Answer:
|
How to approach this question?
- Introduction
- Briefly write about the issues and define land pooling.
- Body
- Describe the potential of land pooling in addressing these issues.
- Discuss the challenges of land pooling.
- Provide a way forward.
- Conclusion
- Conclude on a positive note.
|
Introduction
In India, small fragmented landholdings among over 85% of farmers and low mechanization rates (around 40%) have led to the adoption of innovative approaches like land pooling. It can be explained as combined individuals’ land holdings to create consolidated farms, promoting efficiency, shared resources, and cooperative farming.
Body
Potential of land pooling in addressing the issues:
- Consolidation of fragmented land: Land pooling combines small landholdings, creating larger farms for improved efficiency and economies of scale. The Amaravati Land Pooling Scheme in Andhra Pradesh consolidated 33,000 acres for developing a new capital city.
- Enhanced mechanization and modernization: Land pooling enables widespread adoption of modern technologies, boosting productivity and reducing labour-intensive practices. The Sardar Sarovar Canal Command Area Project in Gujarat saw increased mechanization and precision farming techniques, leading to significant agricultural productivity improvements.
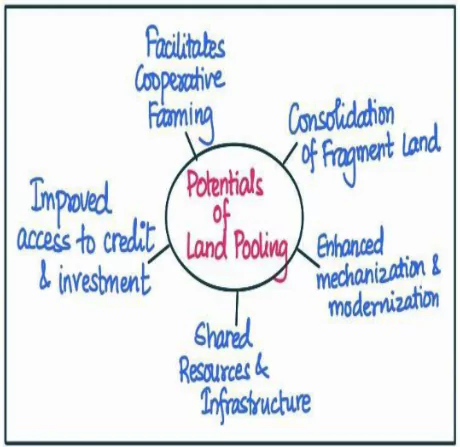 Shared resources and infrastructure: Land pooling promotes resource-sharing among farmers, optimizing resource utilization and reducing individual investment burdens. The Satara DistrictLand Pooling Project in Maharashtra exemplifies this, improving water management through shared irrigation facilities.
Shared resources and infrastructure: Land pooling promotes resource-sharing among farmers, optimizing resource utilization and reducing individual investment burdens. The Satara DistrictLand Pooling Project in Maharashtra exemplifies this, improving water management through shared irrigation facilities.- Improved access to credit and investment: Land pooling attracts investment, improving credit access for mechanization and modernization in agriculture. For instance, the Integrated Cooperative Development Project in Telangana boosted credit and investment, enhancing productivity through modern farming practices.
- Facilitating cooperative farming: Land pooling fosters cooperative farming, enabling shared resources and collective investment in mechanization, addressing fragmented land and financial barriers for small-scale farmers, as seen in the Cooperative Farming Scheme in Punjab.
Challenges in Land Pooling:
- Resistance from farmers: Overcoming reluctance and convincing individual farmers to voluntarily participate in land pooling can be challenging.
- Unequal land values and sizes: Addressing discrepancies in land sizes and values is a challenge in achieving fair and equitable distribution of benefits.
- Infrastructure and resource limitations: Lack of adequate infrastructure and resources can hinder the implementation and effectiveness of land pooling initiatives.
- Coordination and management issues: Managing operations, decision-making, and resolving conflicts within cooperative farming structures pose significant challenges.
Way Forward
- Streamline legal processes: Simplify land pooling regulations for smoother implementation.
- Raise awareness: Educate farmers about land pooling benefits and address concerns.
- Fair compensation and incentives: Provide just compensation and incentives to encourage participation.
- Develop infrastructure: Invest in necessary facilities to support consolidated farms.
- Effective governance: Establish strong leadership and governance for efficient cooperative farming.
Conclusion
With these efforts, there is hope for a future where Indian farmers can overcome land fragmentation and embrace modernization, leading to sustainable agricultural growth.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
 Shared resources and infrastructure: Land pooling promotes resource-sharing among farmers, optimizing resource utilization and reducing individual investment burdens. The Satara DistrictLand Pooling Project in Maharashtra exemplifies this, improving water management through shared irrigation facilities.
Shared resources and infrastructure: Land pooling promotes resource-sharing among farmers, optimizing resource utilization and reducing individual investment burdens. The Satara DistrictLand Pooling Project in Maharashtra exemplifies this, improving water management through shared irrigation facilities.
Latest Comments