Context:
The Indian stock market has become the 4th largest globally, surpassing Hong Kong.
Indian Stock Market Became 4th Largest Stock Market, Surpassing Hongkong
- Indian stock market value: $4.33 trillion (₹366 lakh crore)
- Hong Kong’s total market value: $4.29 trillion
- The Top 3 stock markets in the world are the US, China, and Japan.
Factors Contributing to India’s 4th Largest Stock Market
- Impact of Hong Kong’s Market Decline: The decline in Hong Kong’s stock market due to the weakening appeal of China as an investment destination has helped India emerge as the world’s largest stock market.
- Strong Corporate Performance: Many Indian companies, especially in sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy, are experiencing higher growth and profitability.
- This has helped in attracting investor interest and boosted market capitalization.
- Technological Upgradation: Technological advancements such as online trading platforms and mobile apps have made access to the stock market easy. It has helped in increasing the investor base and facilitated efficient transactions.
- India’s Alternative to China: Economic slowdown and geopolitical uncertainties make China less attractive to investors. However, India’s stable and promising economic environment, coupled with recent reforms has made India a favorable alternative.
Implications of Indian Stock Market Surpassing Hong Kong
- Geopolitical Impact:
- Geopolitical Shift in Power Dynamics: India’s growing influence in the financial world signals its increasing economic and political strength, possibly challenging China’s dominance.
- Enhanced Soft Power: A rising stock market can attract foreign investment which can improve India’s reputation as a stable and appealing investment destination.
- Potential for Cooperation: A stronger Indian economy could encourage deeper economic and strategic cooperation with other regional players like the Quad countries to counterbalance China’s influence.
- Geo-economic Consequences:
- Diversification of Investments: India’s larger market provides more investment options, reducing dependence on the Chinese market and lessening risks linked to its slowdown.
- Rise of the Indian Rupee: Increased foreign investment could elevate the value of the Indian rupee, making it a more significant regional currency and possibly challenging the dominance of the US dollar.
- Growth of Financial Hubs: A larger and more dynamic Indian stock market could transform cities like Mumbai into major financial hubs in the region, attracting capital and expertise.
Challenges and Uncertainties
- Sustaining Growth:
- India must maintain robust economic growth and implement effective financial regulations to retain its position as a top market.
- Domestic Challenges:
- Issues like income inequality and social unrest might hinder India’s economic potential and limit its global impact.
- China’s Reaction:
- China may respond to India’s rise through economic or political measures, creating uncertainties in the regional dynamics.
What is the Stock Market?
- Definition: It is a marketplace where publicly listed companies’ stocks (Equities or Shares) are bought and sold.
- There are two primary stock exchanges:
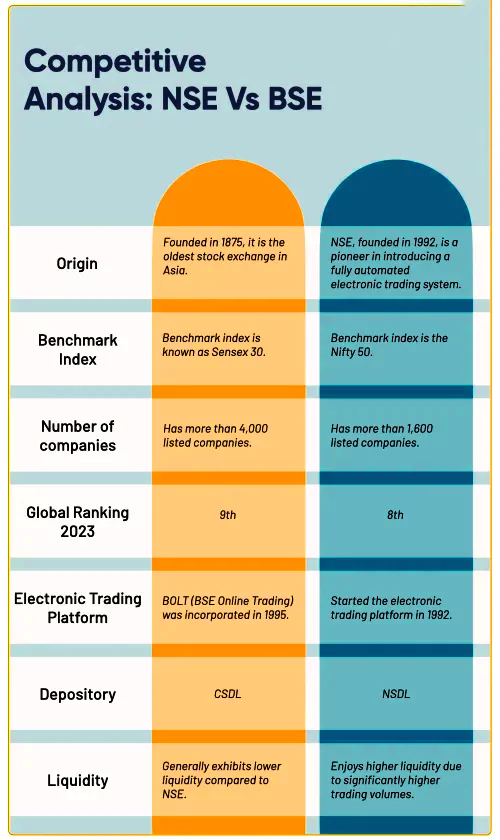
- The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): It is the oldest stock exchange
- The National Stock Exchange (NSE).
- These stock exchanges have their benchmark indices:
- The SENSEX for the BSE
- The NIFTY 50 for the NSE
- These benchmarks track the performance of the top 30 and 50 companies respectively.
- Market Structure:
- Primary Market: Companies release shares to the public through an initial public offering (IPO) to raise funds.
- Secondary Market: Investors buy shares from each other either at the current market price or at a price they both decide on.
- Regulation by: The primary and secondary markets are regulated by SEBI in India.

About Security and Exchange Board of India
- SEBI is a statutory body.
- It was established in 1992.
- It regulates the stock market.
- Its main aim is to save investors’ interest in securities.
|
News Source: Indian Express
![]() 24 Jan 2024
24 Jan 2024

