Context: This article is based on the news “India Russia trade doubled to nearly $50 billion in Jan-Sept: Russian Ambassador” which was published in the Live Mint. The bilateral trade between India and Russia has doubled to almost $50 billion during January-September 2023.
Key Highlights On India Russia Trade
- Trade has increased by around 2.1 times in January- September this year, up to almost 50 billion USD owing to strong demand for hydrocarbons in India.
- This is expected to grow further and substantially surpass the figures of the previous year.
- During April-May of FY 2023-24, India’s trade with Russia saw around a 161% increase compared with the same period last year.
- India and Russia have already achieved the bilateral trade target of $30 billion before the target year of 2025.
- According to Engineering Exports Promotion Council (EEPC) India, amid declining demand for engineering goods from major markets such as the US and China, shipments to Russia continued their uptrend and more than doubled to around US$ 123 million in July 2023 from around US$ 55 million in July 2022, a rise of about 122%.
India Russia Trade: Major Trade Items
- Major exported items from India to Russia: These include iron and steel, drug formulations, biologicals, residual chemicals and allied products, marine products, industrial machinery for dairy, etc. during April-May 2023-24.
- Major imported items from India to Russia: These include crude, coal, coke and briquettes, petroleum products, fertilisers manufacturers, pearl, precious and semi-precious stones, vegetable oils, inorganic chemicals, etc. during April-May 2023-24.
|
About India Russia Trade Relations:
- Time-Tested Bilateral Ties: Russia and India have been longstanding and time-tested partners. The Indo–Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation was signed between India and the Soviet Union in 1971 which specified mutual strategic cooperation.
- India’s Foreign Minister described India’s relationship with Russia as among the steadiest of major relationships in the world.
- Enhanced Cooperation: Since the signing of the “Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership” in 2000, the ties have gained a qualitatively new character with enhanced levels of cooperation in almost all areas of the bilateral relationship.
- India and Russia have maintained cooperation in areas like politics, security, defence, trade and economy, science & technology, culture, and people-to-people ties.
- India-Russia Summit: During the Summit held in December 2021, 28 MoUs and agreements were signed.
- A Joint Statement titled “India-Russia Partnership for Peace, Progress and Prosperity” was also adopted.
India Russia Trade Relations: Significance
- Increasing Bilateral Trade: India and Russia are discussing a free trade agreement (FTA) involving the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU/EAEU), against the backdrop of bilateral economic ties seeing a sharp expansion since the start of the Ukraine conflict.
- EAEU is a free trade agreement that came into being in 2015 to increase economic cooperation and raise the standard of living of its members. Member countries include Russia, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
Impact of Russia- Ukraine Conflict on Bilateral Trade with India:
- Sanctions on Russia: The conflict led to punitive sanctions on Russia by the West. This pushed up global crude oil prices to record highs.
- Negative Impact on India: India experienced spillover effects as stock markets plummeted, inflation reached unprecedented levels, the rupee sharply declined against the US dollar, and foreign exchange reserves suffered a setback.
- Increase in Russian Imports: Sanctions on Russia, in a way, proved to be beneficial for India as it bought cheap crude oil from Moscow.
- In 2021-22, Russia was India’s 18th largest import partner, accounting for $9.86 billion of imports. In comparison, Russia became India’s 4th largest import source during the initial 10-month period in the financial year 2022-2023.
|
- Diversifying Trade: India has diversified its export basket to Russia to include pharmaceuticals, fertilisers, coal, diamonds, chemicals, and ceramics, among other goods.
- Further Diversifying Export Basket: By exploring possibilities in automobiles and spare parts, electronics goods, medical devices, solar photovoltaic modules, textiles, food and agricultural products, etc.
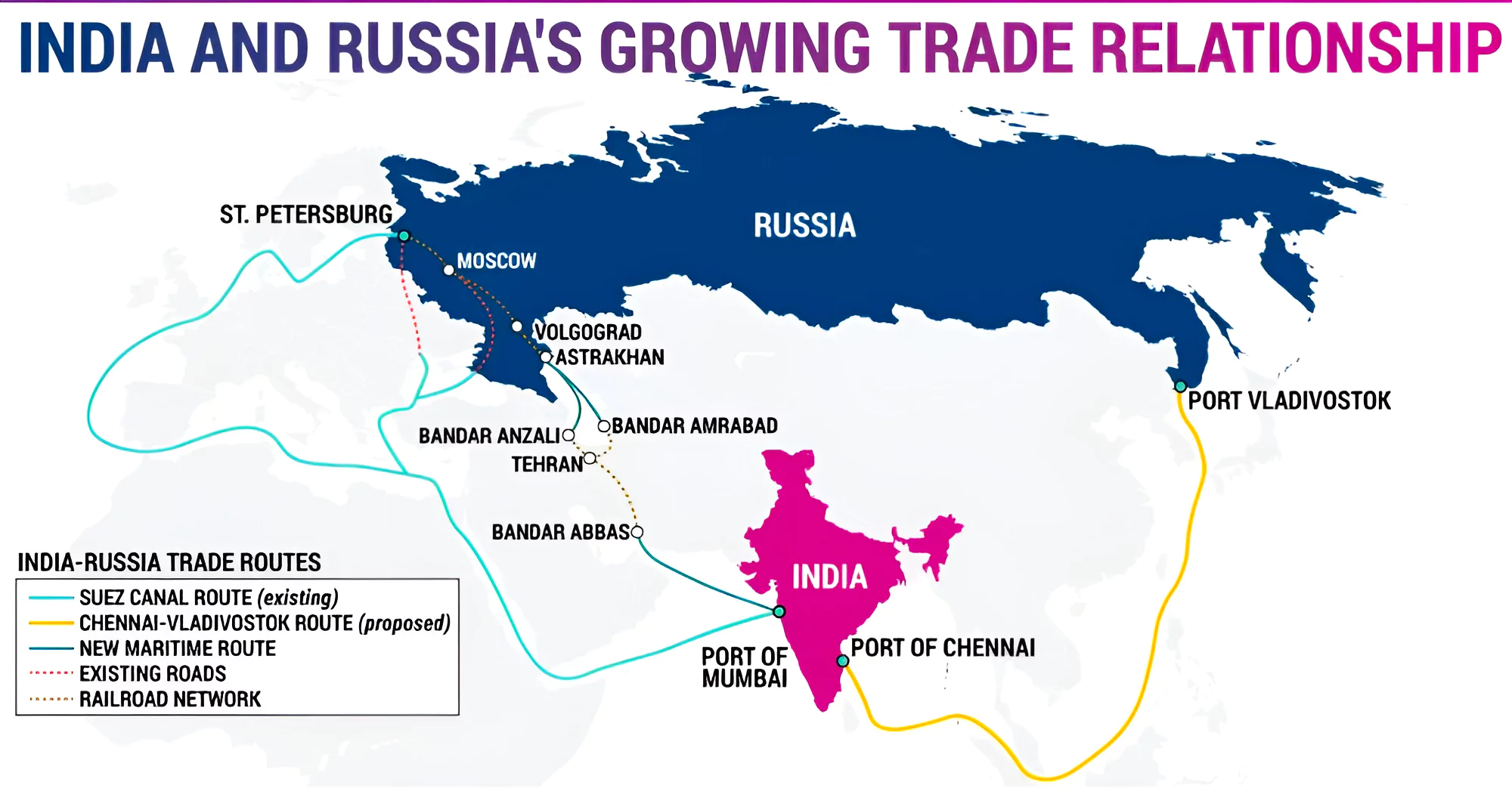
- New Trade Routes: The development of new trade routes like the Eastern Maritime Corridor and the Northern Sea Route will also be of interest in deepening trade ties.
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is another effective connectivity initiative to increase Indo-Russian trade.
- India and Russia are also discussing the possibility of launching a trans-Arctic container shipping line and processing facilities along the Northern Sea Route.
- New Bilateral Investment Treaty: India and Russia are in advanced negotiations for a new Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) that is necessary to boost the confidence of investors.
- BITs are agreements between India and Russia designed to safeguard investments made by investors of both nations.
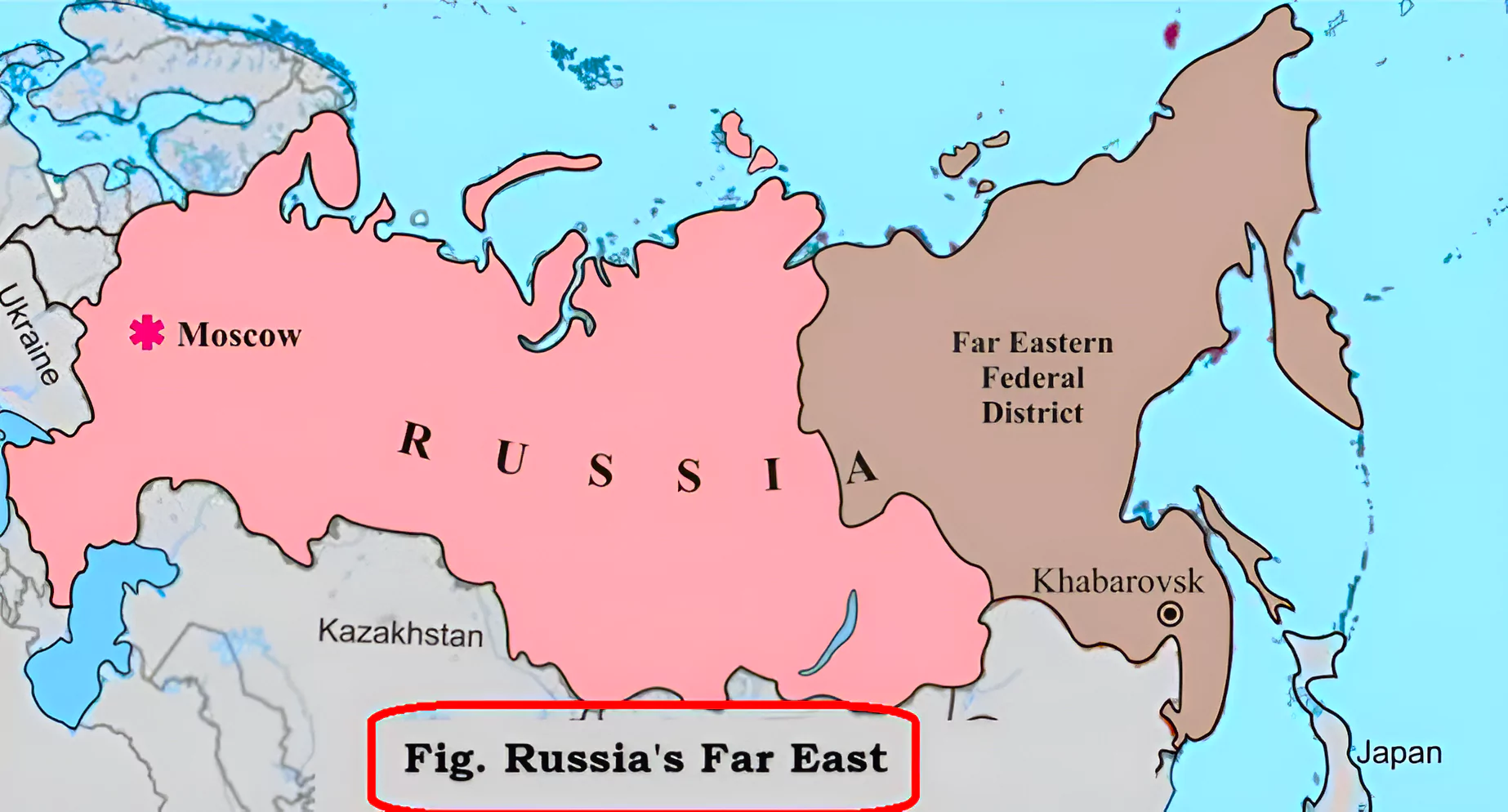
- Increasing India’s Presence in Russia’s Far East: Russia is keen for India to expand its presence at the Vladivostok port. Russia is eager to give the Chennai-Vladivostok Marine Corridor (CVMC) more impetus because it has the potential to strengthen marine relations between India and Russia.
