This phenomenon encapsulates profound transformations in the foundational frameworks that underpin social, economic, and cultural systems that have been significantly influenced by the advent of industrialization in India. Structural social change refers to changes within the structural part of society, such as caste structure, village structure due to Industrialization in India.
Structural changes brought changes in the structural part of society, caused by multiple factors which are explained below.
Regular Shipments: Between 1834 and 1920, ships departed regularly from Indian ports carrying individuals of diverse religions, genders, classes, and castes to work on plantations in Mauritius for a minimum tenure of five years.
Recruitment Epicenter in Bihar: The principal recruitment region for several decades was Bihar, specifically districts like Patna, Gaya, Arrah, Saran, Tirhoot, Champaran, Munger (Monghyr), Bhagalpur, and Purnea.
Introduction of European Goods and Western Factories:
Shift to Agriculture due to High Produce Prices:
Disintegration of Traditional Village Organization:
Bombay became the primary port for raw cotton exports, while Calcutta and Madras became notable for exporting jute and other commodities like coffee, sugar, indigo dyes, and cotton, respectively.
Tea Industry as a Colonial Enterprise:
Colonial Administrators’ Stance
Life Dichotomy Between Planters and Labourers
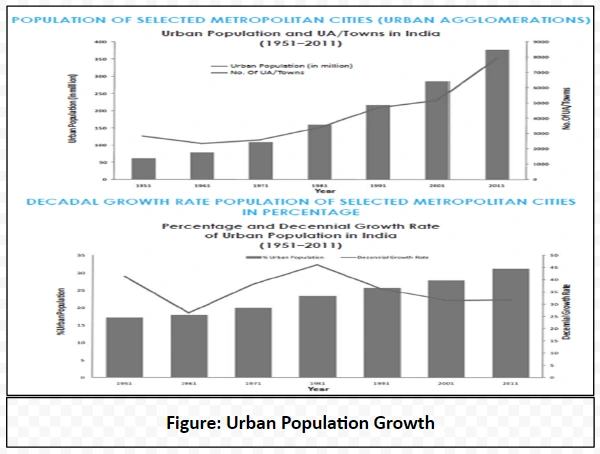
Definition of Urbanisation: It is the process of people moving from rural areas to urban areas, such as towns and cities.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>