![]() 26 Mar 2024
26 Mar 2024

Mixed reality headsets have gained widespread attention with the reveal of the Apple Vision Pro headset.
| Relevancy for Prelims: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, and Information Technology. |
|---|
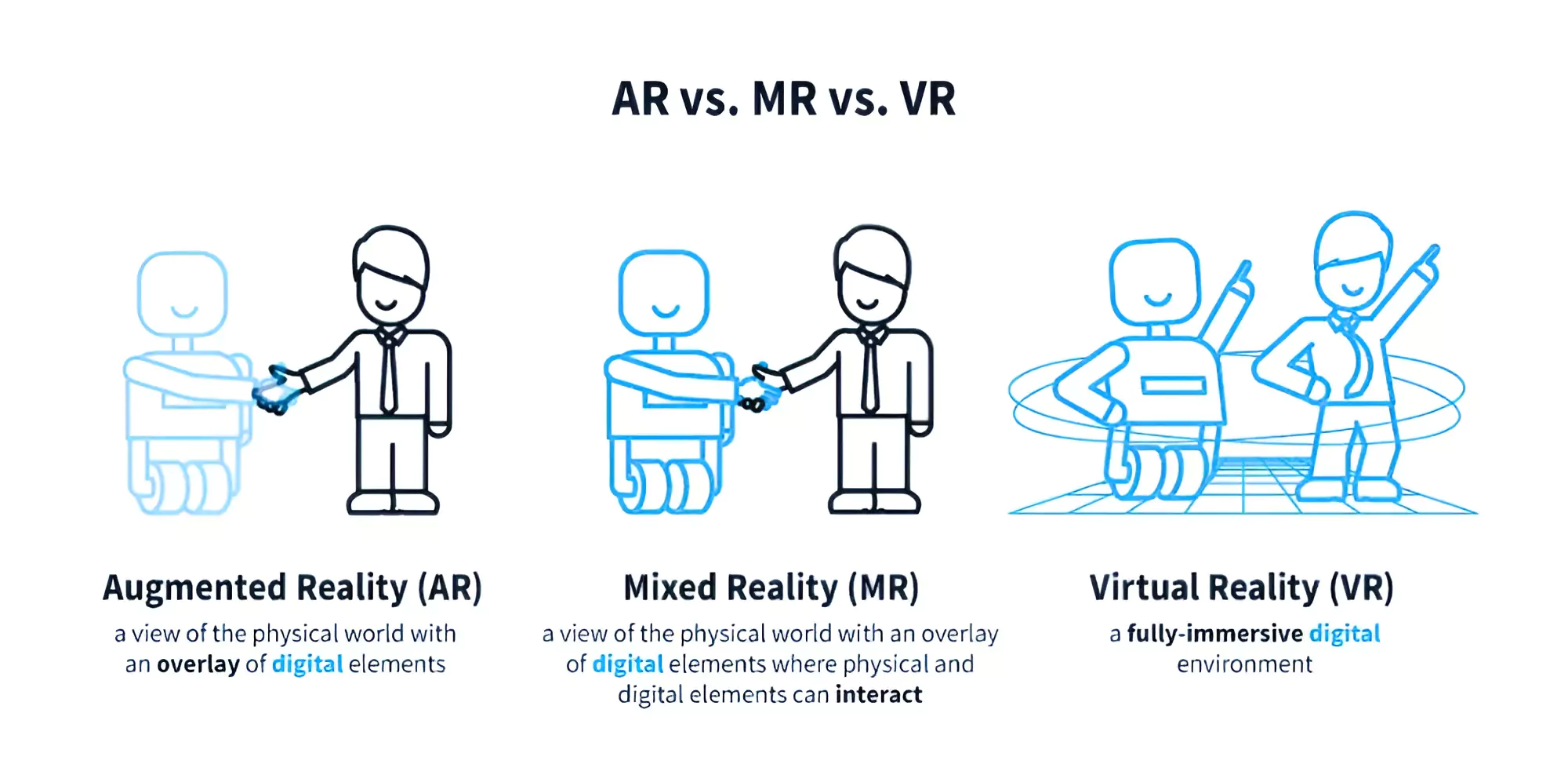 Spatial Computing: According to mixed reality researcher Louis Rosenberg, spatial computing “is a great overarching term for AR, MR, and VR, along with other immersive experiences such as 3D movies and telepresence.
