Answer:
|
How to approach the question
- Introduction
- Write about democratic attitudes briefly
- Body
- Write how social influence and persuasion be effective in building democratic attitudes at the global stage.
- Write limitations of social influence and persuasion in building democratic attitudes at the global stage.
- Write suitable way ahead in this regard.
- Conclusion
- Give appropriate conclusion in this regard.
|
Introduction
Democratic attitudes refer to ethical principles and values which prioritise the protection of individual rights, active participation in decision-making processes, and the promotion of diverse perspectives. In an interconnected global world, a democratic attitude, characterised by inclusivity, transparency, and respect for diverse perspectives, is crucial to foster mutual understanding, promote collaboration, and address ethical dilemmas collectively. Example- Incorporating and respecting the Fundamental Rights of all sections of population.
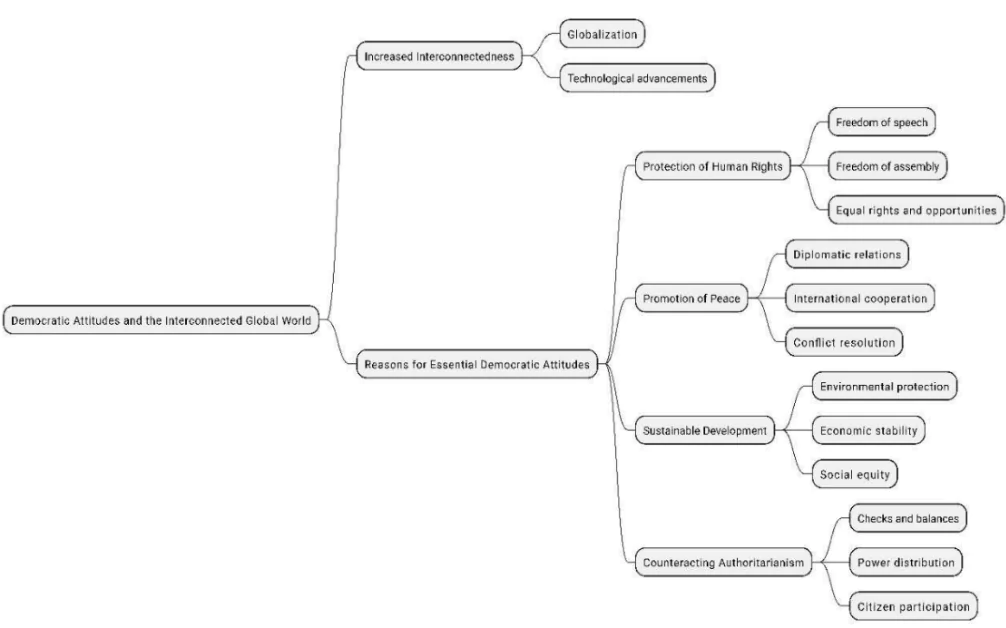
Body
Social influence and persuasion be effective in building democratic attitudes at the global stage through:
- Shared values: By promoting shared values such as freedom, equality, and justice. For example, influential leaders and organisations can advocate for human rights and emphasise the importance of democratic principles in achieving a just society.
- Public diplomacy: Governments can employ persuasive communication strategies to enhance democratic attitudes on the global stage. As done by the Fulbright Program, which promotes democratic values through international educational exchanges.
- Role modelling: Influential democratic countries can serve as role models for others, inspiring them to embrace democratic principles. Nations like Sweden can inspire others to adopt Feminist foreign policy.
- Social media activism: They have become powerful tools for social influence and persuasion. Grassroots movements like the Black Lives Matter movement have utilised these platforms to mobilise citizens, raise awareness about democratic principles.
- Global partnerships: Organisations like the United Nations and NGOs like Amnesty International play a crucial role in promoting democratic norms and providing platforms for persuasive dialogue and cooperation.
- Peaceful transitions: The peaceful transfer of power in countries like South Africa during the end of apartheid or the recent democratic transition in Sudan can serve as powerful examples that inspire and influence others to pursue democratic governance.
Limitations of social influence and persuasion in building democratic attitudes at the global stage:
- Cultural differences: Social influence and persuasion techniques may not be universally effective due to cultural variations. For example, a Western-style political campaign focused on individualistic values may not resonate with collectivist societies.
- Language barriers: Language differences hinder effective social influence across global contexts as it heavily reliant on wordplay, idioms, or specific cultural references may lose their impact when translated or used in a different linguistic context.
- Diverse values and ideologies: Persuasive attempts to promote democratic ideals can clash with deeply entrenched cultural or ideological beliefs. As societies with strong autocratic traditions may resist external influences advocating for democratic values.
- Political interests: Countries may use such techniques to advance their strategic objectives rather than genuinely fostering democratic attitudes leading to scepticism among populations who perceive such efforts as manipulative or self- serving.
- Autocratic regimes: Authoritarian governments often suppress dissent and control information flow which also leads to self-censorship, making it challenging to cultivate democratic attitudes through social influence.
- Lack of trust: Global politics is often marked by a lack of trust and scepticism towards external influences. Attempts to build democratic attitudes may face resistance if they are perceived as undermining national sovereignty or imposing foreign values. Example- 1979 Islamic Revolution in Iran.
Suitable way ahead in this regard:
- Empathy and Active Listening: For example, leaders can engage in town hall meetings where they actively listen to citizens’ concerns and incorporate them into policy decisions.
- Transparent Communication: Political figures can employ regular press conferences and public statements to share accurate information and dispel misinformation, fostering an informed democratic society.
- Encouraging Civil Discourse: Advocate for respectful and constructive dialogue among citizens. Online platforms can implement moderation policies that promote civil discourse, discouraging hate speech and fostering healthy democratic debates.
- Grassroots Mobilisation: To promote democratic values and social justice, global organisations like UN, EU etc. can provide resources and platforms for activists at ground level to mobilise their communities. It can help in promoting democratic attitudes among masses.
- Youth Engagement: Encouraging youth participation in democratic processes through initiatives such as youth parliaments, mock elections, and internships in political offices can empower young individuals to become future democratic leaders.
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Companies can engage in fair labour practices, support philanthropic initiatives, and promote transparency in their operations, strengthening democratic attitudes within society.
Conclusion:
By employing these ethical strategies, along with social influence and persuasion can effectively contribute to the building of democratic attitudes at the global stage, promoting ethical and inclusive governance systems that uphold human rights and foster social justice.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments