Context
According to the India TB Report 2024, 79% of presumptive TB testing was still carried out using 100-year-old sputum smear microscopy and just 21% of cases were detected using a molecular test.
| Presumptive TB refers to a patient presenting symptoms or signs suggestive of TB (previously known as a TB suspect). |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination 2017-25
- The National Strategic Plan 2017-2025 wanted to reduce the number of who are offered sputum smear microscopy from over 9.1 million in 2015 to 5.1 million in 2023 while increasing the number of molecular tests from 40,000 in 2015 to over 14.7 million in 2023.
- However, as per the India TB report, in 2023, India was far from reaching the ambitious target set by NSP 2017-2025.
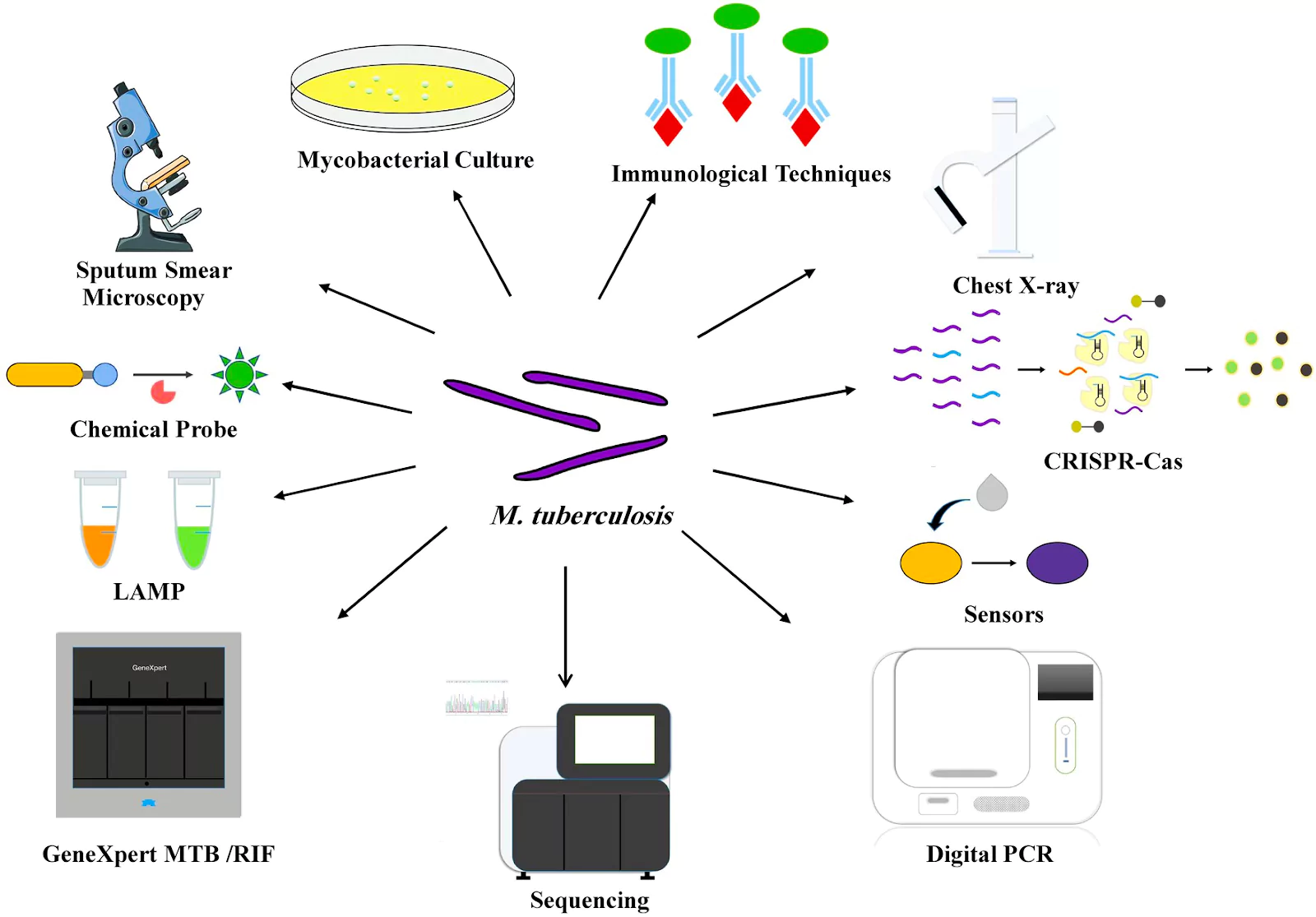
About Sputum Smear Microscopy
- Sputum smear microscopy has been the primary method for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
- It is a simple, rapid and inexpensive technique that is highly specific in areas with a very high prevalence of tuberculosis.
- It also identifies the most infectious patients and is widely applicable in various populations with different socio-economic levels 3,4,5.
 Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.
Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.
Limitations of Sputum Smear Microscopy
- Low Sensitivity: The sensitivity is grossly compromised when the bacterial load is less than 10,000 organisms/ml sputum sample
- Inefficient: a poor track record in extra-pulmonary tuberculosis, pediatric tuberculosis and patients co-infected with HIV and tuberculosis.
- Requirement of serial sputum examinations: some patients who do not come back for repeated sputum examinations become “diagnostic defaulters’’.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Alternative Methods: Molecular Biology Diagnostic Techniques
-
Xpert MTB/RIF:
- It is the most widely used detection method in molecular diagnostics.
- It is a semi-nested real-time fluorescent PCR for the detection of M. tuberculosis and rifampin resistance simultaneously.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification:
- This is a type of Nucleic Acid Amplification Test that employs DNA polymerase and a set of specially designed primers to detect the presence of pathogenic DNA from a patient sample.
-
Digital PCR:
-
- Digital PCR (dPCR) is a new type of nucleic acid quantification technology that requires very small amounts of target molecules, and it performs absolute quantification without the need for a standard curve.
- Therefore, dPCR is precise and sensitive, and most importantly, it can detect single copies of DNA.
Immunological Diagnostic Techniques
-
Tuberculin Skin Test and Interferon-γ Release Assay:
- The tuberculin skin test and the subsequent widely used tuberculin protein derivative test play an important role in the auxiliary diagnosis of TB, especially in paediatrics TB.
- However, these approaches are neither able to effectively distinguish the positive results due to BCG vaccination or M. tuberculosis infection nor provide reliable results for potential immunocompromised TB patients.
-
Immuno-PCR
- The Immuno-PCR (I-PCR) assay detects potential mycobacterial antigens and circulating antibodies in the body fluids of TB patients. Thus, it can be used as a new diagnostic approach for TB.
- I-PCR based on magnetic beads (MBs)/ gold nanoparticles (GNPs) in liquid form produces a reduced background signal, and the automated one-step I-PCR also shortens the detection time.
-
Lateral Flow Urine Lipoarabinomannan Assay:
-
- It is a key lipopolysaccharide and pathogenic factor present in the cell wall of mycobacteria, with a representative structural epitope of M. tuberculosis.
Also Read: Global TB Report 2023 By World Health Organization (WHO)
![]() 8 Apr 2024
8 Apr 2024
 Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.
Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.