Context
Mount Etna Smoke: Mount Etna, the largest volcano in Europe, has been sending up almost perfect rings of smoke into the air.
- The Mount Etna Smoke rings are a rare phenomenon that scientists refer to as volcanic vortex rings, which are produced roughly in the same way as the smoke rings that some cigarette smokers are able to blow out of their mouths.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Mount Etna
- Geographical Location: Mount Etna is on the east coast of Sicily, (Italy) which is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Its strategic location influences both local climate and agricultural practices due to its volcanic ash contributing to fertile soil.
- Physical Features: The summit of Mount Etna features five main craters which are the primary sources of its frequent eruptions.
- Additionally, the mountain is dotted with over 300 vents that vary in size. These vents are scattered along its slopes and contribute to both summit and flank eruptions.
- Eruption Episodes: Mount Etna is one of the most continuously active volcanoes in the world, with an eruptive history that dates back over 500,000 years. The volcano has experienced numerous eruptive events since 1600, including:
- Summit Eruptions: Notable summit eruptions occurred in 2006, 2007-08, twice in 2012, 2018, and most recently in 2021.
- Flank Eruptions: Significant flank eruptions took place in 2001, 2002-03, 2004-05, and 2008-09.
- World Heritage Site: Mount Etna has been designated a World Heritage Site since 2013. According to UNESCO, the volcano’s eruptive history can be traced back 500,000 years, out of which 2,700 years of this activity has been documented.
- Summit Eruption: It refers to volcanic activity occurring at the central vent, usually at or near the very top of the volcano. This is the primary vent where the main conduit from the magma chamber reaches the surface.
- Flank Eruptions: It occurs on the sides or lower parts of a volcano, rather than at the peak. These eruptions emerge from side vents or fissures that are typically connected to the main magma conduit but can have separate pathways.
|
About Volcanoes
- According to the US Geological Survey: “Volcanoes are openings, or vents where lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.”
- They can be found on land and in the ocean and are formed when material significantly hotter than its surroundings is erupted onto the surface of the Earth.
- The material could be liquid rock (known as “magma”, when it’s underground and “lava” when it breaks through the surface), ash, and/or gasses.
- According to NASA, the rise of magma can take place in three different ways.
