Context:
Recently, there has been an explosion in the amount of data on somatic variants due to increasing ability to sequence the genetic material in individual cells using advanced microfluidics and high-throughput sequencers.
About Human Genome
- The human genome is the blueprint of our genetic makeup and it has 23 pairs of chromosomes, one inherited from each of our parents.
- Process of Human Genome Formation:
- The ovum and the sperm carry these blueprints from our parents.
- After fertilisation, the combined single cell starts to divide by copying the genetic material to nearly a trillion cells that make up the human body.
- Various studies have estimated that there is an error rate of 0.64-0.78 mutations per billion base pairs per division.
SMaHT Network
- The U.S. recently launched a programme focused on understanding the breadth of somatic mosaicism called the Somatic Mosaicism across Human Tissues (SMaHT) Network.
- Mosaicism is when a person has two or more genetically different sets of cells in their body.
- Aim: Discovering somatic variants, developing tools and resources with which to study them, and improving the ability to analyse, interpret, and organise them in different biological and clinical contexts.
|
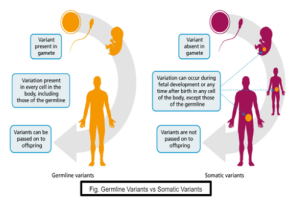
About Somatic Genetic Variants
- An error that occurs in the DNA after birth but during development is called a somatic genetic mutation.
- For example, Skin Cancer, Lung Cancer etc.
- Their occurrence is driven by the repeated copy and pasting of the genome which means there will be more somatic genetic mutations in the older individuals.
- Sometimes, a somatic genetic mutation can render a cell fitter than others, which lead to the formation of tumours. So these mutations are called driver mutations. It plays an important role in the development of cancers.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 28 Aug 2023
28 Aug 2023
