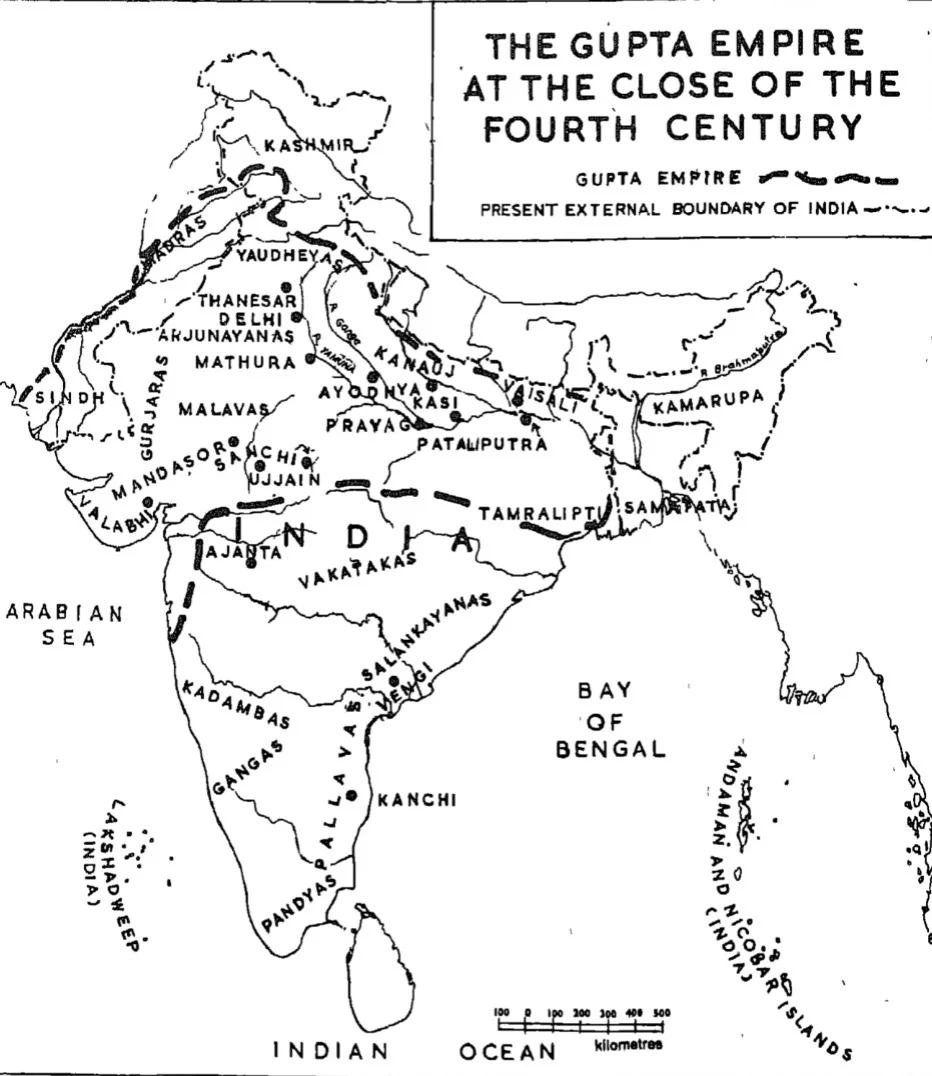
The Gupta Empire emerged in ancient India around the 3rd century AD, following the decline of previous dynasties like the Satavahanas and Kushans. Despite not being as vast as the Mauryan Empire, the Guptas ruled with a strong central government, uniting North India for over a hundred years. Their administration, marked by political titles and a feudal system, played a crucial role in shaping the empire’s governance and stability.
Administration of the Gupta Empire: Structure, Officials and Judicial System
A. Emergence of the Gupta Empire
-
- Origin: The Gupta Empire rose in the middle of the 3rd century AD after the decline of Satavahanas, Kushans and Murundas.
- Murundas were kinsmen of Kushans who ruled central India from 230 AD to 250 AD after the decline of Kushans in North India.
- Guptas were possibly the feudatories of Kushans in Uttar Pradesh, with centre of power in Prayaga.
- It is mostly believed that Guptas were of Vaisya origin.
- Strong Central Governance: Though the Gupta Empire was not as large as the Mauryan Empire, it kept North India united for more than a century.
-
-
- It featured a strong central government, bringing many kingdoms under its hegemony.
- Extent of Gupta Rule: The rule of the Guptas extended over Anuganga (middle Gangetic Basin), Prayag, Saketa (modern Ayodha) and Magadh.
- It also covered major parts of the West and Northwest and reached the East coast of Deccan as far as the Pallava Kingdom.
- Reasons for the Rise of the Gupta Empire
-
- Availability of fertile land in Madhyadesha region covering Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- They had access to iron ores from south Bihar and Central India.
- They had proximity to areas in North India which were carrying Silk trade with the Byzantine Empire.
B. Administration of the Gupta Empire
-
- Titles and Royal Authority: During the Gupta age, political hierarchies can be identified by the titles adopted. Kings assumed the titles Paramabhattaraka, Maharajadhiraja, Parameswara, Samrat and Chakravartin.
- Divine Claims of Gupta Kings: Some historians have suggested that the Gupta Kings claimed divine status. For example, Samudragupta was compared to Purusha (Supreme Being) in the Allahabad inscription.
-
- Strong Central Government: It featured a strong central government, bringing many kingdoms under its hegemony.
- Feudalism: as an institution began to take root during this period.
- Administrative Efficiency: The Gupta rulers did not require as many officials as the Mauryas because of the lower participation of the State in economic activities and the presence of guilds to administer.
- Recruitment: to various posts was not only confined to the upper varnas.
- Most posts became hereditary, weakening royal control.
- Kumaramatyas: The most important officers of the empire were Kumaramatyas, who were possibly paid in cash.
-
-
- King was looked upon as God Vishnu, the protector and preserver.
- They were connected with Gods through epithets like Parama-Daivata (the foremost worshipper of the gods) and params-bhagavata (the foremost worshiper of Vasudeva Krishna) and Parameshvara.
- Kingship was hereditary, but there was the absence of a firm practice of primogeniture.
-
-
- The king was assisted in his administration by a council consisting of a chief minister, a Senapati or commander-in-chief of the army and other important officials.
- The king maintained close contact with the provincial administration through a class of officials called Kumaramatyas and Ayuktas.
- Kumaramatyas: The term ‘Kumaramatya’ occurs in six Vaishali seals, and he was associated with an office (Adikarana) of his own.
-
-
-
- He seems to be important among Amatyas and equivalent in status to princes of royal blood.
- Kumaramatyas were attached to the king, crown prince, revenue department or province
- Individuals holding the rank of Kumaramatya had additional designations as well.
- Example: Harisena (son of Dhruvabhuti, a mahadandanayaka) was a Kumaramatya, Sandhivigrahaka and Mahadandanayaka.
Officers in the Gupta Empire
| DESIGNATION |
ROLE |
DESIGNATION |
ROLE |
| Mantriparishad |
Council of ministers |
Akshapataladhikrita |
Keeper of royal records. |
| Amatyas or Sachivas |
Executive officers in charge of various departments |
Saulkika |
Collector of customs and tolls |
| Sandhivigrahaka |
Minister for foreign affairs, war and peace |
Uparikas |
Provincial Governor |
| Mahabaladhikrita and Mahadandanayaka |
Superior posts in army |
Mahapratiara |
Chief of the palace guards |
| Mahashvapati |
Commander of Cavalry |
Khadyatapakita |
Superintendent of the Royal kitchen. |
| Dandapashika |
The chief officer of the police department. |
Dutakas |
Spies |
| Pilupati |
head of the elephants department. |
Asvapati |
Head of the horse department. |
| Narapati: Head of footsoldiers |
-
- “Lokpala”, also possibly referred to as a provincial governor.
-
-
- Standing Army and Feudatory Support: The king maintained a standing army, which was supplemented occasionally by the forces of feudatories.
