Context
Mumbai and Dubai experienced contrasting extreme weather occurrences triggered by an anticyclone.
Extreme Weather Events in Mumbai and Dubai
Heat Wave in Mumbai: The Konkan coast of India, especially the city of Mumbai, has been undergoing a humid heat wave characterized by intense humidity.
- Santa Cruz weather station in the city recorded a maximum temperature of 37.9 degree Celsius (°C) and had a high relative humidity of 55 per cent.
- Heat waves are particularly lethal when high temperatures combine with high humidity, which is commonly referred to as a wet bulb.
- In such conditions, sweat from the human body isn’t able to evaporate, failing to stabilize the body temperature, which could ultimately cause heat stroke.
Floods in Dubai: Torrential rain accompanied by lightning inundated large areas of the city, causing flooding.
- Other Emirati cities like Sharjah and Abu Dhabi received excess rainfall with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) receiving its highest rainfall in 75 years, when records began.
- Other countries in the region like Oman and parts of Saudi Arabia and Bahrain received excessive rainfall, with 18 people killed in Oman due to flash flooding.
- Reason Behind Extreme Events: Both of these incidents were triggered by a vast anticyclone along with some localized weather phenomena, and further fuelled by general warming and increased moisture levels in the atmosphere.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
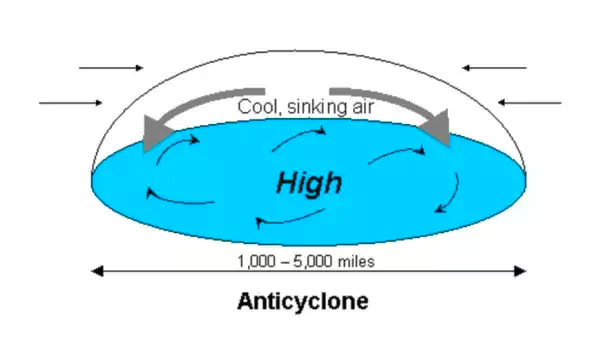
About Anticyclone
An anticyclone also known as a high pressure area is an area of high atmospheric pressure where winds blow in a downward sinking motion and in the process, compress and heat up. This causes dry and hot weather.
- Direction of Winds: The wind flows clockwise around it in the Northern Hemisphere, and counter-clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Impact: The net result of the anticyclone is a large-scale heat dome with air sinking, compressing and warming.
| Pressure System |
Pressure Condition at the centre |
Pattern of Wind Direction |
| Nothern Hemisphere |
Southern Hemisphere |
| Cyclone |
Low |
Anticlockwise |
Clockwise |
| anticyclone |
High |
Clockwise |
Anticlockwise |
Heat dome: It occurs when an area of high-pressure stays over a region for days and weeks. It traps warm air for an extended period.
- The longer that air remains trapped, the more the sun works to heat the air, producing warmer conditions with every passing day.
- Heat domes, if they last for a long period, may cause deadly heat waves.
|
Characteristics of Anticyclones:
- Season: Anticyclones can occur in both winter and summer with varying effects, but both are typified by low wind speeds due to a weak pressure gradient and stable conditions with no cloud.
- Expanse: Anticyclones can be very large, typically at least 3,000 km wide which is much larger than depressions.
Weather Condition Associated with Anticyclones
- Clear Skies: Anti-cyclones are associated with clear skies as the sinking air suppresses cloud formation.
- Calm Winds: The winds remain calm and gentle during an anticyclone, and there is almost no formation of clouds because here the air sinks rather than rises.
- Fog and Mist: Anticyclones can cause fog or mist to form, especially in low-lying or highly humid areas.
- Light Winds: Weak pressure gradients associated with anticyclones result in calm or light winds at the surface.
- From the high-pressure system’s center, the air tends to diverge outward, creating mild breezes or occasionally stagnant air.
- Blocking Weather pattern: They are generally related to large-scale and elongated heat waves but they also form a blocking pattern which doesn’t let other weather systems pass by and create conditions for extreme weather on their peripheries as well.
![]() 18 Apr 2024
18 Apr 2024
