Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: ISRO, Gaganyaan Mission, Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1), Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES).
Relevancy for Mains: ISRO conducted safety tests for Gaganyaan Mission, Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1), Significance and Challenges of Gaganyaan mission for India. |
Safety Test For Gaganyaan
- The Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) will demonstrate the performance of the Crew Escape System of the Gaganyaan project.
- It marks the first in a series of tests for launching an Indian astronaut into space by 2025.
What is Gaganyaan mission?
- About: It is India’s first human spaceflight mission. As part of the programme, two unmanned missions and one manned mission will be taking place.
- A 3 member Indian crew will be sent to space for a period of seven days.
- Aim: To demonstrate the capability to launch human beings (three crew members) to low earth orbit and bring them back safely to earth by landing them in either the Bay of Bengal or the Arabian Sea.
- Launch vehicle: Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3)
- Total cost of Programme ~ 9023.00 crores
- Significance: After this manned mission, India will become the 4th country after Russia, US and China to send humans in space.
|
What is Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1)?
- New Test Vehicle: The TV-D1 flight will demonstrate the new Test Vehicle. Thus, the test has been named Test Vehicle-Demonstration 1 (TV-D1).
- Payloads: The payloads consist of the Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES) with their fast-acting solid motors, along with CM fairing (CMF) and Interface Adapters.
- Crew module: It will demonstrate a basic version of the crew module — the capsule in which the astronauts will be seated during the Gaganyaan human space flight. The crew module will be empty for the test.
- Functioning of Crew Escape System: The test will check the functioning of systems for separating the crew module from the rocket in case of a mid-flight emergency (abort mission) and the escape of astronauts.
- Simulation of abort condition: Flight will “simulate the abort condition during the ascent trajectory corresponding to a Mach number of 1.2 encountered in the Gaganyaan mission”, including crew module separation and its safe recovery.
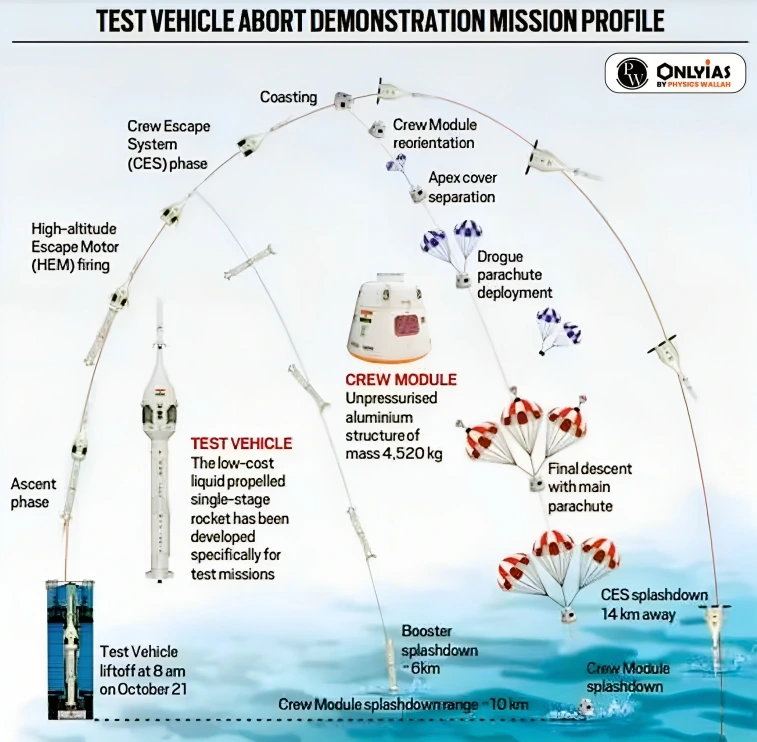
Test Vehicle for the test
- For the TV-D1 mission, ISRO will use a low-cost basic rocket it has built specifically to test systems.
- The full-fledged test flight of the crew module into space and back will be carried out on the human rated LVM3 rocket in 2024.
- It will use existing liquid propulsion technology, but has innovations such as the throttleable and restartable L110 Vikas engine which is capable of controlling propellant use.
- Vikas engine forms the core second stage of the LVM3 rocket.
What is a Crew Escape System (CES)?
