Context
A recent study has discovered that the desert formed by the drying Aral Sea has significantly increased dustiness in Central Asia.
- Apart from the Aral Sea, other regions in West and Central Asia have also transformed into ‘dust bowls’.
- Lake Urmia in Iran and Lake Hamoun on the Iran-Afghanistan border have significantly diminished in size over recent decades.
About the Aral Sea
It is also known as Orol Dengizi (Uzbek) or Aral Tengizi (Kazakh).
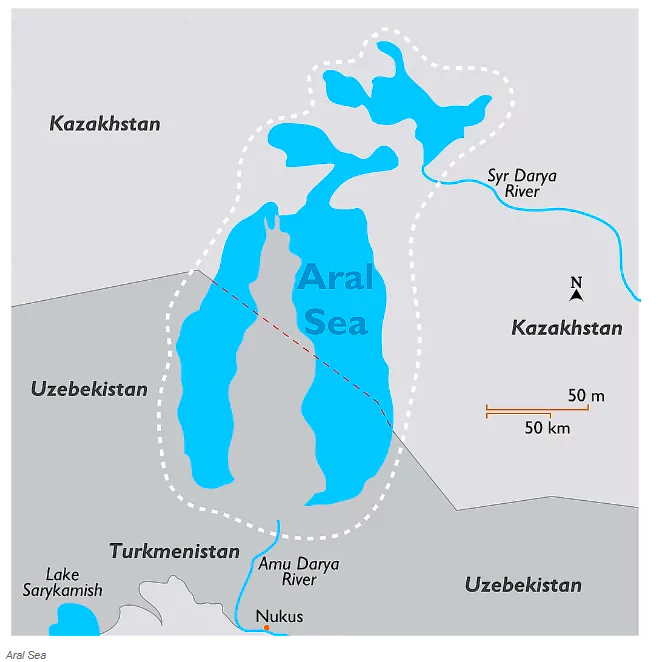
- It was the fourth largest inland lake in Central Asia.
- After the 1960s, It dried up and got converted into desert.
- Desert name: The Aralkum Desert
- It is smaller than neighboring deserts:
- Karakum (350,000 sq km) in Turkmenistan and
- Kyzylkum (300,000 sq km) in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan.
- Despite its size, the Aralkum Desert is a major human-made dust source worldwide.
- Location of Aral Sea : It lies across the border between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, extending from the south to the north.
- Climate: The area has a desert-continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Major rivers: The Amu Darya, known as Oxus in ancient times, and the Syr Darya, also called Jaxartes.
- They flowed from the Pamir and Tien Shan mountain ranges, respectively.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What are the socio-economic impacts of the Aral Sea Crisis?
The key findings of the report shows various socio-economic impacts of the Aral Sea Crisis;
- Increased Desertification: Over the past three decades, the drying of the Aral Sea has caused a 7% rise in dust levels across Central Asia. During the period from 1985 to 2015, emissions of dust from the expanding desert nearly doubled, increasing from 14 to 27 million tonnes.
- More cooling and heating: The two fold rise in dust emissions over the Aral Sea/Aralkum area has caused more cooling and heating at both the surface and in the air.
- Dust cools during the day by blocking sunlight and warms at night by releasing heat from the ground.
- The overall effect of dust on temperature depends on factors like dust amount, time of day, season, surface brightness, and dust properties.
| Desertification is when drylands become less productive because of natural or human-made causes.
Impacts of Desertification
- Destruction of Vegetation
- Soil Infertility
- Water pollution
- Loss of biodiversity & extinction of species
- Rise of famine, poverty, social conflicts
- Forces mass migrations i.e. environmental migration.
- Food Security Issues
|
- Dust storm: The aral sea has become a source of dust storms.
- Impact of Dust:
- Deteriorated air qualities: It can affect air quality in cities hundreds of kilometers away, thus can affect Dushanbe, capital of Tajikistan and Asgabat, capital of Turkmenistan.
| The Siberian High
It is a big area of cold, dry air that gathers in northeastern Eurasia from November to February. |
-
-
- Change in weather pattern: It can pressure air to go up by up to +0.76 Pascal each month.
- It can make the Siberian High stronger in winter and the Central Asian warm low weaker in summer.
- The dust events are seasonal and occur more in June, September, November, December and March .
- Health problems: Dust-Related Health Issues: The emergence of the Aralkum Desert has resulted in increased dust storms.
-
- People living nearby have breathing issues from breathing in tiny dust particles.
- Its dust is more harmful because it carries leftover chemicals from past farming.
- Waterborne Diseases: The remaining water in the Aral Sea became highly saline and polluted due to which Waterborne diseases increased, affecting public health.
- Reduced agricultural productivity: The dust can negatively affect agricultural areas downwind from the Aralkum Desert.
- Loss of Livelihoods:
- Fishing Industry: The fishing industry near the Aral Sea collapsed when the water level dropped. This caused fishing communities to lose their main source of money, which led to poverty and job loss.
- Agriculture: The diminishing sea size disturbed the usual farming methods. Fields that previously depended on the sea’s water for irrigation became unproductive, affecting crop yields and people’s ways of earning a living.
- Water Conflicts: Irrigation projects diverting rivers caused conflicts among countries sharing the Aral Sea basin (like Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan),
- The issue has worsened geopolitical disputes due to water scarcity.
- Economic Decline:
- Tourism: The Aral Sea used to attract tourists, but its vanishing hurt tourism earnings, impacting local economies.
- Trade Routes: The decrease of the sea disturbed old trade paths, impacting trade and connections between countries.
International efforts to address the Aral Sea Crisis
Here are some international efforts to address the Aral Sea crisis:
United Nations Joint Programme:
- A consortium of United Nations agencies, including UNDP, the World Health Organization, UNESCO, the UN Population Fund, and UN Volunteers, collaborates through a joint program called “Sustaining Livelihoods Affected by the Aral Sea Crisis.”
- Their tireless work aims to improve the lives and livelihoods of those impacted by the crisis
UN General Assembly Resolution:
- The United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution recognizing the Aral Sea region as a “zone of ecological innovations and technologies.”
- The resolution calls on all member countries to support the region.
- It focuses on the role of science and technology in overcoming challenges
- It also encourages investment in innovative solutions grounded in local knowledge.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Comprehensive Program of Measures:
- In 2018, the Presidents of Central Asian countries convened in Turkmenistan and established the Comprehensive Program of Measures to Mitigate the Consequences of the Aral Disaster and the Development of the Aral Sea Region.
- This program addresses water conservation, ecological protection, and coordinated efforts among Central Asian nations
- In October 2019, the United Nations team in Uzbekistan helped the government arrange a major conference.
- Two primary financing instruments:
- The International Fund for Saving the Aral Sea, created by neighboring countries, deals with economic, social, or humanitarian issues.
- The UN Trust Fund, with multiple partners, focuses on human security.
![]() 18 Apr 2024
18 Apr 2024
