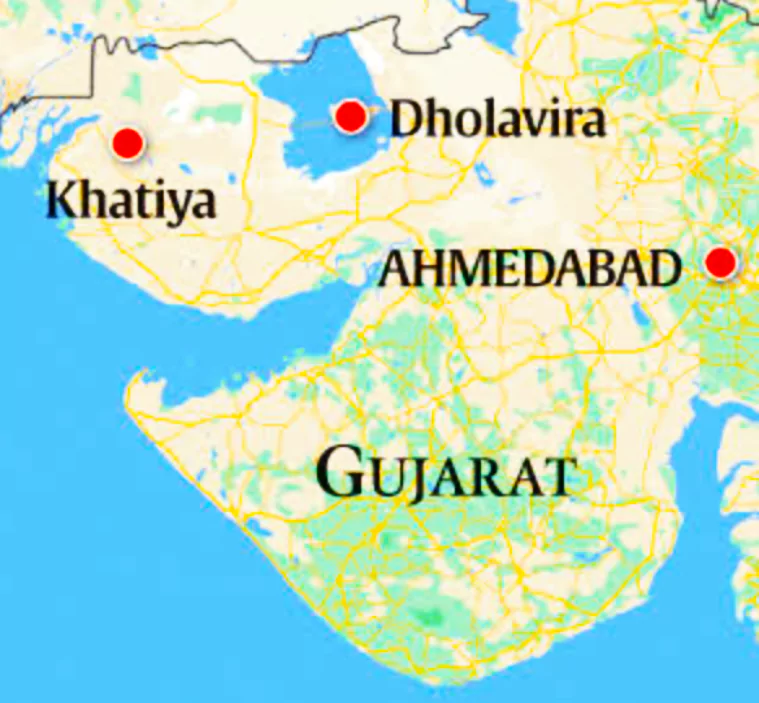
- Dholavira: It is the UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the biggest metropolises of the Harappan civilisation, is also in Kutch.
- It is 150 kilometres away from Khatiya that’s among the western-most of the Harappan sites in India.
- Given the distance, researchers believe that it is unlikely that people in the urban settlements of Dholavira were buried at the Khatiya site.
- Desalpar and Khirsara, Kotda Bhadli and Nadapa: These are the other well-known Harappan sites in western Kutch.
-
- But each of them is a site of urban and post-urban periods of the Harappan civilisation and more than 50 km away from Khatiya.
- Being a pre-urban Harappan cemetery, there is a possibility that either there was a big settlement in Khatiya or there were smaller settlements around Khatiya and the cemetery was a common burial ground for them.
About Juna Khatiya
- It is located in Kutch district, Gujarat.
- It is one of the biggest Harappan burial sites with the possibility of 500 graves.
- The burials discovered at this site date from 3,200 BCE to 2,600 BCE, predating Dholavira and several other Harappan sites in Gujarat.
- Significant Features:
-
- The site is important because others like Dholavira have a cemetery in and around the town, but no major habitation has been discovered near Juna Khatiya.
- The site demonstrates the transition from earth-mound burials to stone graves.
- The pottery from the site has features and styles similar to those excavated from early Harappan sites in Sindh and Balochistan.
|
Also Read: Indus Valley Civilization
![]() 4 Apr 2024
4 Apr 2024
