Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, are long-lasting conditions affecting millions globally. They arise from a combination of genetics and lifestyle factors like unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and smoking. NCDs are a major health concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, where they cause a significant portion of deaths.
An Overview of Non-Communicable Diseases
About NCD
These diseases generally are long-lasting and progress slowly, and thus they are sometimes also referred to as chronic diseases.
- They can arise from environmental exposures or from genetically determined abnormalities, which may be evident at birth or which may become apparent later in life.
- Of all NCD deaths, 77% are in low- and middle-income countries.
Cause of NCD
Combination of genetics and lifestyle factors.
- Unhealthy lifestyles: can lead to lifestyle diseases such as: Diabetes, Hypertension (high blood pressure), Heart disease, and Cancer
- WHO estimates that, combined, these four groups of conditions account for 82 % of all deaths from non-communicable diseases.
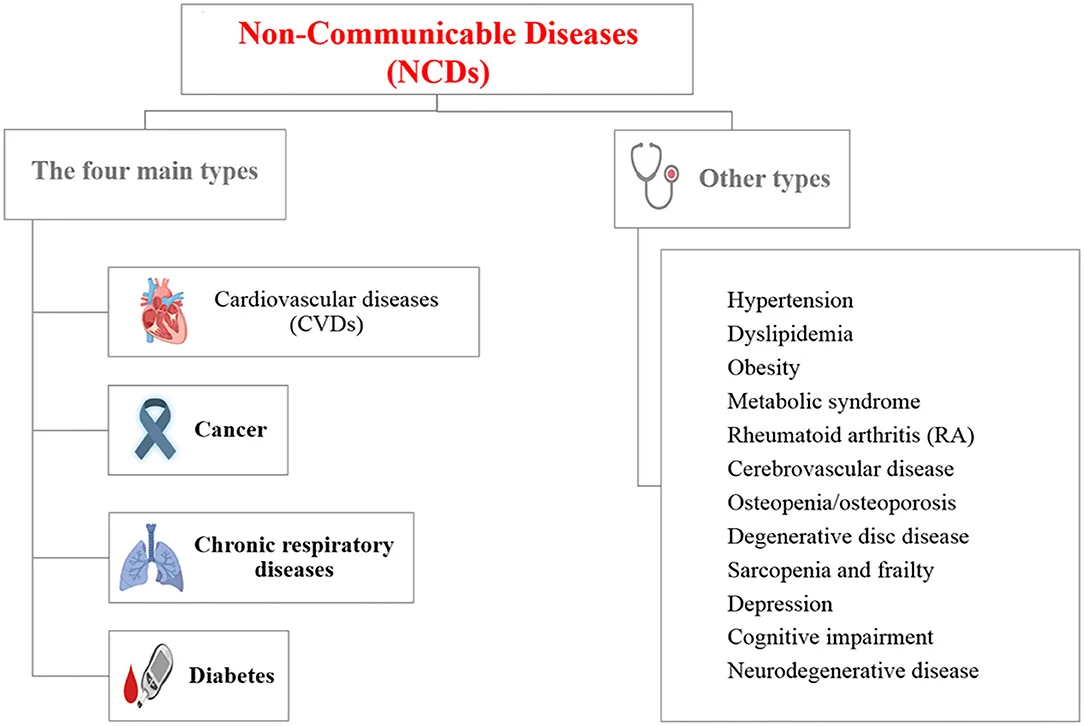
- Other NCDs include: Mental health conditions (e.g., depression), Trauma
- Risk factors for NCDs: Lack of physical activity, Poor diet, Inadequate sleep, Stress, Smoking, Excessive alcohol consumption, Tobacco chewing
Classification of NCD
World Health Organization (WHO) has identified four major types of noncommunicable diseases:
- Cardiovascular disease (e.g., heart attack, stroke) account for most NCD deaths (17.9 million annually).
- Cancers (9.3 million).
- Chronic respiratory diseases (4.1 million).
- Diabetes (2.0 million- including kidney disease deaths caused by diabetes).
Cancer
About: Cancer is a serious disease where cells grow uncontrollably and form tumors. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
-
-
- Carcinogens: These are agents like radiation, chemicals in tobacco smoke, and some viruses that can damage DNA and trigger abnormal cell growth.
- Genes: Some genes can increase cancer risk when activated.
- Detecting and Diagnosing Cancer: Early detection is key, The sooner cancer is found, the easier it is to treat.
- Tests: Doctors use biopsies (tissue samples), blood tests, and imaging techniques like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect cancer.
- Treating Cancer:There are several approaches to treating cancer:
-
- Surgery: Removing tumors surgically.
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells. (These drugs can have side effects.)
- Metastasis: (cancer spread) is a major concern with malignant tumors.
- Identifying genes linked to cancer risk can help with prevention strategies (e.g., avoiding specific carcinogens)
Conclusion
The four main types of NCDs are cardiovascular disease (heart disease, stroke), cancer, chronic respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma, COPD), and diabetes. These conditions share common risk factors and can significantly impact quality of life. Fortunately, many NCDs are preventable through healthy lifestyle choices and early detection.
