Context

Recently, Nobel laureate and noted Physicist Peter Higgs, known for predicting God’s Particle has passed away.
Peter Higgs- the father of God Particle
- God Particle: In the 1960s, Peter Higgs carried out research using Bose-Einstein Statistics.
- He wrote a paper about a very unstable particle that survives for a fraction of a second after its birth, and then it breaks apart producing other fundamental particles. He called this particle “Higgs Boson Particle” or “God Particle”.
- In 2012, Scientists at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research, located on the Swiss-French border in Switzerland) had found ‘Higgs Boson’ using the Large Hadron Collider, which is a 27 km long particle accelerator built to study fundamental particles.
- Nobel Prize in Physics in 2013 : He was awarded for his work, alongside Francois Englert of Belgium, who independently came with the same theory.
- This Theory is related to how subatomic particles that are building blocks of matter get their mass.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is a Higgs Boson?
- It is one of the 17 fundamental particles that constitutes the Standard Model of Physics,which describes the physics of how the universe is constructed.
What is a Boson?
- A boson is a “force carrier” particle that comes into play when particles interact with each other, with a boson exchanged during this interaction.
- For example, when two electrons interact they exchange a photon — the force-carrying particle of electromagnetic fields.
|
- The Higgs boson, a type of boson, is a force-carrying subatomic particle.
- It carries the force that a particle experiences when traversing the Higgs field (a universal energy field),which is responsible for granting fundamental particles their mass.
- A particle’s mass is directly correlated with its interaction strength with the Higgs boson.
- Therefore, Electrons possess a specific mass, while protons have more, and neutrons slightly surpass protons.
- A Higgs boson can also interact with another Higgs boson — this is how we know that its mass is greater than that of protons or neutrons.
- Features:
- The Higgs Boson has a mass of 125 billion electron volts, approximately 130 times more massive than protons.
- It is also chargeless with zero spin,a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum.
- It is only elementary particles with no spin.
- Significance of Higgs Boson Study : Researchers aspire to employ the Higgs Boson as a mechanism for learning deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including the enigma of dark matter.
Standard Model of Particle Physics
- The Standard Model of Particle Physics is scientists’ current best theory to describe the most basic building blocks of the universe.
- It explains how particles called quarks (which make up protons and neutrons) and leptons (which include electrons) make up all known matter.
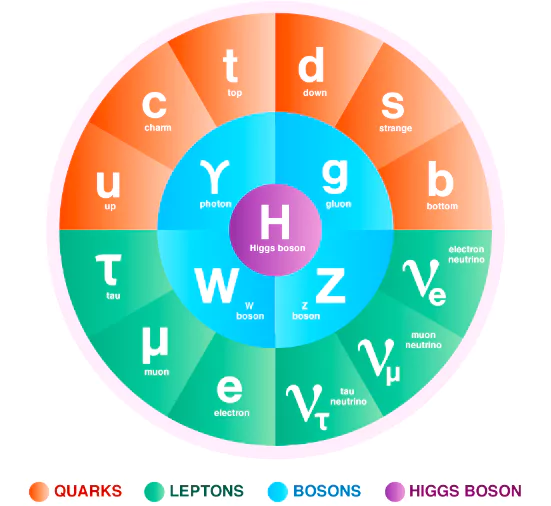 It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.
It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons. - The Standard Model explains three of the four fundamental forces that govern the universe: electromagnetism, the strong force, and the weak force.
- Electromagnetism is carried by photons and involves the interaction of electric fields and magnetic fields.
- The strong force, which is carried by gluons, binds together atomic nuclei to make them stable.
- The weak force, carried by W and Z bosons, causes nuclear reactions that have powered our Sun and other stars for billions of years.
- The fourth fundamental force is gravity, which is not adequately explained by the Standard Model.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Recent Experiment of Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
- LHC generated a Higgs boson by colliding together billions of high-energy protons which resulted in a release of immense energy that forms various particles.
CERN (European Council for Nuclear Research):
- Aim: To study the basic constituents of matter ie. fundamental particles and to advance the boundaries of human knowledge by delving into the smallest building blocks of our universe.
- Founded in : 1954.
- Location: at Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, Switzerland.
- Member states: 23 members with India being the associate member.
- Main area of research: Particle physics.
- Instruments: It uses purpose-built particle accelerators and detectors.
|
-
- Being heavy, the Higgs boson is unstable and breaks down into lighter particles.
- It can decay into a lepton pair and a photon in three different ways.
- Recent evidence indicates Higgs Boson Decay: It says that a Higgs boson will decay to a Z boson and a photon 0.1% of the time.
- This means the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) needed to have created at least 1,000 Higgs bosons to have been able to spot one of them decaying to a Z boson and a photon.
Also Read: Amaterasu: Rare And Super-Energetic Particle
![]() 11 Apr 2024
11 Apr 2024

 It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.
It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.