Context:
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to succeed the incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps of previous centuries as the world’s light source of choice.
Invention of Blue LEDs Wins Physics Nobel
- In October 2014, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences celebrated the advancements in lighting technology by awarding the Nobel Prize in Physics for developing light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Also Refer: Nobel Prize Winners 2023 List, Name And Fields
About Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs):
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): Are semiconductor devices that can emit light when an electric current passes through it.
- Diode: It is an electronic component that allows current to flow in only one direction.
- Semiconductors: They are materials which have a conductivity between conductors (generally metals) and nonconductors or insulators (such as most ceramics).
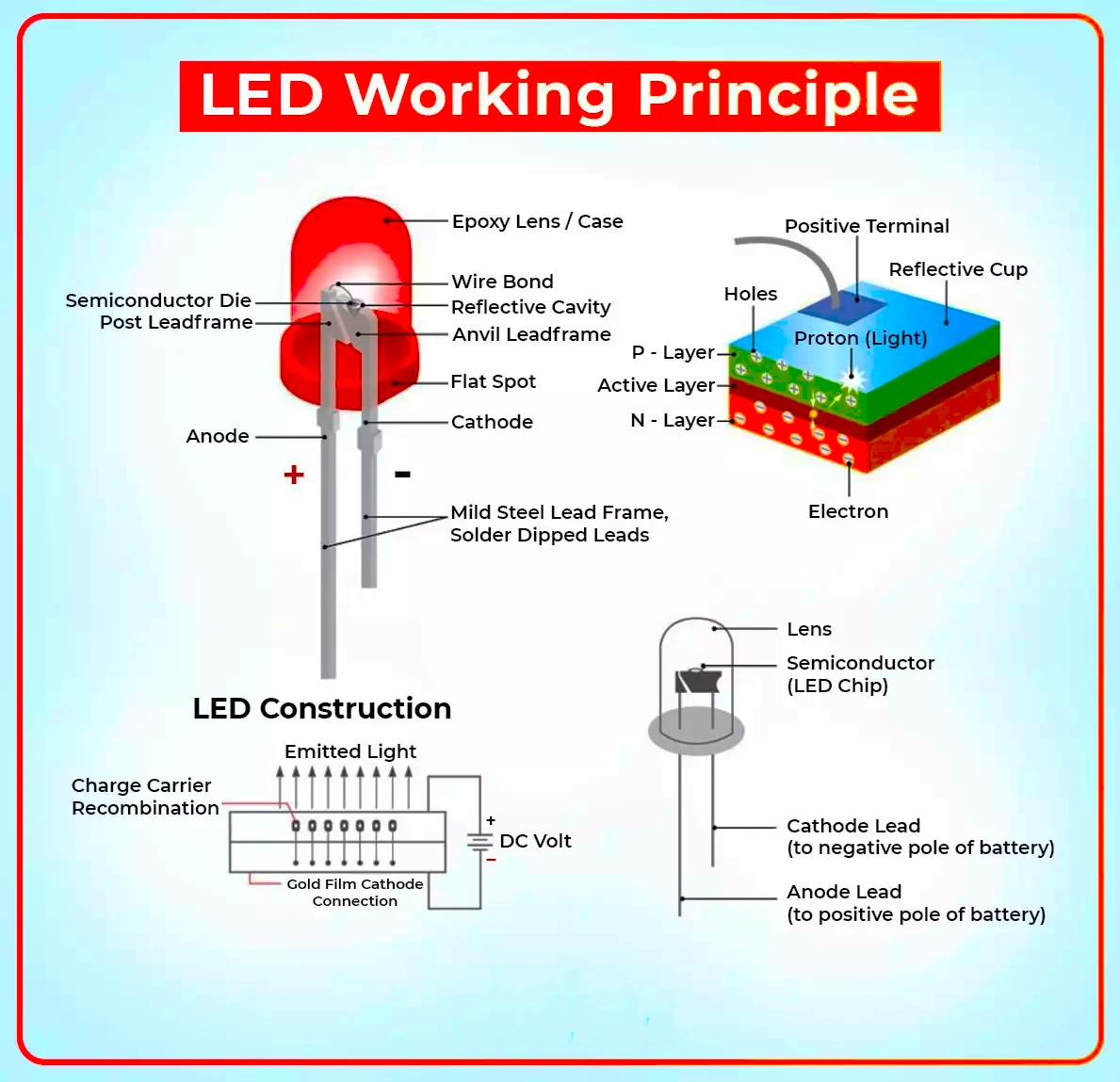
Working of LEDs
- Basis: It is based on the electroluminescence effect in which the energy released corresponds to visible light frequencies.
- Electroluminescence refers to the generation of light resulting from the interaction between an electric field and a solid material.
- Follows Haitz’s Law: It asserts that the expense per unit of light emitted by an LED will decrease by 10 times, and the light output will increase by 20 times for a specific light frequency over each decade.
- Blue Light: An LED has four important parts: die, substrate, phosphor, and lens. The “die” is a special part made of gallium nitride (GaN), and it gives off blue light when electricity is sent through it.
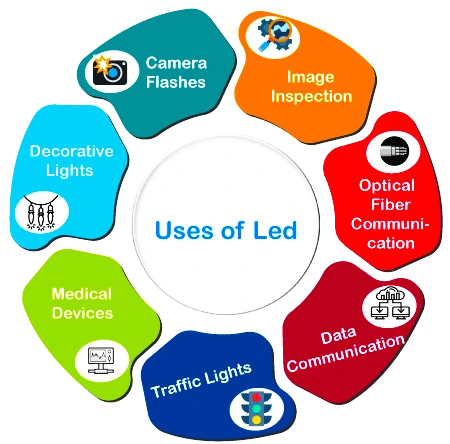
Significance of LEDs
- Higher Efficiency: LEDs are more efficient, durable, and have better contrast than incandescent and fluorescent lights which contributes to cost savings.
- LEDs emit light in a specific direction, unlike incandescent and CFL, which emit light and heat in all directions.
- Higher Durability: LED’s are more durable with higher light contrast (up to 300 lumens amount of visible light emitted per second) which further reduces material waste.
About Compact Fluorescent Lighting (CFL)
- An electric current flows between electrodes at each end of a tube containing gases.
- This reaction produces ultraviolet (UV) light and heat. The UV light is transformed into visible light when it strikes a phosphor coating on the inside of the bulb.
About Incandescent bulbs
- It produce light using electricity to heat a metal filament until it becomes “white” hot or is said to incandescent.
- As a result, incandescent bulbs release 90% of their energy as heat.
|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 17 Jan 2024
17 Jan 2024

