Matter, the fundamental substance composing the universe, is the cornerstone of our understanding of the physical world. Everything in the universe that is composed of both mass and volume, meaning they occupy space and have weight is called matter. The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
Particle Nature of Matter: Particle Nature with Dettol Drops
School of thought
Two schools of thought emerged regarding the nature of matter, one school believed matter to be continuous like a block of wood (continuous) and the other believed that matter to be made up of particles like sand (particulate).
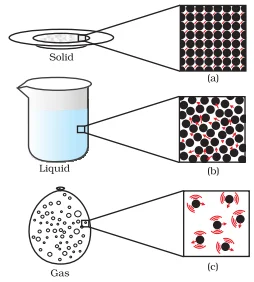
The Solid State: Matter’s Stability in States
The Liquid State: Liquids in the Realm of States
The Gaseous State: States of Matter in Expansive Gas
Temperature: States of matter Through Temperature Changes
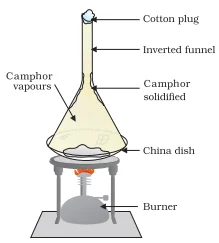
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid starts to change into gas at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point.
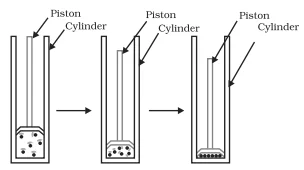
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that pressure and temperature determine the state of a substance, whether it will be solid, liquid or gas.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>