Context:
Recently, a study has been published in ‘Cell Stem Cell’ that researchers have created the first functional 3D printed brain tissue.
What is 3D Printing?
- It is also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three dimensional object layer-by-layer using a computer created design.
- This is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing processes, where a final design is cut from a larger block of material.
What Materials Can Be Used in 3D Printing?
- There are a variety of 3D printing materials, including thermoplastics such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), metals (including powders), resins and ceramics.
3D Printing Technologies
There are three broad types of 3D printing technology
- Sintering is a technology where the material is heated, but not to the point of melting, to create high resolution items. Metal powder is used for direct metal laser sintering while thermoplastic powders are used for selective laser sintering.
- Melting methods of 3D printing include powder bed fusion, electron beam melting and direct energy deposition,
- These use lasers, electric arcs or electron beams to print objects by melting the materials together at high temperatures.
- Stereolithography utilises photopolymerization to create parts.
- This technology uses the correct light source to interact with the material in a selective manner to cure and solidify a cross section of the object in thin layers.
|
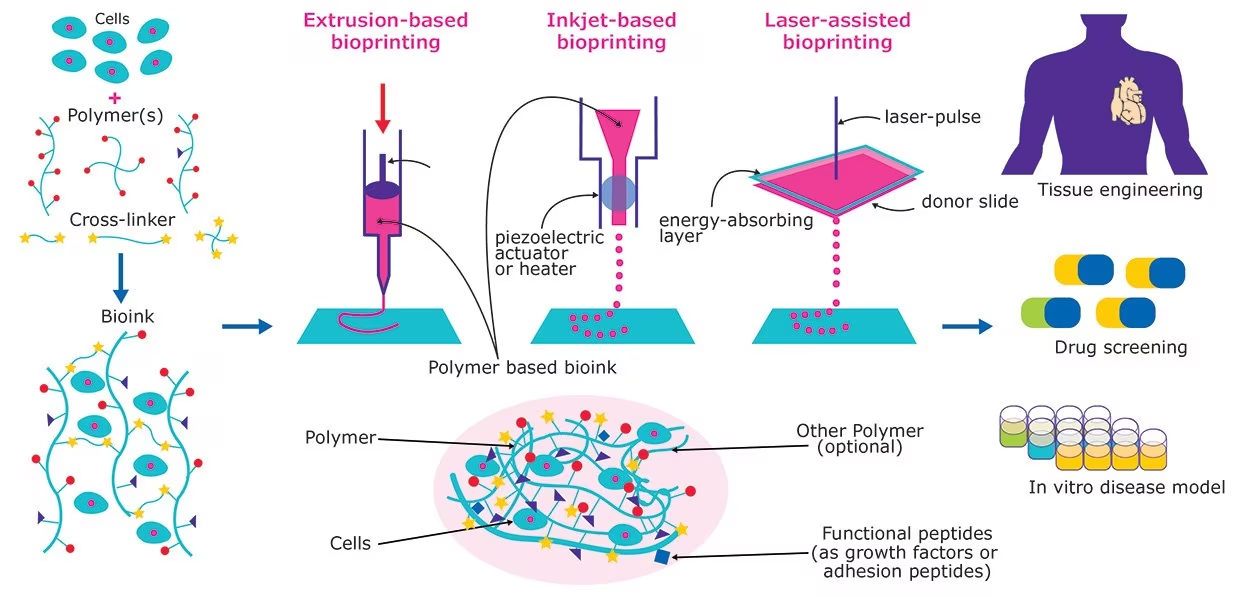
What Is 3D Bioprinting?
- A Computer-guided Process: 3D Bioprinting is a computer-guided process that builds layers of materials, cells, and other components to build living structures.