- Divergence: When tectonic plates (massive, irregularly shaped slabs of solid rock that carry both continents and oceans and are constantly in motion) move away from each other. The magma rises up to fill in the space.
- Convergence: When the plates move towards each other part of Earth’s crust can be forced deep into its interior. The high heat and pressure cause the crust to melt and rise as magma.
- Hotspots: Magma also rises at the hotspots i.e. hot areas inside of the Earth, where magma gets heated up. As magma gets warmer, it becomes less dense, leading to its rise.
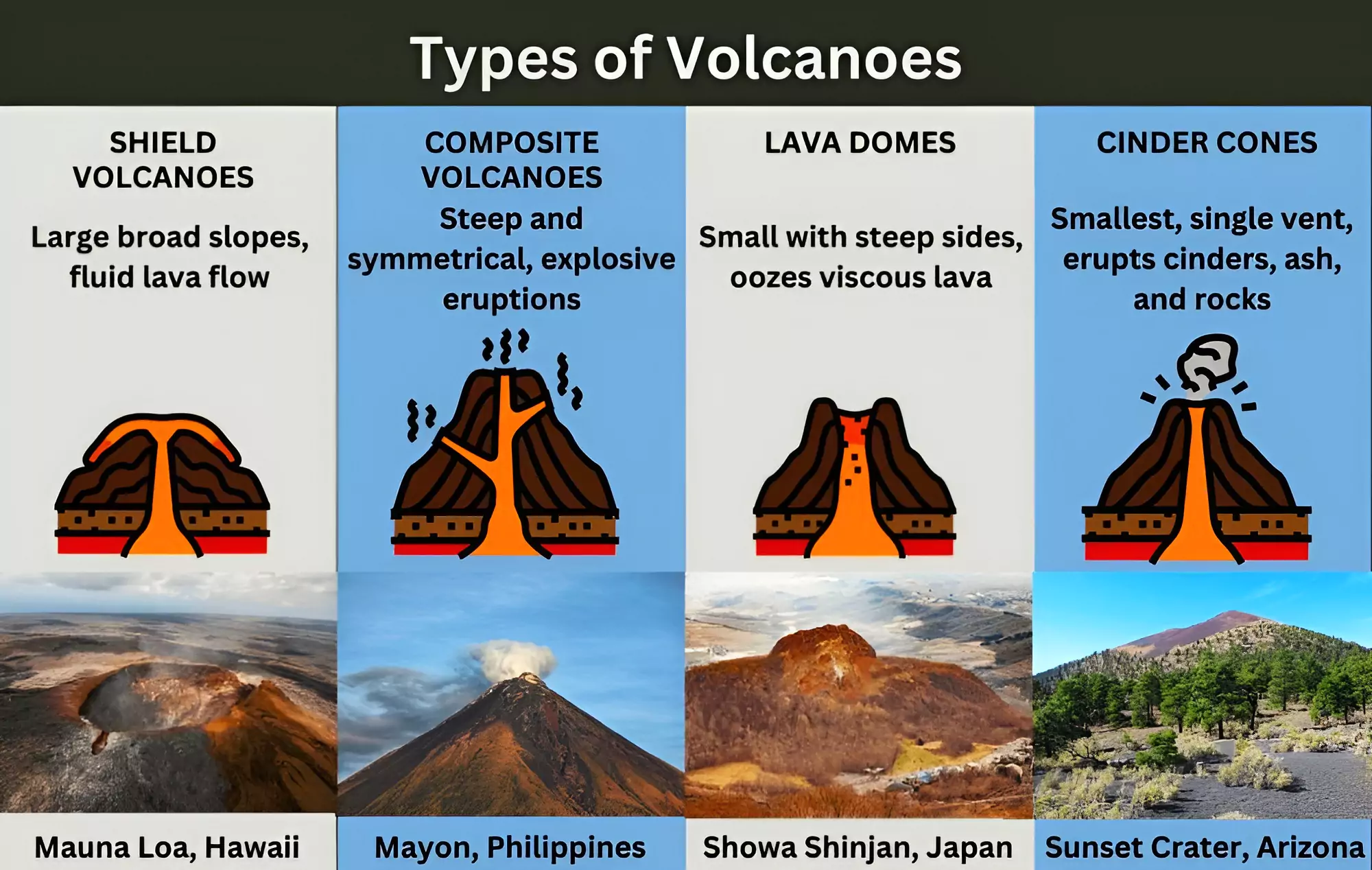
Different Types of Volcanoes
- According to the British Geological Survey, the type of volcano depends on the viscosity of the magma, the amount of gas in the magma, the composition of the magma, and the way the magma reaches the surface.
-
Major Types of Volcanoes:
-
- Stratovolcano/Composite Volcanoes: They are steep-sided volcanoes composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity lava, ash and rock debris.
- These types of volcanoes are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows in alternate layers, the strata that give rise to the name.
- Cinder Cones: Cinder cones are circular or oval cones made up of small fragments of lava from a single vent that have been blown up.
- Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of scoria and pyroclastics that build up around the vent. Most cinder cones erupt only once.
- Shield Volcano: These volcanoes are shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows. These are formed by the eruption of low-viscosity lava that can flow a great distance from a vent.
- Shield volcanoes are more common in oceanic than continental settings. The Hawaiian volcanic chain is a series of shield cones, and they are common in Iceland, as well.
- Lava Domes: They are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent. They are built by slow eruptions of highly viscous lava.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Distribution of Volcanoes Around the World
There are about 500 volcanoes in the world. Most of these volcanoes are found in
three well defined belts.
-
The Circum-Pacific Belt:
- Circum-Pacific region has the greatest concentration of volcanoes, that is why it is called ‘Pacific Ring of Fire‘. It is a horseshoe-shaped zone encircling the Pacific Ocean.
- This ring extends along the Andes mountains of South America to Alaska and from the Aleutian Islands to Japan, Philippines, Indonesia to New Zealand.
- Major Volcanoes: Mount St. Helena, Mauna Loa,Mount Ruapehu, Mount Krakatoa, Mount Fuji.
-
The Mid-World Mountain Belt:
- The Mid-world mountain belt occupies the second position with regard to the numbers of volcanoes.
