![]() 28 Mar 2024
28 Mar 2024
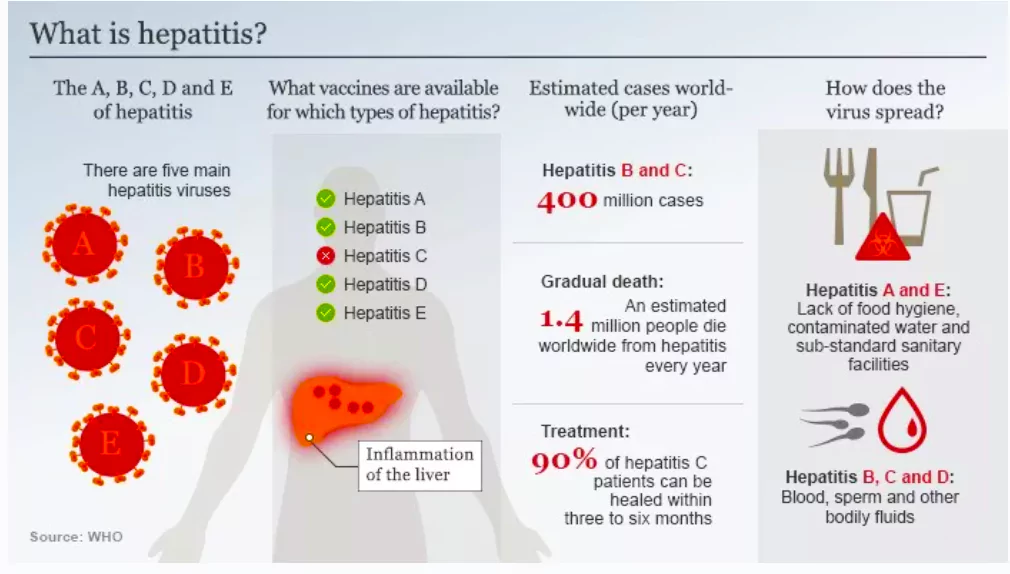
A study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital in New Delhi showed that public knowledge regarding Hepatitis B is considerably deficient in India.
Nobel Prize in Hepatitis C Vaccine
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>