Context: A research paper published in Scientific Reports Journal, has provided important information on Huntington disease, using fruit flies.
More on News:
Fly Models of Huntington Disease
- Methodology: Researchers genetically engineered fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) to express the polyglutamine tract of a mutated human HTT gene (which causes the disease) in the nervous system of fruit flies.
- Solution: Through overexpression of a specific gene called Yod1, the signs of neurodegeneration by the disease were ameliorated.
- Usefulness: Model systems such as fruit flies and yeasts offer scientists unparalleled versatility to investigate the molecular mechanisms triggered by disease genes in humans.
Drosophila Melanogaster as Experiment Organism:
- They are common pests and are important pollinators for plants.
- Scientific Contribution: Drosophila Melanogaster is an important organism that has been widely used in many biological and medical research, often Nobel-winning discoveries.
- They are preferred due to their short lifespan and easy maintenance in laboratory settings
- They have provided important insights into genetic mutations, inheritance patterns, and mapping of genes.
- They have also helped improve the understanding of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s Disease.
|
What is Huntington Disease?
- About: Huntington disease is a neurological genetic disorder which damages nerve cells in the brain causing them to stop working properly. It’s passed on from a person’s parents.
- Genetic Mutation: The reason for the disease is that they carry a mutated version of a gene called HTT. The HTT gene provides a blueprint for a protein called huntingtin, or Htt.
- Htt protein: Nerve cells in the human body require the Htt protein for their normal functioning and survival.
- The mutated gene encodes an abnormal Htt protein that instead destroys the neurons that regulate movement, thinking, and memory.
- Mechanism of Mutation: The normal HTT gene contains a stretch of DNA that specifies the number of times the amino acid glutamine is repeated in the Htt protein about 11 to 31 times.
- The mutant version contains 35 or more repeats up to 150 repeats.
- As the number of repetitions increase, the severity of Huntington disease increases and its debilitation begins at an earlier age.
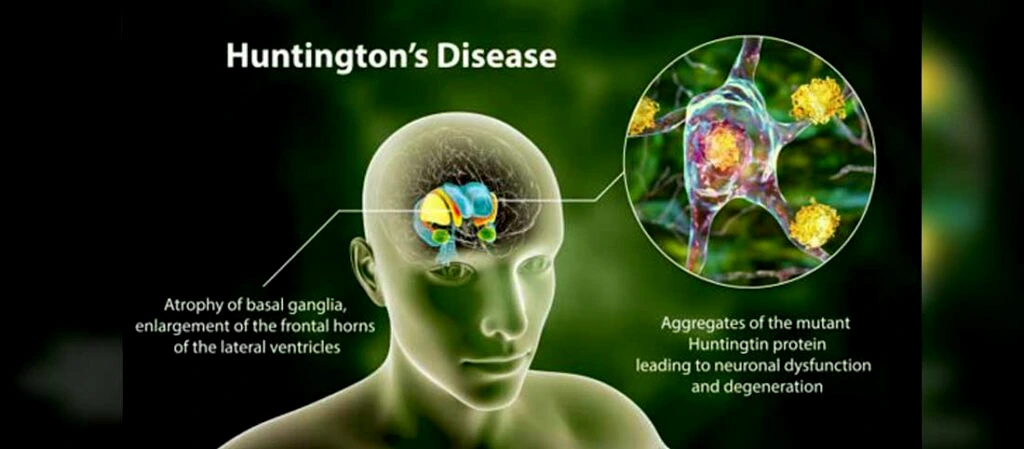
- Glutamines: Their fragments are toxic because they interfere adversely with several cellular processes.
- Glutamine is an important amino acid and is used for removing excess ammonia.
- Challenge: We neither know why some of these genes are expanded nor how exactly the short fragments cause neuronal degeneration.
- Dominant Gene: Of the two copies of the HTT gene, one from the father and one from the mother, The disease is triggered even if only one copy of the gene is mutated.
- Symptoms: Mood swings, difficulty in reasoning, abnormal and uncontrollable jerky movements, and difficulty in speaking, swallowing, and walking.
- Symptoms begin in the ages 30-50, and the patient eventually dies.
Must Read: Parliamentary Committee Report On Mental Health Care
Source: The Hindu
![]() 28 Dec 2023
28 Dec 2023
