![]() June 24, 2024
June 24, 2024
![]() 10416
10416
![]() 0
0
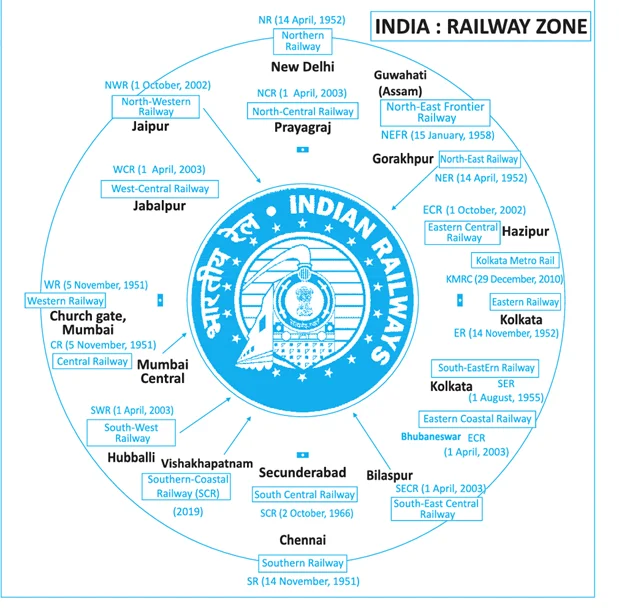
India boasts the fourth-largest railway system globally, behind only the US, Russia, and China. With a vast network spanning over 126,366 km of tracks and over 7,335 stations, Indian Railways is a crucial mode of transportation for millions.
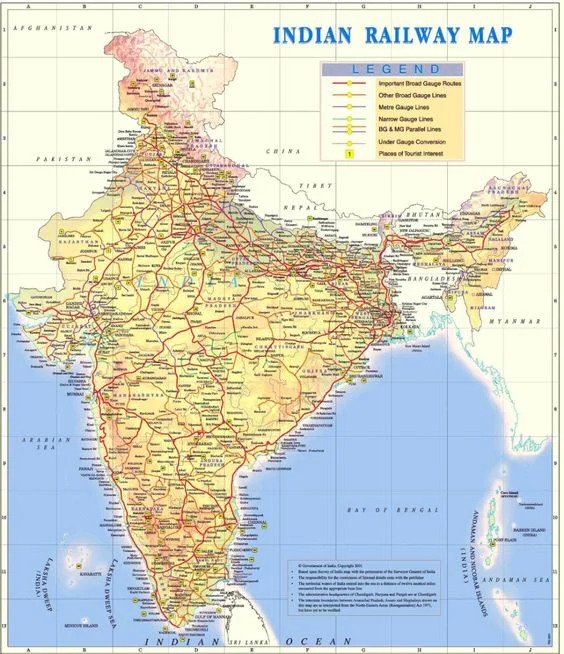
| The Diamond Quadrilateral is an Indian Railways project to establish a high-speed rail network that will connect the four mega cities of India, viz. Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai |
| Trans-Continental Railway Lines | |
| Trans–Siberian Railway (Russia) | St. Petersburg (west) to Vladivostok (east) |
| Trans–Canadian Railways | Halifax (east) to Vancouver (west) |
| Australian Trans–Continental Railway | Perth (west coast) to Sydney (east coast) |
| Orient Express | Paris to Istanbul |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Railways in India continue to evolve, with projects like high-speed rail networks and dedicated freight corridors transforming the nation’s transportation infrastructure. As India marches towards its vision of modernization and connectivity, its railways remain a symbol of progress and development, shaping the future of transportation in the country.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments