![]() May 2, 2024
May 2, 2024
![]() 5588
5588
![]() 0
0
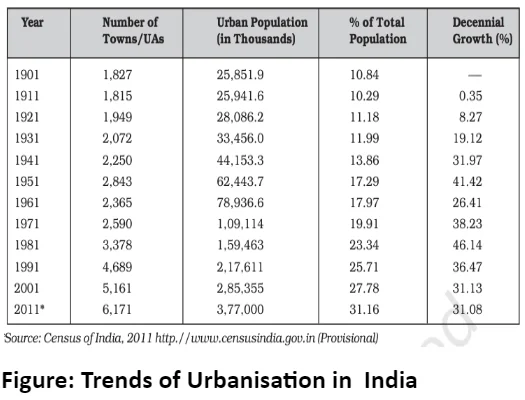
Urban settlements, unlike rural areas, are typically larger and more densely populated. They serve as centers for a diverse range of economic, administrative, and non-agricultural activities. Cities play a crucial role in connecting with surrounding rural regions, facilitating the exchange of goods and services directly or through intermediary market towns. This interconnectedness fosters both direct and indirect links between villages and cities and among different urban centres themselves.
| Functional Classification | Characteristics | Examples |
| Administrative Towns | Serve As Administrative Headquarters. | Chandigarh, New Delhi, Bhopal |
| Industrial Towns | Driven By Industrial Activities. | Mumbai, Salem, Coimbatore |
| Transport Cities | Primarily Engaged In Export And Import Activities | Kandla, Kochchi, Agra |
| Commercial Towns | Specialize In Trade And Commerce. | Kolkata, Saharanpur, Satna |
| Mining Towns | Developed In Mineral-Rich Areas. | Raniganj, Jharia, Digboi |
| Garrison Cantonment Towns | Emerged As Garrison Towns. | Ambala, Jalandhar, Mhow |
| Educational Towns | Started As Educational Centers. | Roorki, Varanasi, Aligarh |
| Religious and Cultural Towns | Came To Prominence Due To Their Religious/Cultural Significance. | Varanasi, Mathura, Amritsar |
| Tourist Towns | Emerged As Tourist Destinations. | Nainital, Mussoorie, Shimla |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Urbanisation in India reflects a dynamic process of growth and transformation, characterized by the emergence of diverse urban settlements catering to various functions and needs. As the country continues to urbanise, understanding the nuances of different urban typologies becomes essential for effective planning and sustainable development.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments