Context
Recently, Florida, US, passed a law that prohibits people under 14 years old from having social media accounts, regardless of parental consent.
About the Florida Social Media Regulation Law
- Closure of Social Media Account: Under the new law, social-media companies are required to close accounts believed to be used by minors under 14.
- The platforms must also cancel accounts at the request of parents or minors, and all information from the accounts must be deleted.
- Restrictions: It also places restrictions on pornographic websites by requiring age verification for those who visit sexually explicit websites.
|
Karnataka High Court Proposes Social Media Age Limit
- Recently, the Karnataka High Court suggested to the Union Government that it should bring in an age limit for the use of social media.
- In March 2023, Utah became the first US state to adopt laws regulating children’s access to social media.
Usage of Social Media by Children
- About Social Media: It refers to digital technological platforms that enable people to talk to each other, get involved, share information, and work together.
- Statistics: As per UN, young people are the driving force of connectivity globally, with 79% of 15 to 24-year-olds online in 2023, compared with 65% for the rest of the world’s population. Around the world, a child goes online for the first time every half second.
- India’s Specific: A recent survey by LocalCircles indicates that urban Indian youngsters spend more time on the Internet.
Exposure of Children to Social Media
- Parental Exposure: Some children are exposed to social media by their parents, who knowingly or unknowingly get them addicted.
- Entertainment: Social media has turned into a hub for entertainment. This acts as a medium attraction for young minds.
- Boredom: In modern society, physical activities have taken a back seat and children are forced to access social media to get over their boredom.
- Easy Access to Digital Devices: Easy access to digital devices has made it easy for children to open a social media account and also use it frequently.
- COVID-19 Period: From the beginning of COVID-19 pandemic period, media devices, internet access and consulting social media rapidly increased. During “lockdown”, the Internet usage allowed communication with peers and the continuity activities such as school teaching.
Reasons for the Increasing Use of Social Media Among Children
- Peer Influence: Children often use social media to connect with peers. The desire to fit in and be part of social circles motivates them to join popular platforms where their friends are already active.
- Entertainment and Content Consumption: Social media platforms offer a wide range of content, including videos, games, and interactive features. Children are drawn to the entertaining and engaging content available on these platforms.
- Educational Opportunities: Some social media platforms offer educational content and opportunities for learning. Children may use these platforms to access educational resources, connect with experts, and participate in online learning communities.
- Parental Influence and Permission: In many cases, children gain access to social media with the permission or encouragement of their parents.
- Influence of Digital Culture: Growing up in a digital age, children are immersed in digital culture. The prevalence of smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices makes it easier for them to access social media, contributing to its increased use.
- Various social media sites promote “infinite scrolling”, display reaction metrics such as likes, feature auto-play videos and have live-streaming and push notifications.
Positive Impacts of Social Media On Children
Here are a few positive impacts of social media on children;
-
Critical Thinking:
- Social media can help children to think critically and build critical skills for the future.
-
Communicate:
- Social media helps children to communicate with people of similar interests, helping build knowledge.
-
Maintain Relation:
- Social media helps maintain relationships with friends and relatives who live far away.
-
Develop the Art of Learning:
- Social media helps individuals to develop and master the art of learning new things in life.
- The digital age and social media have created unprecedented opportunities for children and young people to communicate, learn, socialize, and play, exposing them to new ideas and more diverse sources of information.
-
Transparency:
- Using social media to provide context and evidence fosters transparency, potentially dispelling false narratives and rumors.
-
Support and Solidarity:
-
- Sharing the story on social media may garner support and solidarity from the online community, which can be emotionally uplifting.
Negative Impacts of Social Media on Children
Here are a few negative impacts of social media on children;
-
Violence:
- Social media, with its unfiltered content, can create violent tendencies among children. Involving the child in a social media dispute may have unintended psychological consequences, potentially causing additional stress and harm.
- Mumbai-based Association of Adolescent and Child Care in India (AACCI) surveyed schools in Mumbai and Gurgaon and found that aggression was on the rise.
-
Cyber Bullying:
- Young children, especially girls, are easily the victims of cyberbullying. Social media is the most probable source of such bullying.
- According to the latest cyberbullying statistics, over the last 10 years cyberbullying has rapidly grown, particularly among school-aged young people.
-
Pornography:
- Social media and pornography have close links. The young minds of children can get easily addicted to pornographic material, affecting their academic life.
-
Illegal Betting:
- Social media sites host many illegal betting pages. Children can potentially get addicted to such financially dangerous activities.
-
Mental Instability:
- Children start living in a virtual world looking at social media content. This affects their future mental peace and stability.
- A recent study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) revealed that teens who use social media more than three hours per day may be at heightened risk for mental health problems.
-
Socialization:
- Social media is not a substitute for physical socialization. Excessive social media use can affect a child’s social life.
-
False Information:
- Social media is a hub for false information. Children can be brainwashed easily through propaganda.
- As per a study of UNICEF, only 2% of children and young people have the critical literacy skills they need to judge whether a news story is real or false.
