Know about the origin, powers, and functions of the GST Council, shaping India's tax landscape. Understand its significance and the recent Supreme Court verdict on GST.

The GST council is likely to play a more effective role in ensuring fiscal federalism in the country by giving voice to the states. In the interest of the nation, there must be a consensual decision on issues concerning GST.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
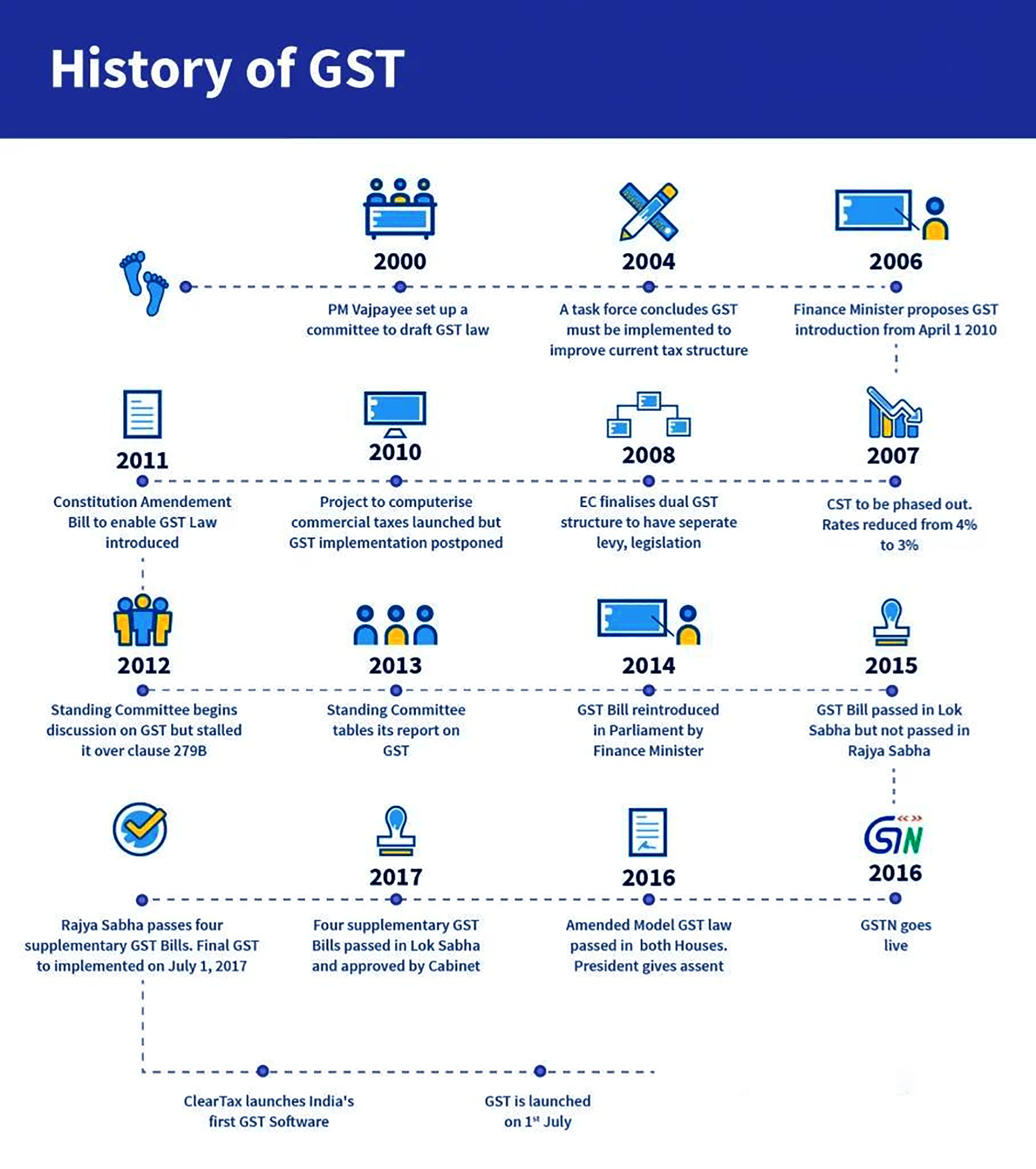
The GST Council is a constitutional body under Article 279A of the Indian constitution.
The GST council was formed for the smooth and efficient administration of the new tax regime under the GST system.
The decision-making will be based on a majority of not less than three-fourths of the weighted votes of the members present and voting at the meeting.
A recent decision of the Supreme Court ruled that the recommendations of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council are not binding on either the Union government or the states.
Goods and Service Tax (GST) is a tax regime that has replaced many indirect taxes in India such as the excise duty, VAT, services tax, etc. It is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
The Government of India brought the 101st Amendment Act of 2016 to introduce the Goods and Service Tax in the country.
GST has subsumed the majority of indirect taxes such as service tax, Value Added Tax (VAT), Central Excise, etc.
Currently, there are five GST slabs: 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>