- Adoption of Kushan Military Techniques: The Guptas learned the use of saddle, reins, buttoned coats, trousers and boots from the Kushans. All these gave them mobility and made them excellent horsemen.
-
- Emphasis on Cavalry and Horse Archery: In the Army, chariots and elephants took backstage. The cavalry and horse archery came to the forefront.
- Military Designations: Seals and inscriptions mention military designations such as Baladhikrita and Mahabaladhikrita (commander of infantry and cavalry).
- Senapati: The standard term “Senapati” does not occur in Gupta inscriptions, but the term could be found in some Vakataka epigraphs.
- A Vaishali seal mentions the Ranabhandagar-Adhikarana, which was the office of the military storehouse.
C. Division of the Empire (Bhuktis →Vishyas→Vithi→Villages)
-
-
- The Gupta Empire was divided into provinces known as Deshas or Bhuktis (provinces), which were administered by Uparikas (governors).
- Uparika: The king directly appointed Uparika, who further appointed the head of the district administration and the district board.
- Uparika carried on the administration with control over the military machinery as well.
- Damodarpur Plates: mention Uparika with the title of maharaja, which indicates his high status and rank in the administrative hierarchy.
- Eran pillar Inscription of Budhagupta: dated Gupta year 165 AD, refers to Maharaja Surashmichandra as a Lokpal, governing the land between the Kalinndi and Narmada rivers.
-
- Division of Provinces: The bhuktis or provinces were divided into districts known as Vishayas, which were headed by officers known as Vishyapatis.
- Vishyapatis: seem to have been generally appointed by the provincial governor.
- Sometimes, even the kings directly appointed the Vishyapatis.
- Prominent members of the town assisted the Vishyapati with administrative duties.
- Urban Administration: organised professional bodies called Guilds (also known as Shrenis) played an important role.
- Guilds looked after their own affairs.
- They punished the members for violations of the law of the guild.
- Local Administrative Units: The administrative units below the district level included clusters of settlements known variously as vithi, bhumi, pathaka and peta.
- Ayuktakas and Vithi-Mahattaras: refer to officials in these areas.
- Gramika and Gramadhyaksha: At the village level, villagers chose these functionaries.
- Mahattara: The Damodarpur copper plate of the reign of Budhagupta mentions an Ashtabula-Adhikarana (a board of eight members) headed by the Mahattara or village headman (sometimes also referred as the head of a family community).
- Sanchi Inscription: of the time of Chandragupta II mentions the Panchmandali, which may have been a corporate body.
- Feudatory System of Gupta
- Feudatory Chiefs and Vassals: The major part of the empire was held by feudatory chiefs or vassals (also known as Samanta).
- The charters issued for vassals living on the fringe of the empire had the Royal ‘Garuda’ seal.
- Feudatory Obligations: They had obligations like personal attendance to the king, paying him a tribute, and presenting daughters for marriage.
D. Judicial System
- Legal Development: It was far more developed than earlier times, and for the first time, civil and criminal law were clearly demarcated.
- Theft and Adultery: came under criminal law, and property disputes came under civil law.
- Inheritance Laws: Elaborate Laws were laid down about inheritance.
- Variety of Courts: There were different courts like Karana, Adhikarana, Aharmasana etc.
- Role of the King in Justice: The King was the upholder of the law and tried the case with the help of Brahamana priests.
- Guild Governance: The guilds of artisans, merchants, etc., were governed by their own laws.
- Varna-Based Legal System:Laws were based on differences in varnas, and culprits belonging to a higher Varna got less punishment.
- Emphasis on Mild Punishments: Punishments were not severe, and imposing a fine was a common punishment.
Conclusion
The Gupta Empire left a lasting legacy in ancient Indian history through its efficient administration and governance. With a centralized government structure, hierarchical titles, and a well-defined feudal system, the Guptas maintained order and stability across their realms. Their judicial system, advancements in governance, and innovative administrative practices set a benchmark for future dynasties, leaving behind a significant imprint on the political landscape of ancient India.