-
Impact on Health:
-
- The addiction of social media, in some instances, has manifested as impatience, aggression, concentration problems, memory issues, headaches, eye and back discomfort, stress, communication difficulties, lethargy, and even depression.
- The sleep pattern of children is affected due to excessive use of social media.
Kidfluencers and Ethical Dilemmas
- Kidfluencers: It refers to children – usually under the age of 16 – who become influencers on social media. Like adult influencers, they are also involved in promoting various brands and company products.
- Concerns: The impact of child monetization on social media (blurring of the line between kidfluencers and child exploitation), the blurring of protection and law enforcement as well as the exposure of these children to the public certainly has its own impact.
Various Ethical Concerns faced by Kidfluencers
- Issue of Privacy: Kidfluencers often share most aspects of their personal lives on social media, which poses a serious risk to children’s privacy and opens up opportunities for potential misuse of personal information.
- Issue of Consumerism: Kidfluencers can be influenced by their brand and product promotion, possibly pushing them towards unhealthy consumption from an early age.
- Lack of Clarity: Kidfluencers’ limited understanding of the difference between promotional content and honest content can create a lack of clarity in terms of morals and ethics.
- Impact on Education: Kidfluencers may miss out on important learning experiences at school or in their daily lives. They may feel pressured by the demands of constantly creating engaging content, thereby sacrificing time for formal education and healthy social interactions.
- Impact on Growth and Development: Intense exposure to social media can affect children’s mental health. They may feel pressured to maintain a perfect image on social media, and this can interfere with their identity development.
- Sometimes, bullying and harassment cause online abuse and its psychological impact.
|
Ways to Reduce Negative Impacts of Social Media On Children
- Parental Control: Parents must keep a watch over their children’s social media activity. Parents must win the confidence of their children and guide them.
- Digital Education: It is the responsibility of the parents, teachers as well as authorities to inculcate digital education among children, in order for them to use social media in a beneficial way.
- Regulation of Social Media: Social media companies must self-regulate their activities or the government must make them do it.
- Freedom of opinion and expression is guaranteed by the Indian Constitution. Proper ethical standards for social media usage need to be designed but it should be dynamic too technologies and the way that technologies are used are constantly changing.
- Counseling: Professional counselors can help children overcome the habit and addiction associated with social media.
- Example: The World Health Organization recommends no screen time for babies under 2 and no more than one hour of screen time a day for those aged 2 to 4.
- Technology Solutions: Instead of relying solely on censorship, the government and intermediaries can invest in technology solutions to tackle misinformation and fake news.
- Example: Algorithms can be developed to identify and flag false information, and fact-checking websites can be promoted.
- Self-Regulation: Intermediaries can adopt self-regulatory measures to prevent the spread of fake news and misinformation.
- Example: By setting up internal committees to monitor content and flag any false information and working with fact-checking websites to ensure accuracy.
- Collaborative Approach: The government, intermediaries, and civil society organizations can work together to develop a digital and social media safer environment for children and all.
- Example: By setting up a joint task force to identify and remove false and irrelevant information and promoting media literacy among the public.
- Adopt and Enact Legal Guidelines: The UN Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC) recommended that States take strong measures, including legislation, to protect children from harmful and misleading content.
- Children should also be protected from all forms of violence, including child trafficking, gender-based violence, cyber-aggression, cyber-attacks and information warfare.
- Children’s perspectives and experiences need to be considered when drafting policies that govern the use of young people’s digital use, as well as when designing the technology itself.
- China has issued guidelines for minors who would not be allowed to use most internet services on mobile devices from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m., and that children between the ages of 16 and 18 would only be able to use the internet for two hours a day.
International Actions to Protect Young People Online
- Cybersecurity: The Child Online Protection (COP) Initiative is a multi-stakeholder network launched by the International Telecommunication Union to promote awareness of child safety in the online world and to develop practical tools to assist governments, industry and educators.
- Cyberbullying: The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) has teamed up with social media platforms to answer some of the most common questions about cyberbullying and give advice on ways to deal with it.
- UNICEF’s Kindly initiative aims to end cyberbullying — one message at a time.
- Sexual Exploitation and Abuse: UNICEF supports coordinated national responses to online child sexual exploitation in over 20 countries – using the WePROTECT Global Alliance model – strengthening the capacity of on-the-ground responders to provide services to victims.
- Human Trafficking: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) supports Member States in their efforts to prevent and combat human trafficking, including through online safety awareness activities aimed at children and young people.
- Internet for Trust: UNESCO is leading the global effort to develop regulatory solutions to improve the reliability of information on digital platforms in the face of rising disinformation.
- Convention on the Rights of the Child: Children’s rights are enshrined in this Convention. The UN Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC) monitors implementation of the Convention and has laid out the ways that young people and children should be treated in the digital world, and how their rights should be protected.
Child Online Protection Act in India
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (‘DPDPA’ or ‘Act’): Section 9 of the Act deals with the processing of personal data of children. For everyone under the age of 18, the Section places the following three conditions for processing children’s personal data.
- Obtaining verifiable consent of the parent.
- Processing of personal data to be in alignment with the well-being of a child.
- Ban on tracking or behavioural monitoring of children or targeted advertising directed at children.
About Safer Internet Day
- Supported by: UN agencies and partners, including innovators in the private sector, are forging a digital path towards boosting safety online, especially for children and young people.
- With support from ITU, UNICEF and UNODC, Safer Internet Day is celebrated in February every year.
- Aim: From cyberbullying to social networking to digital identity, each year it aims to raise awareness of emerging online issues and current concerns.
|
Conclusion
Like the coin, social media also has its two sides, it can be a powerful tool and on the other hand, it also poses some ethical challenges that need to be addressed by adopting appropriate measures. In the digital age, instead of banning social media access to our future generation, it would be better to ensure improved parental oversight tools, improved access to data to stop bad actors, alongside major investments in mental health systems and programs.
Also Read: Social Media And Civil Servants
| Prelims PYQ (2020):
In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the funds and other benefits?
1. Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
2. Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
3. Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion.
4. Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b) |
![]() 29 Mar 2024
29 Mar 2024

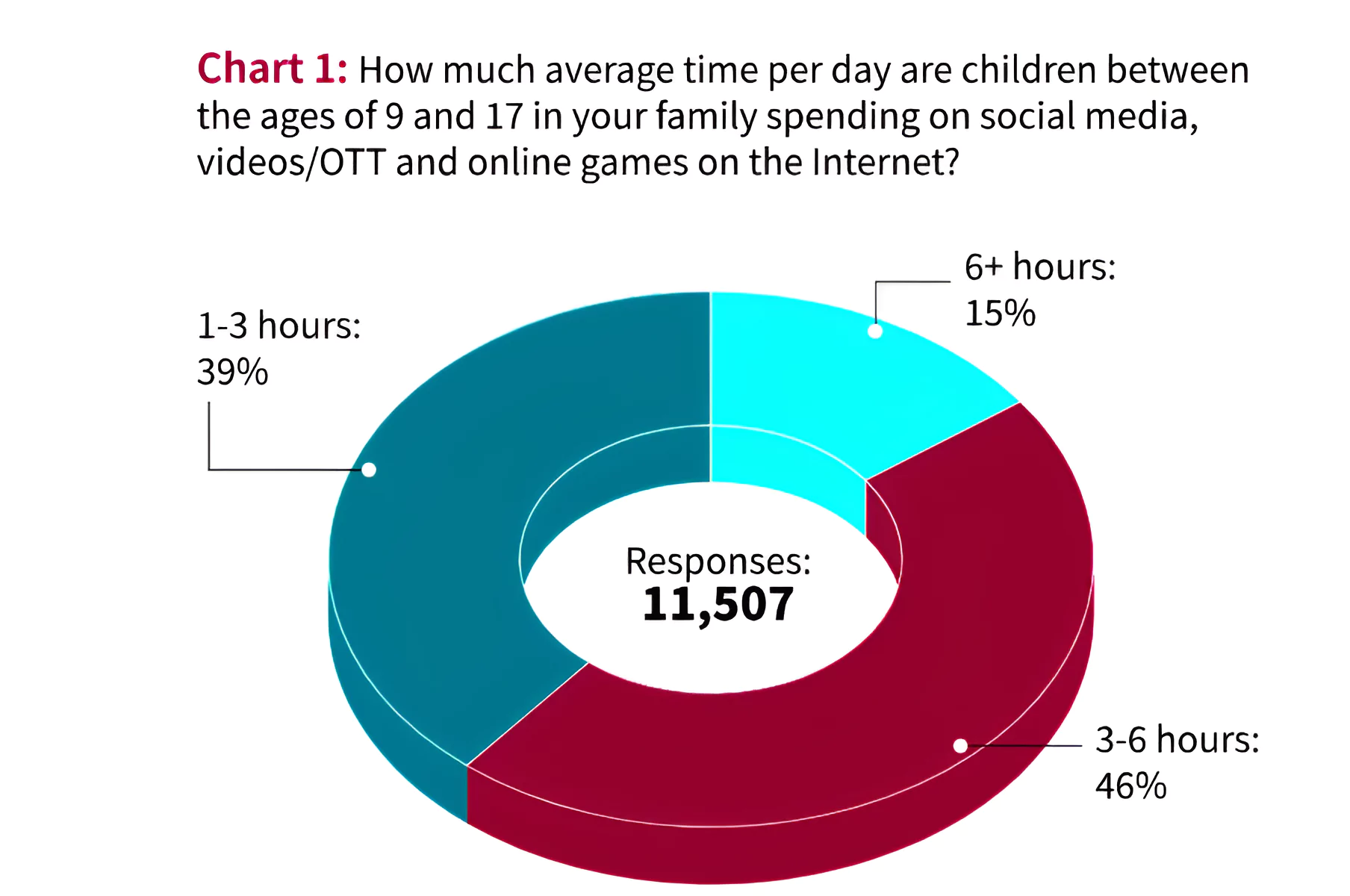 This trend has given rise to a growing addiction to electronic gadgets among children aged 9 to 18.
This trend has given rise to a growing addiction to electronic gadgets among children aged 9 to 18.