- It runs from Alps in Europe to Asia Minor and crossing through Himalayan region joins the Circum-Pacific belt
- Major Volcanoes Mt. Stromboli , Mt. Vesuvius , Mt. Karakoram
- India’s only active volcano is located in Barren island of Andaman, which is also the only confirmed active volcano in South Asia
-
The African Rift Valley Belt:
-
- The African Rift Valley region ranks third. Most of the volcanoes are extinct here.
- Mt. Cameroon is the only active volcano which is situated in Central West Africa.
- Other Volcanoes: Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya, Mount Longonot
About Volcanic Vortex Rings
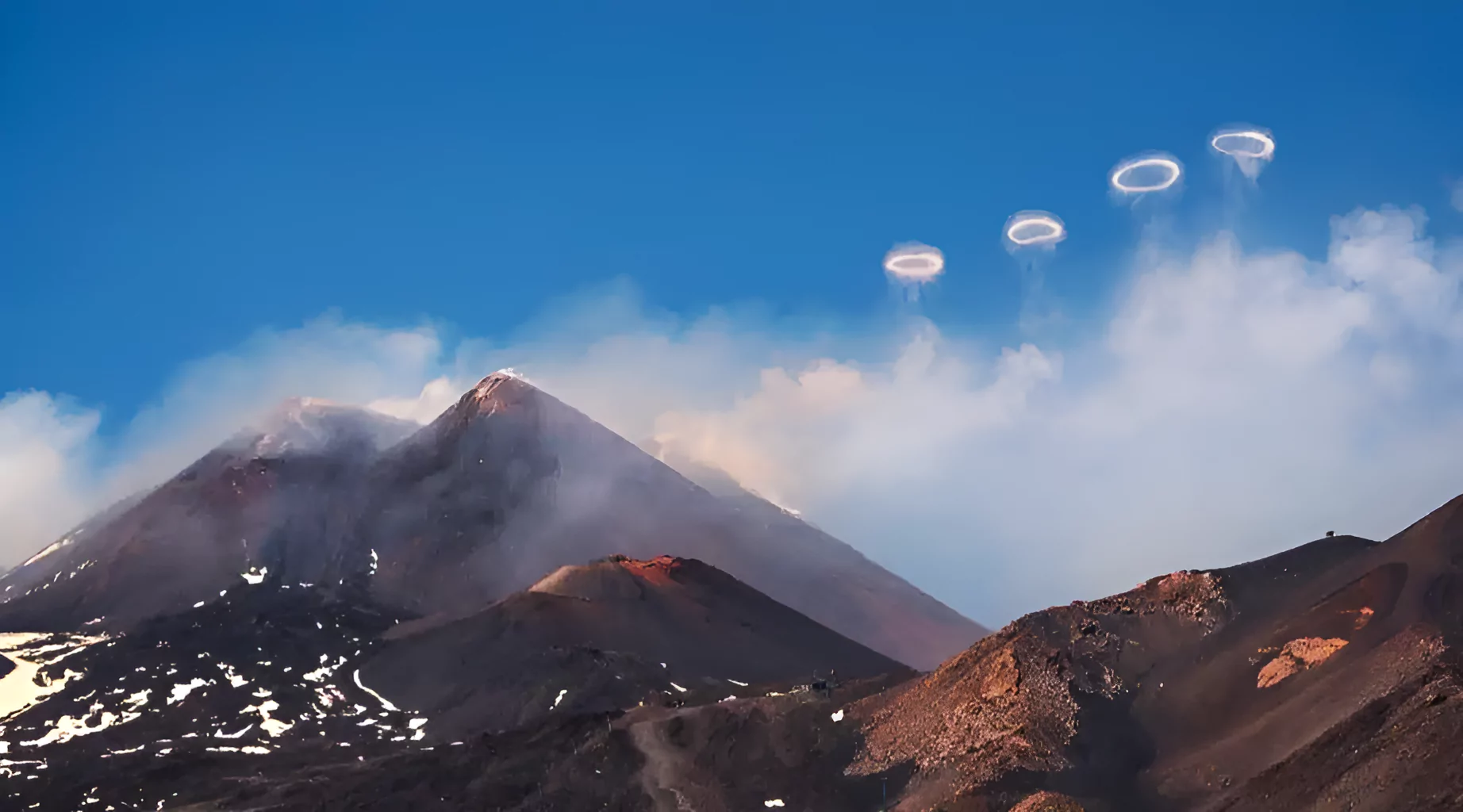

- Volcanic vortex rings are circular loops of gasses, predominantly water vapor, that are expelled into the air in a ring-like formation through a vent in the crater.The vent that has opened up in Mount Etna’s crater is almost perfectly circular, thus the rings that have been seen above it are also circular.