- The CVMC is being utilised to transport metallurgical coal, crude oil, and liquified natural gas from Russia to India.
- India has expressed interest in building a satellite city near Vladivostok.
India Russia Trade Relations: Challenges
- Trade Imbalance: The skewed trade balance has been an area of concern between India and Russia.
- For example, during FY23, India had around a $43 billion trade deficit with Russia, which left their exporters with large surpluses in their Vostro accounts in India.
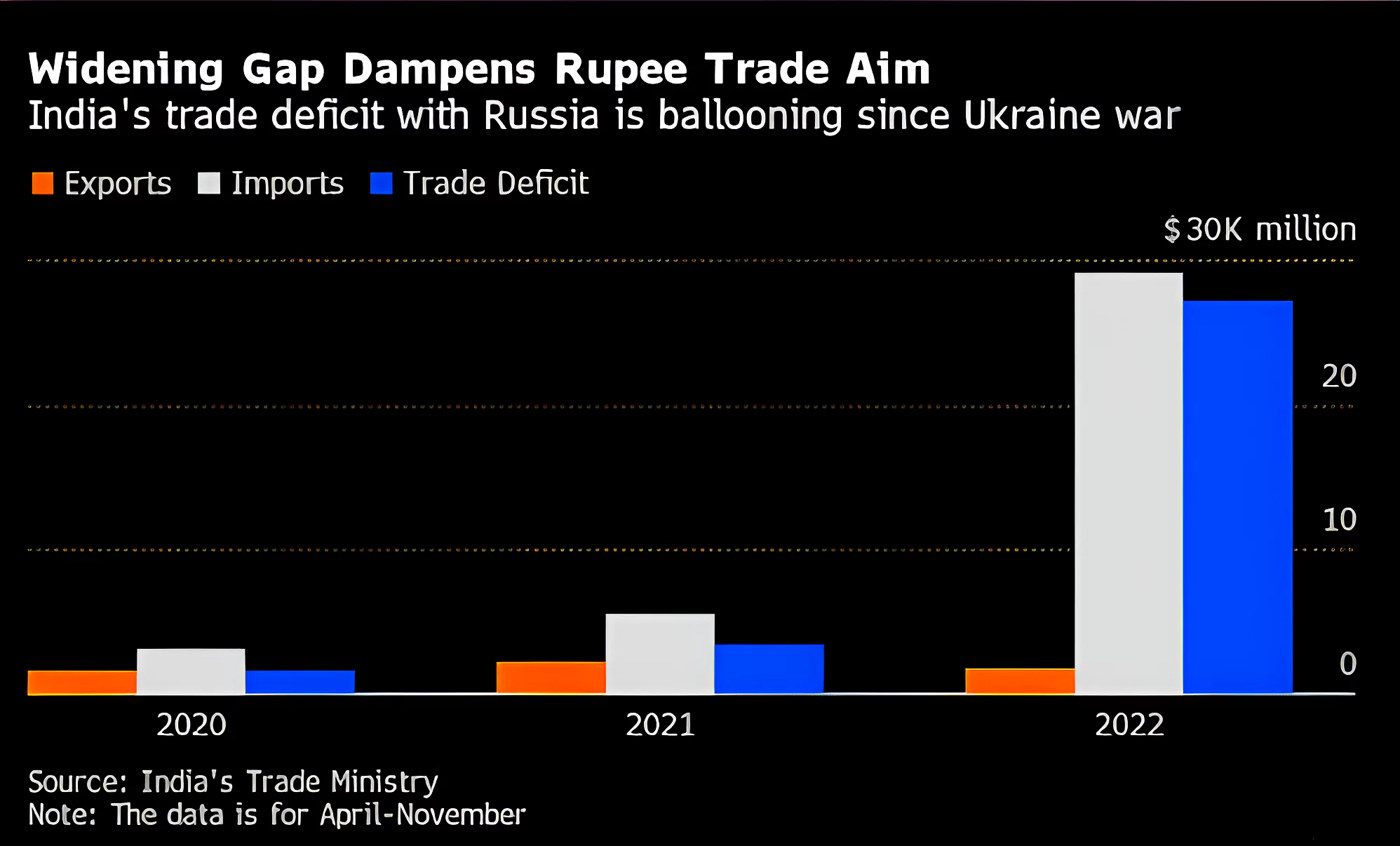
- Challenges in Rupee- Ruble Trade: Indian refiners are using a mix of currencies to settle most of their Russian oil purchases. Both countries previously discussed trading in their local currencies but this is yet to take off because of currency volatility and the high trade deficit.
- For example, the Rupee-Ruble trade since the Ukraine conflict has faced obstacles due to the accumulation of Rupees by the Russian side in India.
- Russia’s Over Dependence on China: China enjoys direct connectivity, advanced logistics supply, high level of trade and profitability with Russia.
- Since the beginning of Russia- Russia-Ukraine conflict, Russia-China cooperation has grown in all directions.
- The trade turnover between India and Russia reached a record $190 billion last year, increased by another 39% in the first quarter of this year compared with the same period in 2022.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity Issues: Inadequate transportation infrastructure and connectivity can impede the smooth flow of goods between India and Russia.
- The absence of a direct trade route and high shipping cost make exports to Russia a costly affair for India, as it doesn’t share a land border with Russia, unlike China.
Way Forward
- Addressing Trade Imbalance: A huge imbalance in trade heavily towards Russia is an issue in the Rupee-Ruble trade. To solve this problem, Russia is keen to import manufacturing equipment including machinery from India. Recently, the Russian President called for increasing mutual investments in pharmacy, manufacturing, and industry.
India’s Investment in Far-East Russia
- In 2019, India announced the “Act Far-East” policy, which led to an increase in India’s cooperation with the Russian Far East in various fields.
- Act Far-East Policy has become a key pillar of the “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership” of India and Russia.
- India has ambitious plans for the resource-rich Russian Far East and announced a $1 billion Line of Credit (LoC) for various projects in the region.
- Connectivity: The Chennai-Vladivostok sea route.
|
- Increasing Asia’s Importance for Russia: To compensate for the decline in trade with the West, Russia is looking much more toward Asia.
- For India, this could mean a broadening of our engagement that was overly reliant on the triad of military, nuclear, and space cooperation.
- Providing Solutions to Short- and Medium-Term Challenges in Business: Payments, logistics, and certification were some of the key areas of issues and it is possible to find solutions to them.
- For example, both sides found ways in the fertiliser trade last year in a much more mutually acceptable way. Many Russian and Indian companies have signed long-term contracts for the supply of fertilizers in demand in India
- Improving Rupee-Ruble Trade: To tackle the accumulation of Indian currency in Russia, increasing Rupee trade with third countries common to both India and Russia, where India has trade surplus can help in ensuring seamless money flow while solving the problem.
- For this, India has taken steps to de-dollarise trade while pushing for the internationalisation of Indian Rupee.
- Russia has also pitched for more use of national currencies in bilateral trade and called for ensuring smoother financial transactions between India and Russia.
- India as China’s Alternative to Russia: Since the start of the Russia- Ukraine conflict, Russian raw material exports to China and imports of Chinese goods have sharply increased. Sanctions from Western countries made Russia vulnerable, which has prompted China to use its economic leverage, forcing humiliating and one-sided concessions.
- However, India provides Russia with a choice of reliable partners, capable of ensuring the inflow of necessary goods to the Russian market.
Also Read: Russia May Pull Out From the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Conclusion:
The evolving dynamics of India Russia trade relations underscore the need for strategic measures to overcome challenges, bolster economic ties, and chart a path towards a more resilient and diversified partnership in the international arena.
| Prelims Question (2019)
Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries?
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: (b) |
![]() 9 Dec 2023
9 Dec 2023



