“This Government will function as a Cabinet and will be jointly responsible for its decisions” – Nehru wrote to to Viceroy Lord Wavell
Do You Know?
|
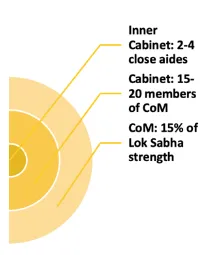
| MERITS | DEMERITS |
| Due to the small unit, a much more efficient decision-making body than a large cabinet. | Reduces the authority and status of the cabinet as the highest decision-making body. |
| Members can meet more often and deal with business much more expeditiously | Circumvents the legal process by allowing outside persons to play an influential role |
| Helps in maintaining secrecy in making decisions on important political issues. | Could induce sense of mistrust among other members of cabinet |
| Cabinet | Council of Ministers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>