The Attorney General of India is a constitutional body under Article 76 of the Indian Constitution.
Power and Rights of the Attorney General of India
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Attorney General of India is a constitutional body under Part- V (Article 76) of the Indian Constitution.
The President of India appoints the Attorney General of India.
The Attorney General has no fixed tenure and can be removed from office by the President of India anytime.
Yes, the Attorney General has the right to participate in the proceedings of both houses of the Indian Parliament.
The Attorney General has the right to audience in all courts within Indian Territory. He enjoys all the privileges and immunities that are enjoyed by the members of the Parliament.
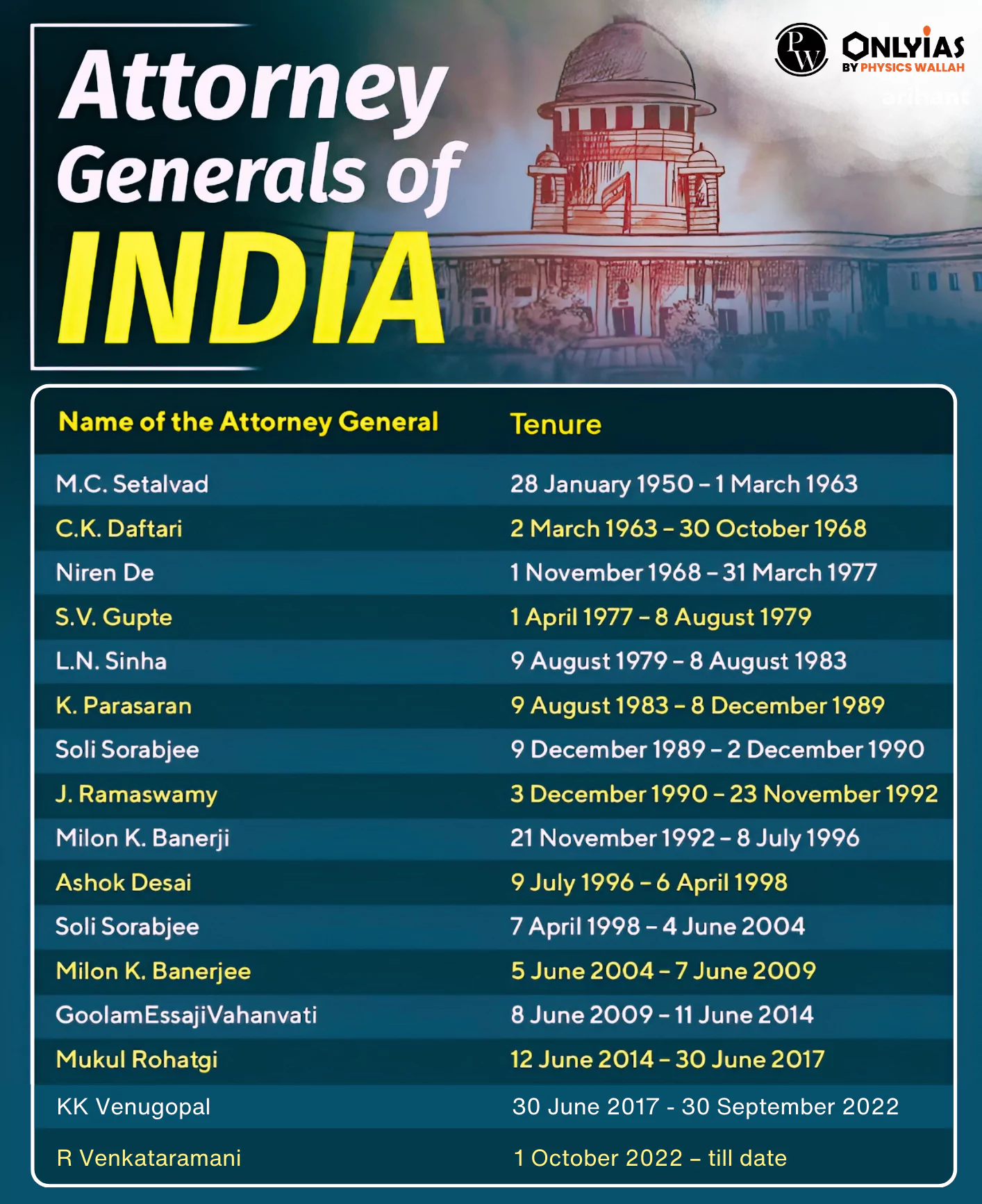
The current Attorney General of India is R. Venkataramani.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>