Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Explain the continental drift theory.
Body
- List the evidence in support of the theory.
Conclusion
|
Introduction:
The theory of continental drift was proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, but it was not widely accepted until the 1950s. Continental drift suggests that the Earth’s continents were once joined together as a single landmass called Pangaea, which began to break apart around 200 million years ago, and have been moving away from each other since then.
Body:
Theory based on evidence:
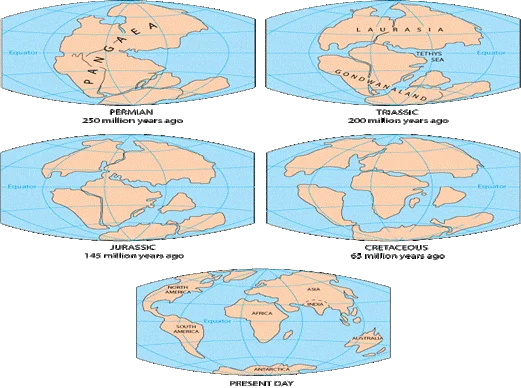
- Fit of the continents: The coastlines of many continents fit together like puzzle pieces, suggesting that they were once part of a larger landmass. Example:- South American and African plate.
- Fossil evidence: Fossils of the same species have been found on opposite sides of oceans, indicating that the continents were once connected. Example :- Gold reserves in South America and Western Africa.
- Rock formations: Similar rock formations and mountain ranges have been found on different continents, suggesting that they were once part of the same landmass.
- Paleoclimate evidence: The distribution of ancient glacial deposits and coal deposits suggest that these areas were once in different climatic zones, which would only make sense if the continents were in different locations at that time.
- Plate tectonics: The theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of the Earth’s crust, provides a mechanism for how the continents could have moved over time.
Conclusion:
The prominent evidence in support of the theory include the matching coastlines, similar geological formations on opposite sides of oceans, and the distribution of fossils across different continents.
