Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Illicit Trade, Global Terrorism Index (GTI), UN Office of Drugs and Crimes (UNODC), Golden Triangle, Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Global Crime Index, and National Investigation Agency (NIA).
Relevancy for Mains: FICCI’s Report on India’s Illegal Economy, Linkages of Illicit Trade, Challenges Associated with Linkages of Illicit Trade, Role of Government Agencies in Checking Illicit Trade in India, and International Conventions. |
FICCI’s Report on India’s Illegal Economy
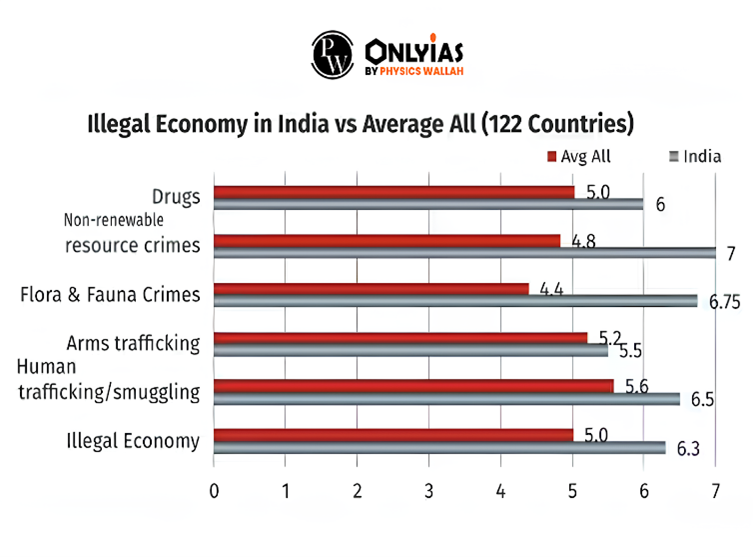
- According to FICCI, the illegal economy in India has an overall score of 6.3, which is higher than the average score of 5 of other 122 countries.
- In the organized crime segment, India has a lower score of 4.3 against 5.2 for an average of 122 countries.
- India has a Global Terrorism Index (GTI) score of 7.43 and a Global Crime Index score of 44.7, reflecting positive developments in these areas compared to the levels observed in 2016.
 Goods Seized: Around 3.5 tonnes of gold, 18 crore cigarette sticks, 140 metric tonnes of red sanders and 90 tonnes of heroin were seized along with other drugs during the last financial year.
Goods Seized: Around 3.5 tonnes of gold, 18 crore cigarette sticks, 140 metric tonnes of red sanders and 90 tonnes of heroin were seized along with other drugs during the last financial year. - Revenue Loss: India has faced an approximate total potential revenue loss of US $13 billion between 2009-2018, involving both mis invoiced imports and exports.
What is an Illicit Trade?
Illicit trade refers to the illegal exchange of goods and/or services, often in violation of national or international laws. It comprises trade of manufacturing and export of counterfeit goods.
- It is vast and full of complexities, however, smuggling and counterfeiting are the most common types of illicit trade.
- Counterfeiting is a practice of manufacturing, importing, exporting, distributing, selling or otherwise dealing in goods, often of inferior quality, under a trademark that is identical to a registered trademark, without the approval of the registered trademark owner.
- Counterfeits are most commonly called “fake goods” or “knock-offs.”
- Smuggling: It is a criminal offense which includes the secret movement of goods across national borders to avoid customs duties or import or export restrictions.
- Smuggling in India report 2021-22 identified 437 instances of duty evasion totalling Rs 3,924 crore, which was a 40 percent jump from 2020-21.
- Money laundering: It is the process of illegally concealing the origin of money, obtained from illicit activities such as drug trafficking, corruption, embezzlement or gambling, by converting it into a legitimate source.
- Based on UN Office of Drugs and Crimes (UNODC) estimates, when the Indian economy surpassed the $3 trillion mark in 2021, the quantum of money laundering in India was estimated at $159 billion which is around 5 percent of GDP.
Also read: India’s GDP Estimates
What are the linkages of Illicit Trade?
- Nexus: There is an intricate nexus between the illegal economy, terror and organized crime. The report highlights the role played by criminal networks in a number of illicit activities, including drug and human trafficking, smuggling of cigarettes, alcohol and illegal trade of wildlife products.
- Financial Flows: Illicit financial flows drain resources from development not only when they leave a country (outflows), but also when they enter a country (inflows).
- They can have detrimental impact by fuelling money laundering and corruption thus undermining the rule of law and the stability of markets.
- Organised Crime and Illegal Economy: Drug trafficking, arms smuggling, counterfeit goods, and wildlife trade are lucrative enterprises that fund criminal networks. The profits generated often support organized crime syndicates, fostering corruption and undermining security.
- India’s location near major drug-producing regions, including the Golden Triangle (Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand) and the Golden Crescent (Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Iran) has been associated with activities that may involve the transportation and distribution of controlled substances.
- FICCI report stated that 3,172 cases of drug seizures were recorded during 2014-2022
- Linkages with Terrorism: Illicit trade generates significant revenue, enabling financial backing for terrorist organizations. The porous borders facilitate the movement of illicit goods and funds. The direct link of these activities with terrorists is a cause of concern.
- For example, according to the United Nations, millions of dollars from the trade of illicit tobacco reach terror outfits such as the Taliban and Al-Qaeda.
