Equality refers to the condition in which all individuals have the same rights, opportunities, and treatment, regardless of their background, characteristics, or circumstances. It is one of the cornerstones of many democratic societies and a core principle enshrined in various human rights declarations and legal frameworks.
Point to Ponder:
|
| Aspect | Natural Inequalities | Socially-Produced Inequalities |
| Origin |
|
|
| Nature |
|
|
| Examples |
|
|
| Differentiation |
|
|
| Root Causes |
|
|
| Challenges to Distinction |
|
|
| Impact of Technology |
|
|
| Dimension | Description | Goals and Emphasis |
| Political |
|
|
| Social |
|
|
| Economic |
|
|
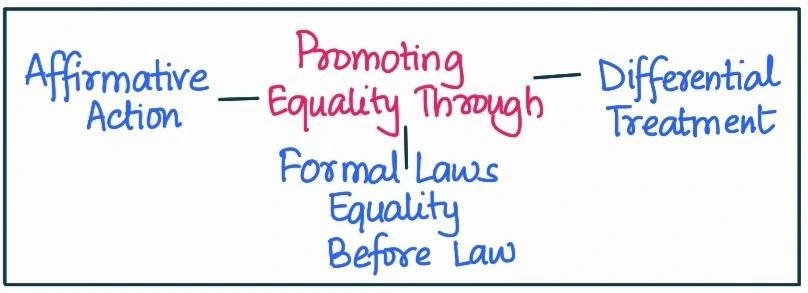
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Excerpt from Article 15 of the Indian ConstitutionProhibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. (1) The State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them. (2) No citizen shall, on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them, be subject to any disability, liability, restriction or condition with regard to- (a) access to shops, public restaurants, hotels and places of public entertainment; or (b) the use of wells, tanks, bathing ghats, roads and places of public resort maintained wholly or partly out of State funds or dedicated to the use of the general public. |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>