The crew escape system (also known as Launch Abort System or Launch Escape System) is an emergency exit option critical to manned space missions. It is designed to pull away the crew module, take it to a safe altitude and bring it safely back on the earth in the event of a launch abort or during the vehicle’s ascent.
- It has five types of solid motors which generate the thrust needed for various mission requirements–
- Crew escape system jettisoning motor
- High-altitude escape motor (four of them)
- Low-altitude escape motor
- Low-altitude pitch motor
- High-altitude pitch motor.
Significance of test flight
- Simulation for Gaganyaan mission: It is a near-complete system integrated for a flight test.
- Its success set the stage for the remaining qualification tests and unmanned missions, leading to the first Gaganyaan mission with Indian astronauts.
- Crew safety: Scientists aim to ensure the safety of the crew who would be actually sent in the Crew Module on an LVM-3 rocket on the Gaganyaan mission.
|
What are the significance of Gaganyaan mission for India?
- A Platform for Innovation: Gaganyaan mission will help scientists to better understand the effects of microgravity on the human body and to develop new technologies for space exploration.
- The ISRO is considering a minimum of 10 microgravity experiments for the mission, including space medicine, sensor development for medical devices, etc.
- Scientific Exploration: It is a significant step towards India’s ambitious goals in space exploration, including setting up an Indian Space Station by 2035 and sending an Indian astronaut to the moon by 2040.
- Advanced technology capability: It will help in undertaking human space exploration, sample return missions and scientific exploration.
- It will give way to progress towards a sustained and affordable human and robotic programme to explore the solar system and beyond.
- Developmental collaboration: Gaganyaan mission will boost future capability to actively collaborate in global space station development & to carry out scientific experiments of interest to the nation.
-
- It will help in creating a broad framework for wider Academia – Industry partnership in taking up development activities for national development.
- Economy: Ample scope for employment generation and human resource development in advanced science and R&D activities.
-
- The mission will also boost India’s tourism industry, as people from all over the world will want to visit the country to see where its astronauts were trained and launched.
- Space Diplomacy: The Gaganyaan mission will help India to forge closer ties with other spacefaring nations.
- India has already signed agreements with Russia, the United States, and France to collaborate on the mission.
- India joined the US-led Artemis Accord for international partnership on planetary exploration and research.
What are the challenges with the Gaganyaan mission?
- Long Delay in project: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has been facing delays with the Gaganyaan mission which was scheduled to launch in 2022. The reasons for delay include:
- COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the work schedules of space agencies as well as disrupted the supply chain disruptions.
- Risks of failure: Sending humans to space missions is extremely dangerous, evident in the failure of the Russian Soyuz FG rocket with two astronauts aboard.
- The mission marked its first failure in 55 launches.
- Radiation: Astronauts on space stations are exposed to radiation levels more than ten times that of Earth, which can increase the risk of cancer and harm the central nervous system.
- This radiation exposure may also lead to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and fatigue.
- Challenges of gravity: Transitioning between gravity fields poses challenges that can impact hand-eye and head-eye coordination.
- As per NASA, in absence of gravity, the human body experiences mineral loss in bones, leading to a higher risk of osteoporosis-related fractures even after returning from a space mission.
- Isolation: Regardless of their training, astronauts are susceptible to behavioral issues due to the isolation they experience.
- Isolation can give rise to depression, fatigue, sleep disorders, and psychiatric conditions.
- Harsh Environment: Space presents a hostile environment with no atmosphere. In such conditions, without pressure, creating challenges for human body.
- To address this, the ‘Gaganyaan’ mission must simulate an Earth-like atmosphere within a confined space.
Also read: New Targets for ISRO: Indian Space Station by 2035, Indian on Moon by 2040
Conclusion:
The successful execution of this Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 for the Gaganyaan will mark a critical milestone in India’s journey towards achieving human spaceflight capabilities and will reinforce ISRO’s commitment to advancing space exploration. It will elevate India’s reputation as a technologically advanced nation and a player in international space exploration.
| Prelims Question (2018)
With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
1. PSLVs launch the satellite useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
2. Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the samevposition in the sky, asbviewed from a particular location in Earth.
3. GSLV Mk III is a fourstaged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a) |
![]() 20 Oct 2023
20 Oct 2023

