Context: Recently, the Delhi High Court sought the Cente’s stand in a plea challenging the order of the Civil Aviation Ministry, prohibiting the carrying of receive-only GPS devices on aircraft.
Delhi High Court Notice to Centre Unlawful Seizure of GPS device
- Allegations of Unlawful Seizure: A division bench issued notice to the Centre on the plea moved by an environmental scientist seeking suitable damages for the “unlawful seizure” of his GPS device at Delhi Airport on June 2, 2022.
About Global Positioning System (GPS):
- It is a satellite-based radio-navigation system used for monitoring and control.
- Origin: The U.S. Department of Defence started the GPS program in 1973 and launched the first satellite in 1978.
- GPS is a U.S.-owned utility that provides users with positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services.
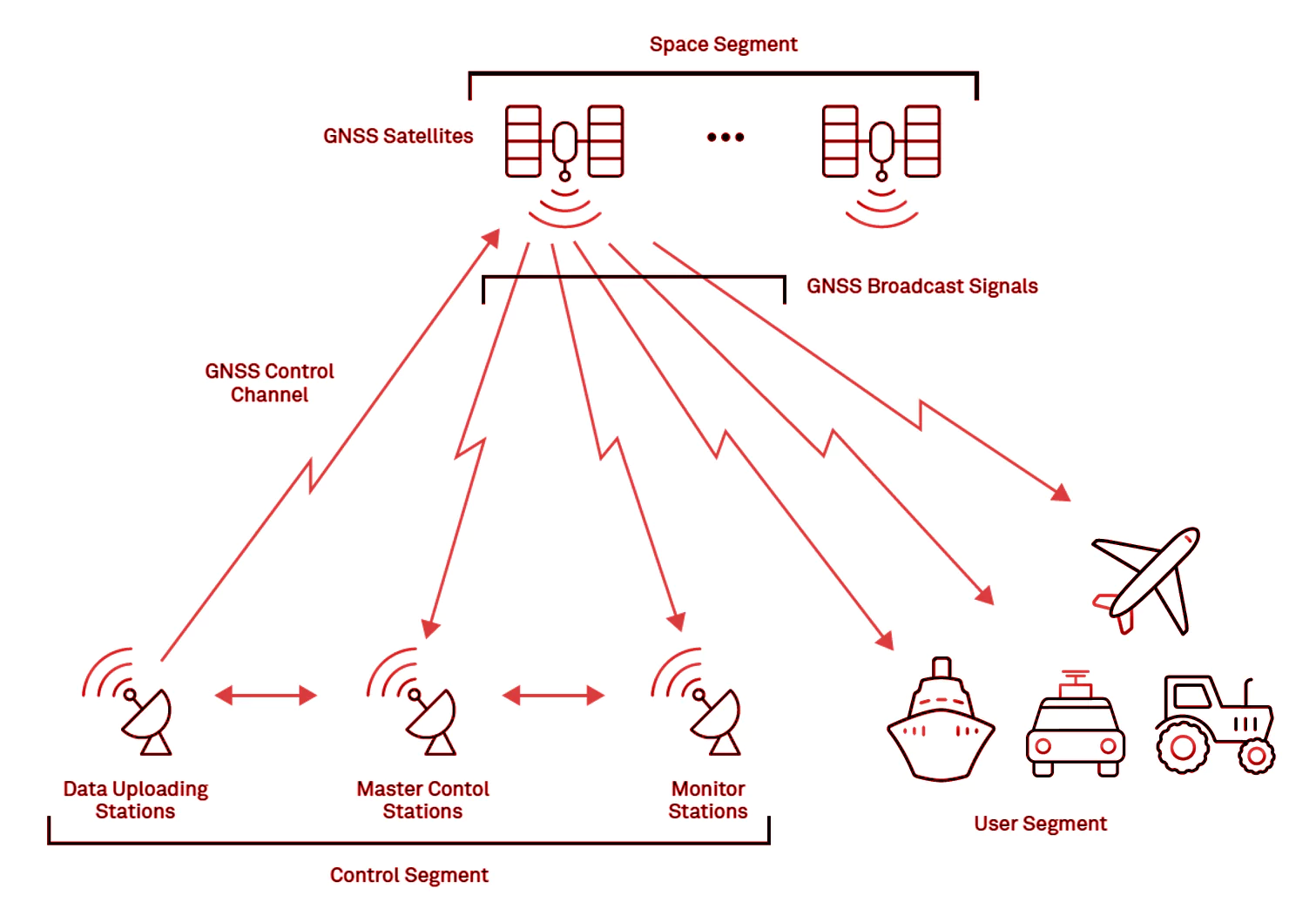
- This system consists of three segments:
- Space (Satellites): The satellites circling the Earth, transmitting signals to users on geographical position and time of day.
- Ground control: The Control Segment comprises Earth-based monitor stations, master control stations and ground antenna. Control activities include tracking and operating the satellites in space and monitoring transmissions.
- User equipment: GPS receivers and transmitters including items like watches, smartphones and telematic devices.
- GPS Satellite Constellation: The modern GPS consists of 24 satellites moving around the earth in six orbits.
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS): The services provided by the GPS system are designed to meet the SPS performance standard, the latest edition of which was published in April 2020.
- In essence, the SPS standard tells application developers and users anywhere in the world what they can expect from the GPS system
How does GPS work?
- GPS Satellite Broadcasting: Each GPS satellite continuously broadcasts a radio signal containing information about its location in orbit, operational status, and the time at which the signal is emitted.
- Encoding Technique: The signals are encoded with code-division multiple access. This allows multiple signals to be transmitted in the same channel and for a receiver to be able to disentangle them.
- Encoding Types: the coarse/acquisition mode, which civilians can use to access coarse GPS data, and the precise mode, which is encrypted and is for military use.
- On a smartphone, a GPS receiver picks a signal and uses it to calculate its precise distance from the satellite.
What are the applications of GPS?
- Aviation: Modern aircraft are fitted with multiple GPS receivers which provide pilots (and sometimes passengers) with a real-time aircraft position and map of each flight’s progress.
- Marine: GPS is also used to position and map dredging operations in rivers, wharves and sandbars, so other boats know precisely where it is deep enough for them to operate.
- Farming: High-accuracy GPS maps soil sample locations, allowing farmers to see where the soil is most fertile across individual fields or entire farms.
- Surveying: Surveyors use GPS to accurately map and accurately measure the earth’s surface and underwater features.
- Sports and Fitness Tracking: GPS-enabled sports watches and fitness trackers provide real-time data on distance, speed, elevation, and heart rate, allowing users to set goals, track their workouts, and analyze their performance over time.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, rely heavily on GPS technology for navigation, stabilization, and geofencing.
What are the limitations of GPS?
- Time-Keeping: Good timekeeping is essential to ensure the GPS system works as well as possible.
- For example, not adjusting for the 38-microsecond offset between the satellites’ clocks and the ground could lead to an error of 10 km within a single day.
- Indoor Limitations of GPS: GPS is generally useless indoors as radio waves will be blocked by physical barriers, such as walls, and other objects.
- Accuracy Constraints: Regular GPS cannot pinpoint locations to greater than 3-m accuracy.
- Due to these limitations, GPS cannot be used to, for instance, track the movement patterns of retail customers in a store and analyze their shopping habits.
Also Read: NavIC
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 6 Dec 2023
6 Dec 2023
