Initiated in 2020, the Genome India Project (GIP) seeks to gather 10,000 genetic samples nationwide, aiming to construct a reference genome. This endeavor, coordinated by the Centre for Brain Research at the Indian Institute of Science, underscores India’s advancements in precision medicine, enhancing our comprehension of diseases and facilitating personalised healthcare.
Genome India Project
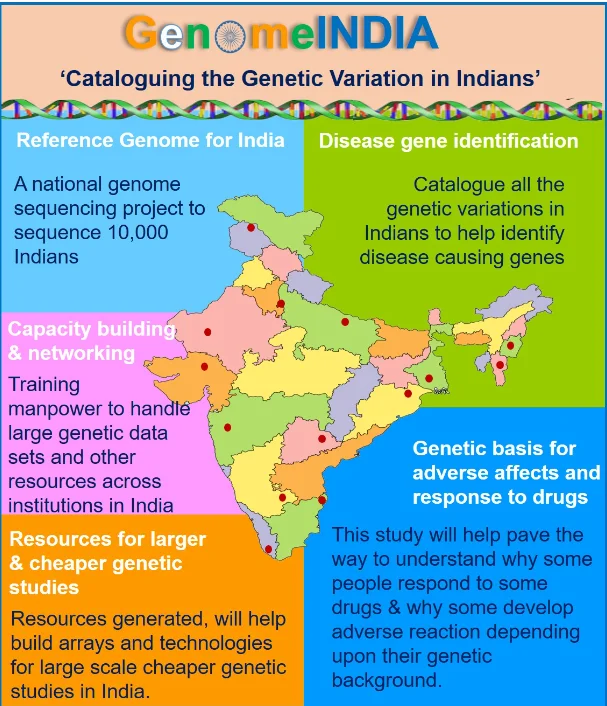
About: Taking inspiration from the Human Genome Project, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) initiated the ambitious Genome India Project (GIP) on 3rd January 2020.
- Aim: To collect 10,000 genetic samples from citizens across India, to build a reference genome.
- Whole-genome sequencing and subsequent data analysis of the genetic data of these 10,000 individuals would be carried out.
- Significance: This would aid our understanding of the nature of diseases affecting the Indian population and then ultimately support the development of predictive diagnostic markers.
- It would also open new vistas for advancing next-generation personalised medicine in the country, paving the way for predicting health and disease outcomes.
- The initiative would also support the development of targeted preventive care, as it has the potential to help identify those population groups which are more susceptible to various risk factors for certain diseases.
- For instance, if a region shows a tendency towards a specific disease, customised interventions can be made in the region, accordingly, leading to more effective treatment overall.
- This initiative would help lay the foundation of personalised healthcare for a very large group of persons on the planet.
- Administration: This project is led by the Centre for Brain Research at Bengaluru-based Indian Institute of Science, which acts as the central coordinator between a collaboration of 20 leading institutions, each collecting samples and conducting its own research.
- This initiative reflects India’s progress in gene therapies and precision medicine and its movement towards emerging next-generation medicine which yields the possibilities for greater customisation, safety, and earlier detection.
Human Microbiome Initiative of Select Endogamous Population of India
About: Health and disease outcomes are determined by interactions between the genome and the environment.
- An important component of the environment in the context of human health is the human microbiota.
- Aim: The Human Microbiome Initiative of select endogamous populations of India aims at comprehensive characterisation of human-associated microbes in carefully selected endogamous population groups with diverse dietary habits including key tribal populations which are not much influenced by modern lifestyle.
- The study is investigating the influence of diet, lifestyle, geography and age on gut microbiome using targeted metagenomic and whole metagenomic approaches.
- The study would also attempt to find the association between microbial enterotypes and three distinct Ayurvedic Prakriti types.
- Procedure: Health and disease outcomes are determined by interactions between the genome and the environment.
- An important component of the environment in the context of human health is the human microbiota.
Conclusion:
The Genome India Project and Human Microbiome Initiative made significant progress in comprehending genetic and environmental factors shaping health in India. Through these endeavors, promising avenues for personalised medicine and microbiome-based interventions emerge, heralding a new era of tailored healthcare solutions.
