![]() 16 Dec 2023
16 Dec 2023
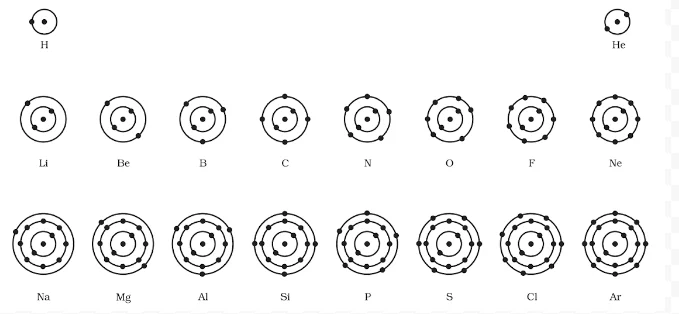
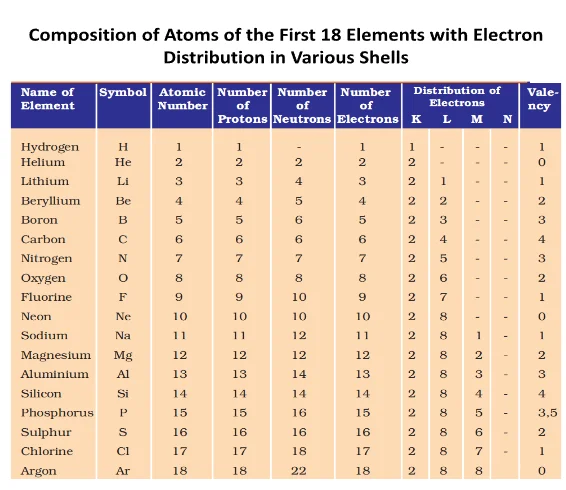
Electrons, the subatomic particles with negative charge, orbit the nucleus of an atom in distinct energy levels known as electron shells. These shells, labeled as K, L, M, and so on, are arranged in increasing order of energy. Charge carriers fill these orbits sequentially, with the innermost shell holding the lowest energy charge carriers and subsequent shells accommodating higher energy negative charge carriers.
What rules govern Electron distribution in Atomic shells, and what is the maximum capacity in each orbit?
<div class="new-fform">
</div>