The British claimed paramountcy in India, asserting their ultimate authority over princely states, starting in the 18th century. This concept justified their dominance and control over Indian territories, economy, and governance. It became a cornerstone of British colonial rule, shaping Indian politics and society profoundly until independence in 1947.
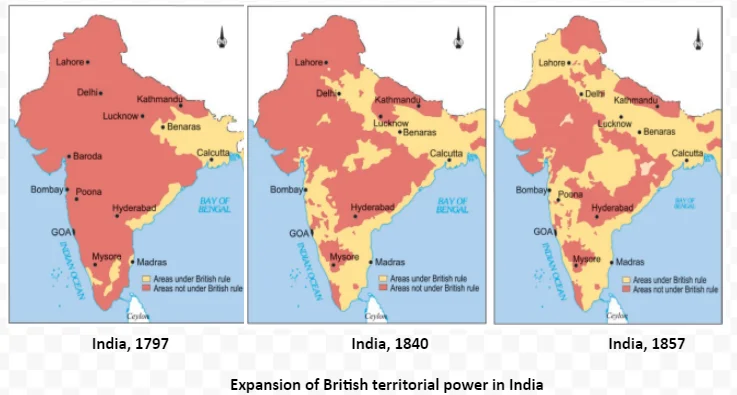
Major Shift: In the early nineteenth century, the Company adopted an aggressive policy of territorial expansion.
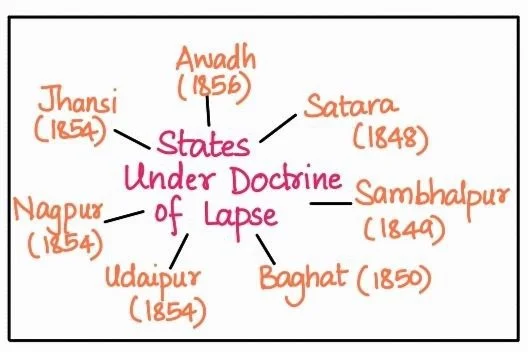
Annexation: This final wave of annexations in India occurred under Lord Dalhousie, who served as Governor-General from 1848 to 1856.
Before Warren Hastings: The Company gained control not only in Bengal but also in Bombay and Madras, which were divided into administrative units called Presidencies.
Rely on Mughal Army: Though colonial rule in India introduced administrative and reform ideas, it relied mainly on the Mughal army consisting mainly of cavalry (sawars) and infantry (paidal soldiers) supplied by the local zamindars.
Impact of Technology: The transformation of the East India Company from a trading entity into a territorial colonial power was significantly accelerated by the introduction of steam technology in the early nineteenth century.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Claim to Paramountcy asserted British dominion over Indian states. Doctrines like Lapse facilitated annexations. The Company transformed from a trading entity to a colonial power with its own administrative and military structures. By 1857, British dominance was established, setting the stage for a future clash with Indian nationalism.
| Related Articles | |
| BRITISH POLICY IN INDIA | INDIAN ECONOMY NOTES |
| LORD DALHAOUSIE (JAMES BROUN-RAMSAY, 1ST MARQUESS OF DALHOUSIE) | Supreme Court of India: Jurisdiction, Powers, & Constitutional Role |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>