Spatial Computing: According to mixed reality researcher Louis Rosenberg, spatial computing “is a great overarching term for AR, MR, and VR, along with other immersive experiences such as 3D movies and telepresence.Extended Reality:
|
|---|
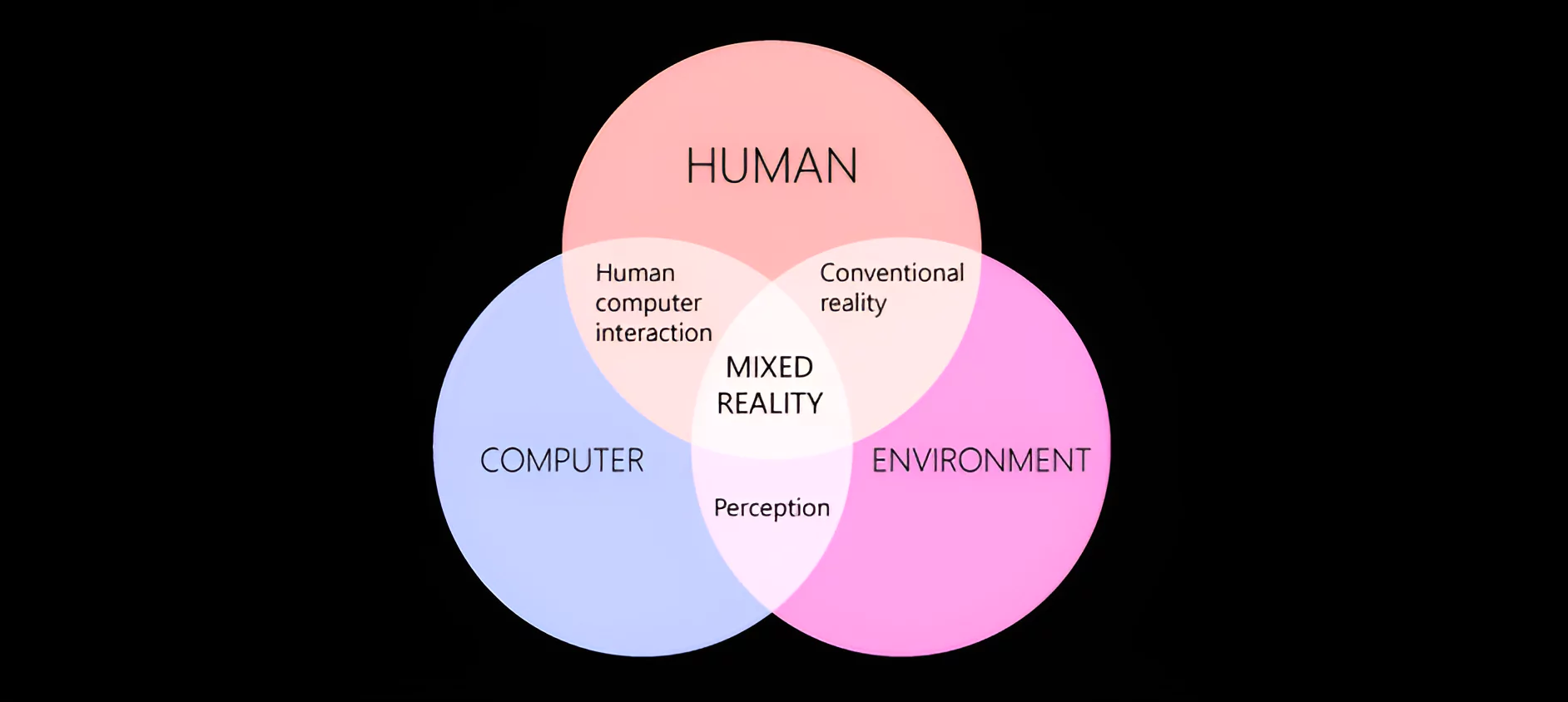 Collaboration: MR can facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to interact with the same virtual environment from different locations.
Collaboration: MR can facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to interact with the same virtual environment from different locations. 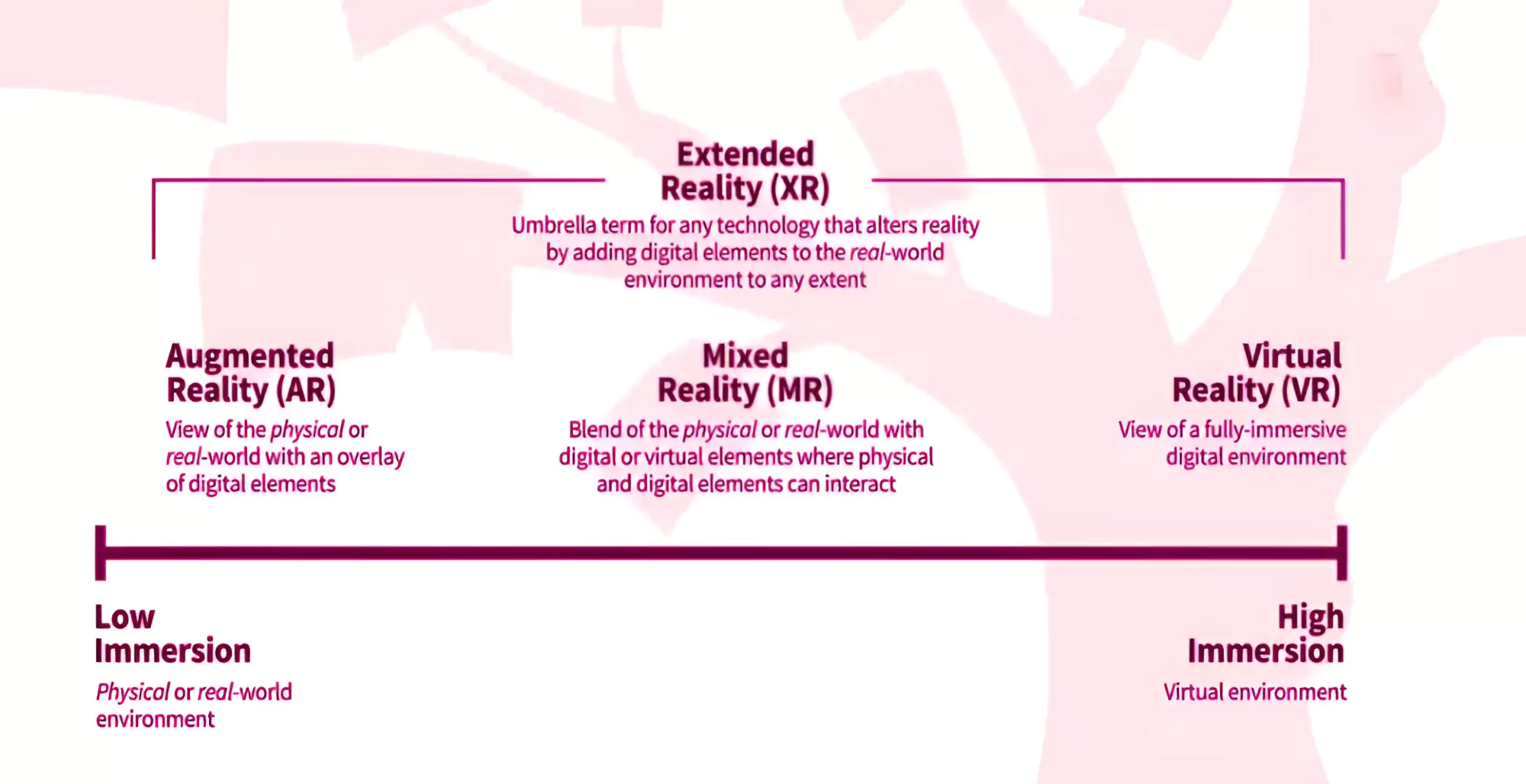 Mixed Reality Spectrum: It is a way of describing how physical and digital worlds can be combined in different ways to create immersive experiences.
Mixed Reality Spectrum: It is a way of describing how physical and digital worlds can be combined in different ways to create immersive experiences. 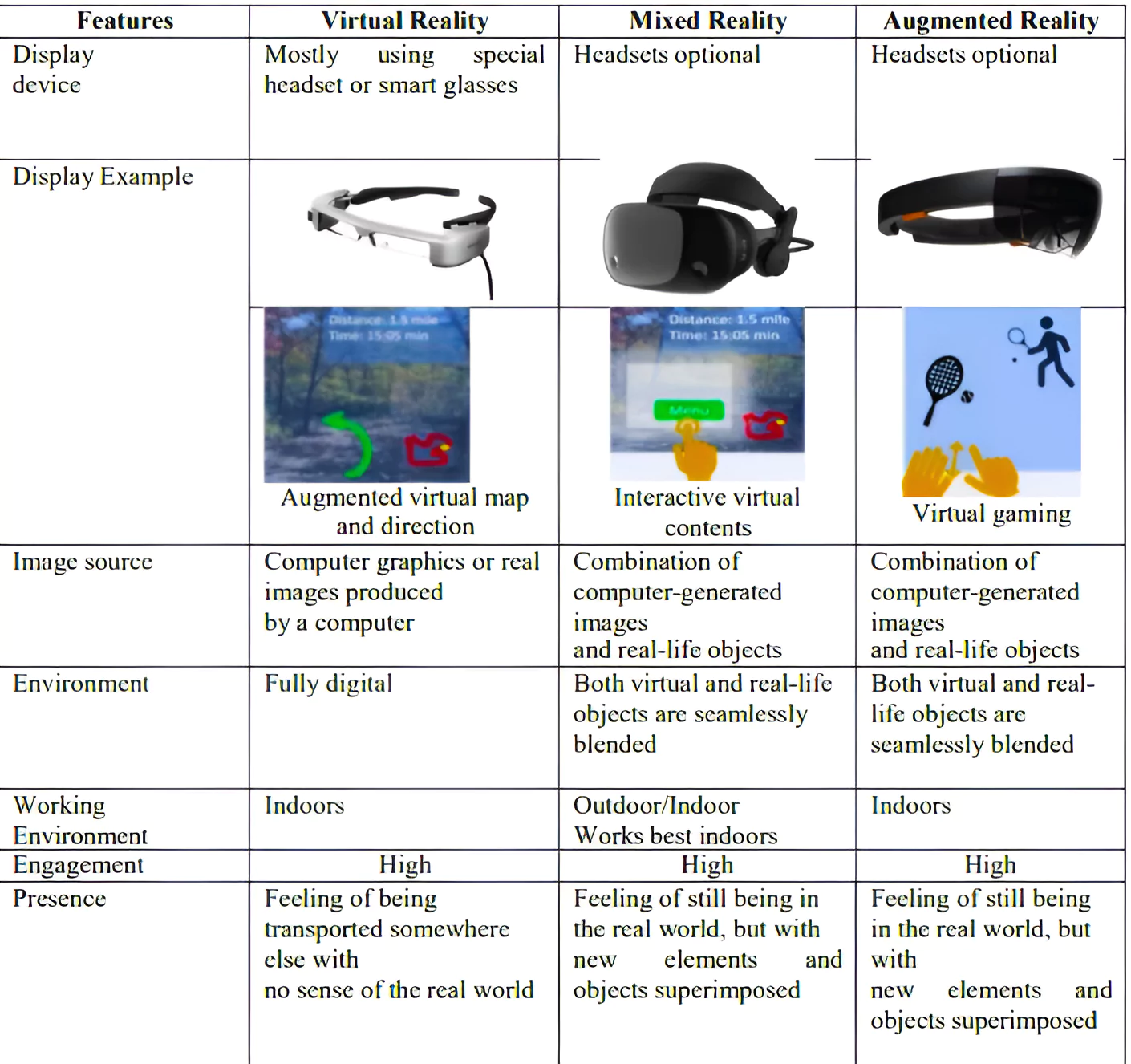
Mixed Reality Program in India:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>