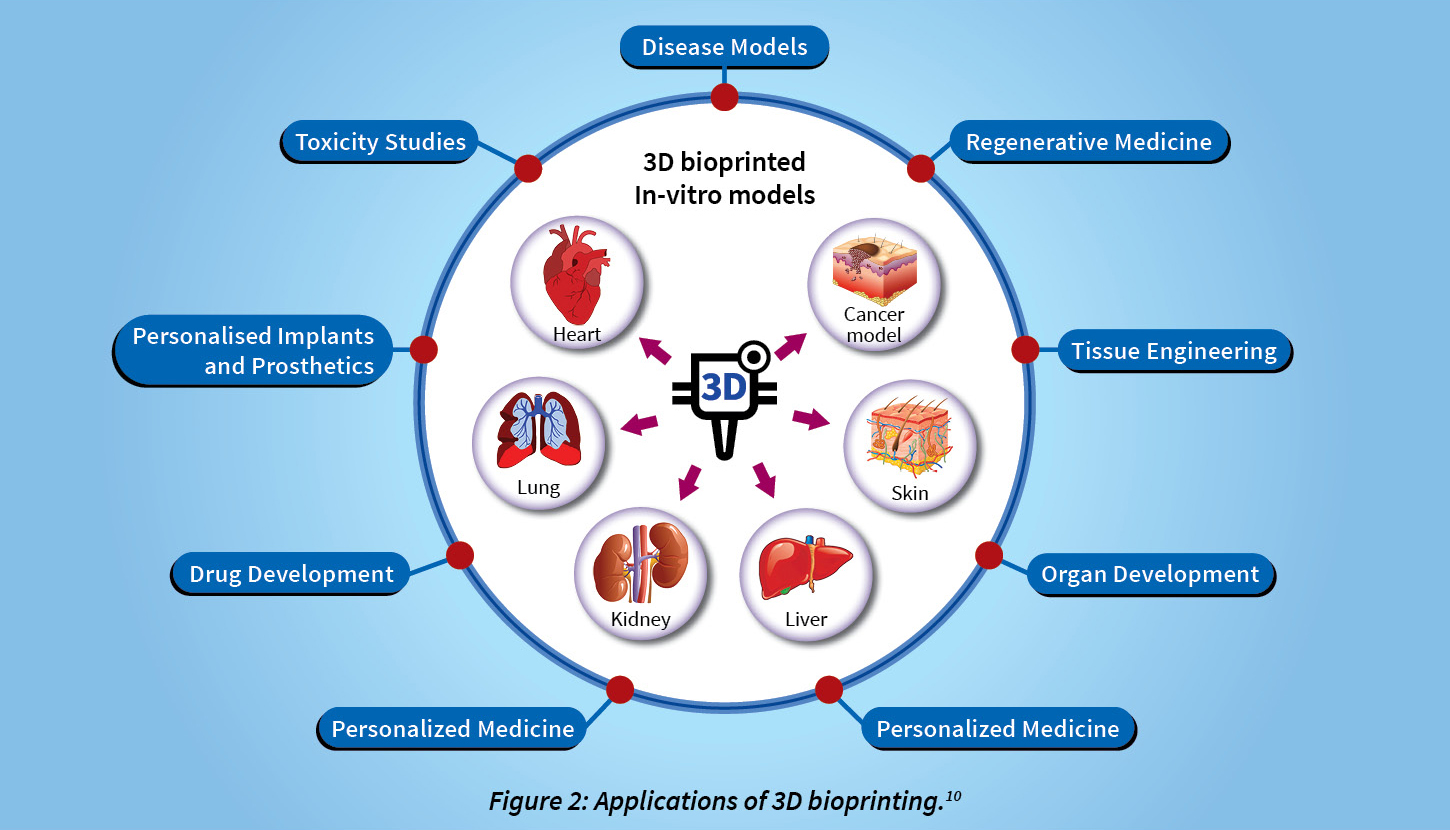
- Significance: It has huge potential for creating tissues that replicate, and in some cases even replace the real deal.
First Functional 3D Printed Brain Tissue
- A New Significant Tool for Scientists: It provides neuroscientists with a new tool for studying communication between brain cells and other parts of the human brain.
- Feature: It can develop and form connections in the same way as real human brain tissue.
- Usability: Many labs should be able to use it as it doesn’t need special bioprinting equipment.
- Significance:
- To Treat Diseases: It leads to better ways of treating diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Easy to Maintain: It is easy to keep healthy and can be studied with microscopes and other equipment typically found in most laboratories.
- Understanding Complex Working: Now it is possible to print the tissue by design and neuroscientists can have a defined system to look at how the human brain network operates.
- Concern: It is challenging to print functional human brain tissue and so far most 3D-printed tissues lack proper connections between cells.
- Neurons need to be able to mature while keeping the tissue structure intact, and supporting cells are essential for the tissue to function properly.
- Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. All neurons comprises three different parts- dendrites, cell body and axon.
- These are small, simplified, 3D copies of organs created outside of a living body, usually grown by treating combinations of tissues or stem cells with the nutrients and chemical signals (growth factors) that encourage them to differentiate and self-organize.
- These are a special type of cell found in multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals, which are yet to develop traits/characters that distinguish specific tissues from one another.
- These cells exist in both fully developed humans and their embryos, however, each contains a slightly different type of stem cell with different tasks.
Alzheimer’s Disease
- It is a chronic neurological condition characterized by worsening short term memory loss. Symptoms progress over time as the condition deteriorates.
Parkinson’s Disease
- It is a degenerative neurological disorder that mostly affects a person’s motor functions along with thinking, mood, and, in later stages, memory.
|
Conclusion
The precision of this 3D printing method allows control over cell types and arrangements, unlike miniature lab grown organs used for brain research called brain organoids. It can be used to look at the molecular mechanisms underlying brain development, human development, developmental disabilities, neurodegenerative disorders, and more. It will improve the process to create more specific brain tissues with guideable cells.
Also Read: Neuralink: Ethical Perspective
News Source: Science Alert
![]() 12 Feb 2024
12 Feb 2024

