The Kalachuri dynasty, reigning from the 10th to 12th centuries, governed over two kingdoms: Chedi in Central India and Haihaya in Southern India. They were renowned figures from ancient epics and Puranas, with Tripuri as their capital near Jabalpur. The dynasty’s name, derived from “Kali” meaning long mustache and “Churi” meaning sharp knife, symbolized their authority and prowess.
An Overview Kalachuri Dynasty
- Etymology of “Kalachuri”: The name “Kalachuri” is derived from “Kali,” meaning long moustache, and “Churi,” meaning sharp knife.
- Gangeyadeva, a significant ruler, aimed to establish the Chedis as the dominant power in North India.
- Alternative Names: They are also known as Katasuris, Haihayas, and Chedis.
- Centralized Rule in Central India: Their rule primarily focused on Central India, with Tripuri as its capital from the 8th to the 11th century, before declining in the 12th century. T
- Territorial Expansion: The kingdom’s territories extended to areas like Gorakhpur, Ratnapur, and Rajpur in eastern Gujarat.
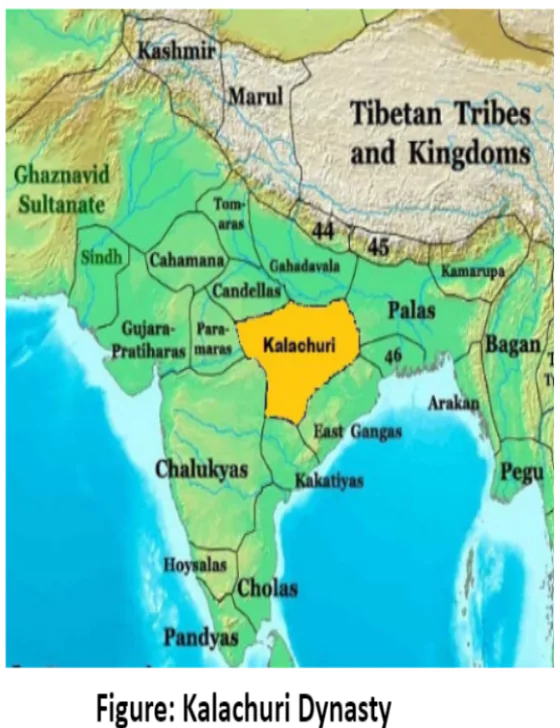 Northern Maharashtra Rule: Early Kalachuri family governed northern Maharashtra, Gujarat, Malwa, and parts of the western Deccan, likely centered at Mahishmati in the Narmada River valley.
Northern Maharashtra Rule: Early Kalachuri family governed northern Maharashtra, Gujarat, Malwa, and parts of the western Deccan, likely centered at Mahishmati in the Narmada River valley.
- Kalachuri power waned with the rise of the Badami Chalukyas but persisted in Malwa until later years.
- Deccan Rise: Another Kalachuri dynasty emerged in the Deccan, tracing lineage to Krishna.
- Bijjala, established Kalachuri authority in Karnataka by wresting power from the Kalyani Chalukyas.
- The Kalachuris’ period in Karnataka coincided with the rise of the Lingayat Hindu sect.
- Central India Rule: The well-known Kalachuri family in central India had Tripuri as its base, beginning around the 8th century.
- Kokalla-I (845-855 AD): Founder of Kalachuris dynasty.
- Military Victories: He was known for defeating Turkish troops (Turushkas) of Sindh and through marriage allied with the Chandella.
- Early Power Center: Their earliest seat of power was Mahismati on the Narmada.
- Famous Poet: Rajasekhara lived in the Kalachuri court.
- Gangeyadeva (c. 1015–41): and his son Karna (c. 1041–1073) led successful military campaigns, expanding territory but facing subsequent decline.
- Dynastic Resurgence: Despite several capable rulers, the dynasty declined in the late 10th century but resurged under Gangeyadeva around 1015 AD in Jabalpur.
- Territorial Expansion: His son, Karna (the greatest ruler of this dynasty), undertook significant territorial expansions including Banaras and Prayagraj extending up to West Bengal and allied with the Chalukyas against the Malwa.
- Sarayupara and Ratanpur Rule: Sarayupara Kalachuris ruled along the Sarayu River, extending from modern Bahraich to Gonda in Uttar Pradesh from the late 8th to the late 11th century.
- Ratanpur Kalachuris: initially feudatories of the Tripuri Kalachuris, rose to prominence under Jajalladeva I in the early 12th century, splitting into Ratanpur and Raipur branches by the 15th century.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
2. Important Rulers
- Kokalla I: He founded the Kalachuri dynasty and expanded his territory by winning the Konkan area.
- Kokalla allied with Rashtrakuta King Krishna II against Chalukyas and Pratiharas. He had 18 sons, leading to dynastic divisions.
- Samkaragana: The eldest son of Kokalla, Samkaragana, succeeded his father.
- He won a fierce battle against Somavansi rulers of South Kosala and expanded his territory near Ratnapur.
- During his reign, matrimonial alliances were forged with the Rashtrakutas.
- Balaharsha and Yuvraja: Following Samkaragana, his sons Balaharsha and Yuvraja ascended the throne around the mid-10th century AD.
- Yuvraja defeated Rashtrakuta forces, celebrated in the drama “Viddhasalabhanjika” by poet Rajasekara.
- He is credited with battles against Kashmir and the Himalayan region.
- Yuvaraja I: the Kalachuris participated in Rashtrakuta politics.
- They engaged in conflicts with various kingdoms like south Kosala, Kalinga, Gauda, and Vanga.
- Lakshmanaraja: son of Yuvraja, was a notable conqueror in the second half of the 10th century AD.
- He invaded territories in Vangala, south Bengal, and defeated the king of South Kosala.
- He also conquered Lata in the west and defeated the king of Gurjara.
- Samkaragana II and Yuvraja II: Sons of Lakshmanaraja, they faced internal revolts and challenges during the late 10th century AD.
- Their uncle Taila II raided their dominions and emerged as a powerful ruler, enhancing the dynasty’s prestige through military successes.
- Gangeyadeva: the kingdom successfully avoided raids by Sultan Mahmud, maintaining its power.
- He assumed titles like ‘Trikalingadhipati’ and ‘Vikramaditya’.
- Gangeyadeva issued coins of various metals and sizes, showcasing his authority.
- Karna: Son of Gangeyadeva, Karna expanded the kingdom’s territory to include Allahabad, conquered by his father.
- He carried out victorious campaigns along the eastern coast, defeating dynasties like Pallavas, Kungas, Muralas, and Pandyas.
- Karna abdicated in favor of his son Yasahkarna in 1072 AD.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
The Kalachuri dynasty, with its significant rulers like Gangeyadeva and Karna, left a lasting impact on Indian history. Despite facing challenges and declines, they managed to resurge and expand their territories, leaving behind a legacy of military conquests and cultural patronage. Their contributions to Central and Southern India remain integral to understanding the region’s historical narrative.
![]() May 14, 2024
May 14, 2024
![]() 7012
7012
![]() 0
0
 Northern Maharashtra Rule: Early Kalachuri family governed northern Maharashtra, Gujarat, Malwa, and parts of the western Deccan, likely centered at Mahishmati in the Narmada River valley.
Northern Maharashtra Rule: Early Kalachuri family governed northern Maharashtra, Gujarat, Malwa, and parts of the western Deccan, likely centered at Mahishmati in the Narmada River valley.