Also read: Global Peace Index
What challenges are associated with Linkages of Illicit Trade?
- Economic Impact of Violence for India: Central and state governments suffer heavy losses by way of loss of sales tax, customs and excise tax etc. Further dealing with both terrorism and crime has resulted in a considerable economic cost.
- In 2021, India’s economic cost for violence was at US $1170 billion at purchasing power parity (PPP) which accounts for approximately 6% of GDP.
- Enforcement: As perpetrators of illicit trade are becoming increasingly sophisticated, well-connected and adequately funded, the activities of counterfeiting and smuggling are presenting a bigger challenge for enforcement authorities and governments globally.
- Breeding Ground for Criminal Activities: Financial gains are further deployed for illegal activities such as drug trafficking and other organized crimes.
What are the reasons for high volume of Illicit trade?
- Price differentials in various markets resulting in purchasing power mismatch.
- Lack of stringent enforcement.
- Technological advancement leading to ease of creation of replicas.
- Legal and regulatory vulnerabilities.
- Differential import tariff across nations.
- Consumer obliviousness.
|
-
- For instance, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) study suggested that money laundering and terror funding was consequential to illicit trade in tobacco.
- Visible Consequences: Such as adverse impact on innovation, investment, brand reputation, health and wellness and national security are well-known. However, the bigger concern is the manner in which it is impacting the social fabric of nations.
- Technology Adoption: Online marketplaces have become a preferred hub for illicit operators owing to their wider reach and ease of access.
- Downfall of Local Industries: Illicit trade drastically cuts prices of locally manufactured goods thereby destroying the market for local products, resulting in local industries to break down. The impact of the problem is to the extent that it leads to unemployment.
- Dilution of Brand Value: Inferior products tarnish the reputation of the manufacturer and dilute the brand image over time. Manufacturers lose their trust as consumers unknowingly buy fake products.
Also read: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
Role of Government Agencies in Checking Illicit Trade in India
- Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI): It investigates a wide range of criminal activities, including corruption, economic offenses, and cases related to organized crime.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB): It coordinates with other law enforcement agencies to address the illicit drug trade and associated criminal activities.
- Enforcement Directorate (ED): It investigates economic offenses, including money laundering and illicit financial activities and plays a crucial role in tracking and seizing assets acquired through illicit means.
- National Investigation Agency (NIA): It investigates and combats terrorism and offenses that have national and transnational implications.
What are the international conventions against illicit trade that India has signed?
- United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs 1961.
- United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971.
- United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
- United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime, 2000.
- World Trade Organization Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
Way Forward
The 6 Cs approach
- Cognisance of Terrorism and Organised Crime Under Regulatory Framework
- Continuous and Critical Evaluation of Illicit Financial Flows
- Central Nodal Agency for Greater Coordination
- Creating Awareness and Changing Consumer Preferences
- Combating Trade Based Money Laundering
- Cooperation and Coordination at International Level
|
- Combating Terror Financing: Terror financing is more dangerous than terrorism itself, because the ‘Means and Methods‘ of terrorism are nurtured from such funding. The government has taken several proactive measures, but there is a need to choke the flow of funds by nefarious entities.
- Customized Approaches: India’s geographical location is sandwiched between two of the world’s biggest drug producing zones, presence of porous borders, cross border terrorism etc. call for a customized approach to deal with illicit trade and associated issues.
- For instance, to curb digital piracy one could adopt technical controls, including digital rights management (DRM), network management, and content identification systems.
- Integrated Anti-Counterfeit Approach: It is vital that enforcement agencies take into account the diverse methods used by criminals and the ever evolving technological advancements used during these activities.
- For instance, the finished leather trade which is a continuing cause of concern for luxury brands such as Louis Vuitton, operates in the Dharavi slum area in Mumbai which lacks any formal addresses and securing adequate police protection when executing an anticounterfeiting raid becomes a challenging task.
- Consumer Awareness: A combined effort involving manufacturers, government and various enforcement agencies is critical to generate consciousness amongst consumers by running targeted campaigns, highlighting dangers of buying and using these goods, etc.
- Improving Regulatory Landscape: Stringent anti-piracy regulations are a must to enforce IP rights and empower various enforcement agencies in India. There are certain gray areas and other laws including the Information Technology Act, Indian Contract Act, Companies Act, 2013, intellectual property, laws in copyrights and trademarks etc. Thus, there is a need for a separate e-Commerce law in the country.
- Miscellaneous: Safeguarding India’s economic stability, Ensuring fair competition and ease of doing business, adoption of anti-counterfeit technologies, investing in research and development and collaboration with stakeholders.
Conclusion
India’s growing global trade prominence raises the risk of trade-based illicit financial flows, potentially affecting economic progress and supporting terrorism and criminal activities. To counter these risks, India should adopt a comprehensive approach tailored to its unique circumstances and challenges.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question:
Consider the following heavy industries:
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refmeries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decru:bonizing how many of the above industries?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Ans: C |
![]() 30 Sep 2023
30 Sep 2023

 Goods Seized: Around 3.5 tonnes of gold, 18 crore cigarette sticks, 140 metric tonnes of red sanders and 90 tonnes of heroin were seized along with other drugs during the last financial year.
Goods Seized: Around 3.5 tonnes of gold, 18 crore cigarette sticks, 140 metric tonnes of red sanders and 90 tonnes of heroin were seized along with other drugs during the last financial year.