![]() 29 Mar 2024
29 Mar 2024
English
हिन्दी
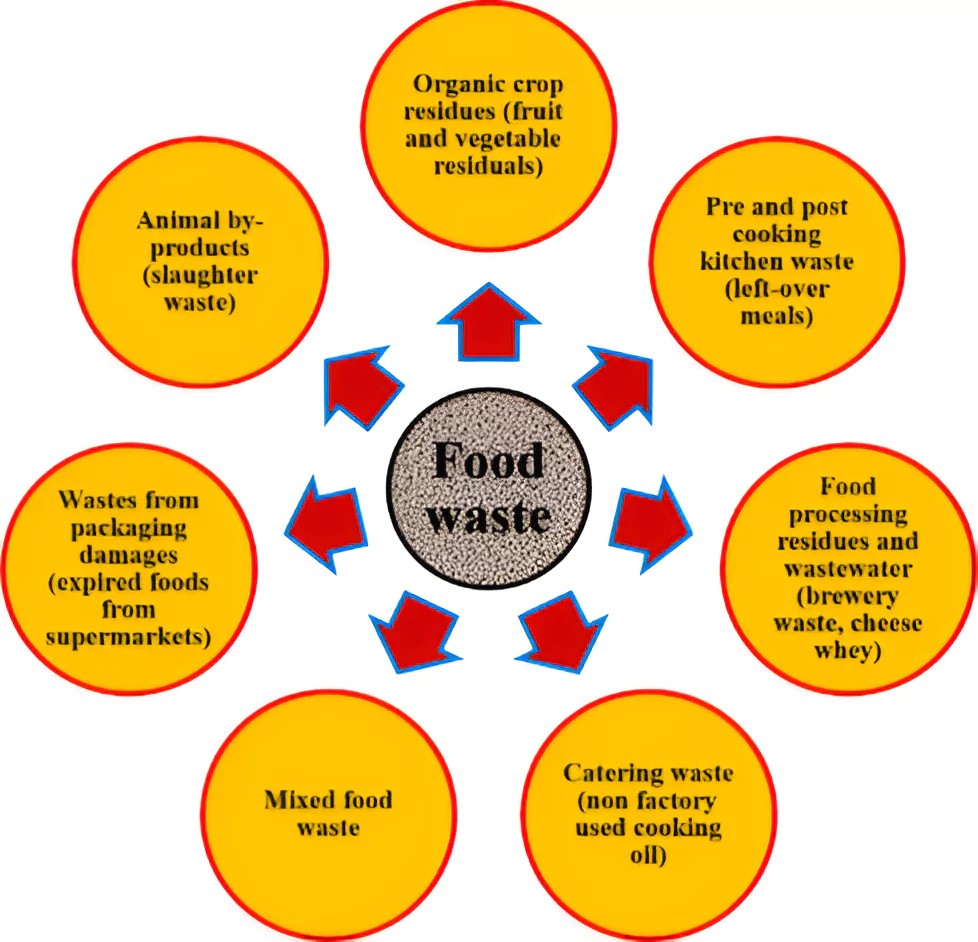
Recently, The Food Waste Index Report 2024 by the UN Environment Programme was released ahead of the International Day of Zero Waste (March 30).
International Day of Zero waste
|
|---|


| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>