- These rings can remain in the air for up to 10 minutes, but tend to disintegrate quickly if conditions are windy and turbulent.
-
Formation of Volcanic Vortex Rings:
- Rapid Gas Emission: The formation involves rapid ejection of gas through a narrow circular conduit in a volcano’s crater. This rapid expulsion is the initial trigger for the development of the vortex ring.
- Pressure and Motion Dynamics: Similar to dolphins blowing bubble rings, the volcanic gasses are compressed and pushed through the vent, which creates a high-pressure pulse that molds the gas into a circular vortex.
- Stabilization and Travel: Once formed, the cohesive forces within the gas maintain the ring’s structure, allowing it to rise intact through the atmosphere unless disrupted by external forces like wind.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
Significance of Volcanic Vortex Rings:
-
- Research Value: Studying volcanic vortex rings helps scientists understand eruption dynamics and plume behavior, which are critical for predicting ash dispersion and assessing aviation risks.
- Environmental Impact: Understanding these rings also aids in evaluating the environmental impact of the ash and gasses released during eruptions, which can affect air quality and climate.
- Volcanic vortex rings have been observed at volcanoes such as Redoubt in Alaska, Tungurahua in Ecuador, Pacaya in Guatemala, Eyjafjallajökull and Hekla in Iceland, Stromboli in Italy, Aso and Sakurajima in Japan, Yasur in Vanuatu, Whakaari in New Zealand etc.
- Mt Etna is well known for producing Volcanic Vortex rings. It was found that Mt Etna produced dozens of gas rings every day last year too.
Positive Consequences of Volcanic Eruptions
Positive consequences of volcanic eruptions are;
-
Climatic Benefits:
- Solar Radiation Cooling: Volcanic particles can shade incoming solar radiation, causing temporary cooling effects on the planet that may last from months to years.
-
Agricultural and Ecological Benefits:
- Soil Fertility: The breakdown of some types of volcanic ash and lava contributes to soil rich in nutrients, enhancing land for crops and forest growth.
- Creation of New Landforms: Volcanoes form islands, plateaus, and mountains, which can be rich in minerals and fertile soils.
-
Economic and Geothermal Advantages:
-
- Mineral Resources: Volcanic activity brings valuable mineral resources to the surface, including metallic ores and diamonds.
- Geothermal Energy: Regions with volcanic activity often have potential for geothermal power generation, tapping into the Earth’s internal heat.
- Tourism and Recreation: Volcanic landscapes attract tourists, benefiting local economies and sometimes leading to the establishment of national parks centered around volcanic features.
Negative Consequences of Volcanic Eruptions
Negative consequences of volcanic eruptions are;
-
Environmental and Climatic Hazards:
- Stratospheric Ash: Volcanic ashes can remain in the stratosphere for 2-5 years, where they participate in chemical reactions that destroy ozone molecules.
- Greenhouse Gasses: Eruptions release large amounts of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, contributing to global warming.
- Loss of Flora and Fauna: Lava flows can destroy entire ecosystems, killing plants and animals which serve as carbon sinks.
-
Human and Structural Damage:
- Physical Destruction: Advancing lava can engulf cities and landscapes, while pyroclastic materials like cinders and volcanic bombs can cause fatalities and injuries.
- Volcanic Earthquakes and Mudflows: Associated seismic activity and lahars (mudflows of volcanic ash mixed with water) can devastate nearby areas.
- Health Risks: Eruptions can cause respiratory illnesses, burns, and injuries due to falls, while ash can lead to hazardous driving conditions and deteriorate water quality.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
-
- Agricultural Disruption: Ash fall can damage crops and reduce periods of rain, negatively impacting agricultural productivity.
- Tsunamis: In coastal regions, underwater volcanic activity can trigger tsunamis, causing extensive damage.
Also Read: Why Is Japan Prone To Earthquakes And Tsunamis?
| Prelims PYQ (2014):
Which of the following adds/ads carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on the planet Earth?
1. Volcanic action
2. Respiration
3. Photosynthesis
4. Decay of organic matter
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c) |
![]() 13 Apr 2024
13 Apr 2024




