Context
The recent identification, by several cybersecurity conglomerates, of complex hacker groups using generative AI solutions has raised concerns with AI models being leveraged for translating and identifying coding errors to maximize the impact of cyberattacks.
SlashNext’s 2023 State of Phishing Report
As per SlashNext’s 2023 State of Phishing Report, there has been a 1,265% increase in phishing incidents/emails, along with a 967% increase in credential phishing since the fourth quarter of 2022 arising from the exacerbated utilization/manipulation of generative AI.
- SlashNext is the leader in SaaS-based Integrated Cloud Messaging Security across email, web, and mobile.
- As per a study conducted by Deep Instinct, around 75% of professionals witnessed an upsurge in cyberattacks in the past year alone, while 85% of the surveyed respondents have attributed the increased risk to generative AI.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
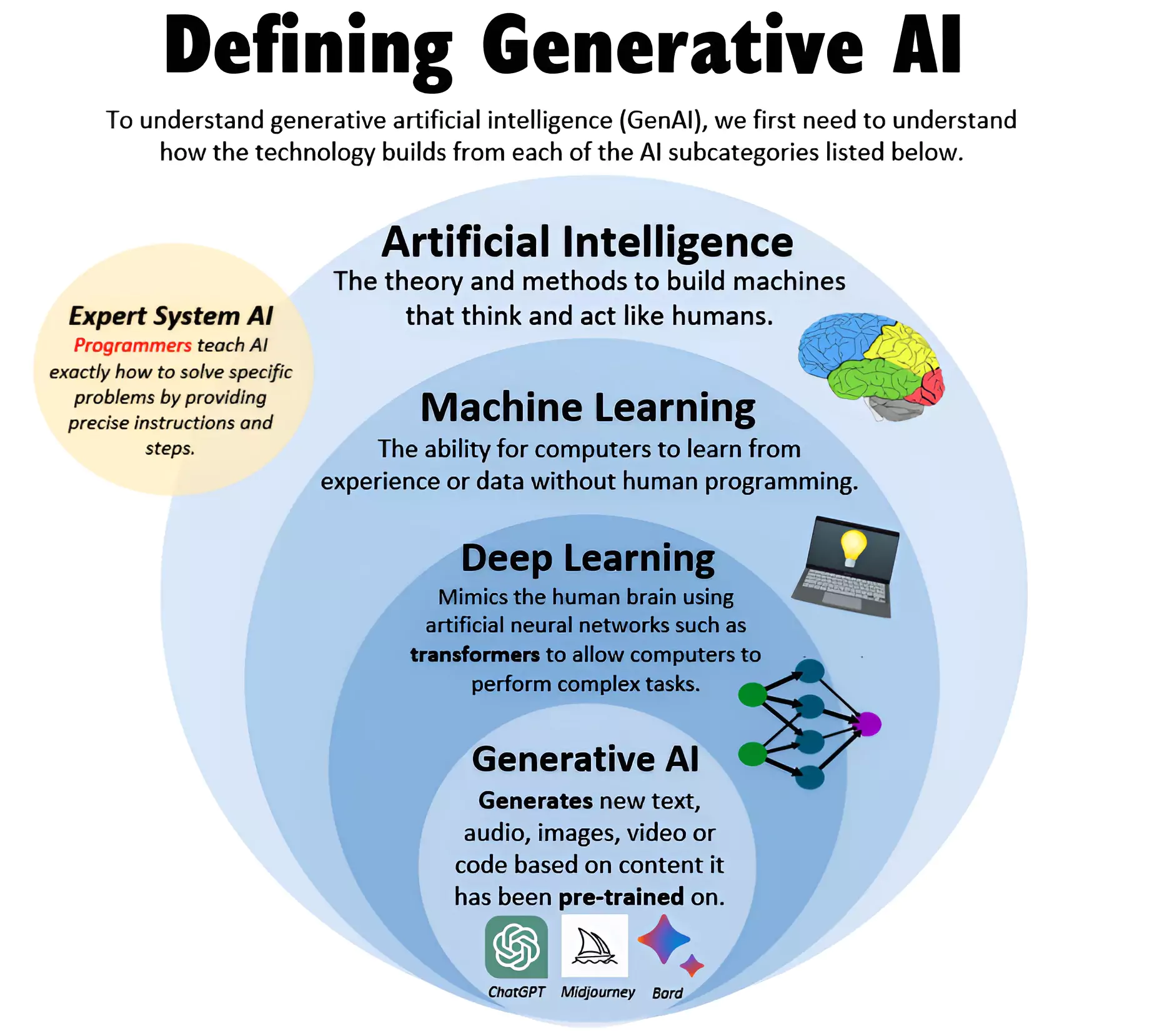
About Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Generative Artificial Intelligence is a type of AI technology that can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data.
- Deals With: It utilizes deep learning, neural networks, and machine learning techniques to enable computers to produce content that closely resembles human-created output autonomously.
- Examples: ChatGPT, DALL-E and Bard.
- In recent years, a high investment is observed in GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), LLMs (Large Language Models), GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformers), and Image Generation to experiment.
About Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
-
- Types of Artificial Intelligence:
- Weak Artificial Intelligence: It embodies a system designed to carry out one particular job.
- Example: Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri.
- Strong Artificial Intelligence: These systems carry on the tasks considered to be human-like. They are programmed to handle situations in which they may be required to problem solve without having a person intervene.
- Example: These kinds of systems can be found in applications like self-driving cars or in hospital operating rooms.
- AI Innovations:
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
- LLMs (Large Language Models)
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformers)
- Image Generation to experiment
- Create commercial offerings like DALL-E for Image Generation
- ChatGPT for Text Generation
|
- Outcomes: Generative AI, while, has exceptionally transformed various sectors such as education, banking, health care, and manufacturing, it has also transformed the paradigm of cyber-risks and safety.
- With the generative AI industry projected to increase global GDP by as much as $7 to $10 trillion, the development of generative AI solutions (such as ChatGPT in November 2022) has spurred a vicious cycle of advantages and disadvantages.
Significance of Generative AI
It enables the creation of new and unique content, whether it’s images, music, or text. Example: Automated Journalism:
- Generative AI such as ChatGPT can produce written content for news outlets, summarizing events, financial reports, and sports matches quickly and accurately, freeing human journalists to focus on in-depth stories and analysis.
- Claude, a chatbot made by Anthropic, can be made to repeat lyrics from well-known songs.
- Stable Diffusion, made by Stability AI, reproduces features of others’ images, including the watermark of Getty, on whose archive it was trained.
- Automation and Efficiency: It automates the process of content creation, saving time and resources.
- Example: Graphic Design: AI can create logos, marketing materials, and other graphics, enabling designers to rapidly prototype ideas and iterate on concepts.
- Architecture and Engineering: AI can generate building designs and urban plans, considering optimal use of space, environmental impact, and aesthetic appeal.
- Personalization and Customization: Generative models can be trained on specific data or preferences, allowing for personalized recommendations, tailored content, and customized user experiences.
- Example: Generative AI can create customized educational content, adapting to the learning pace and style of individual students, making education more accessible and effective.
- Exploration and Inspiration: Generative AI can provide inspiration to artists, designers, and writers by generating diverse variations, exploring creative possibilities, and serving as a starting point for further creative exploration.
- Example: OpenAI, which makes perhaps the most advanced generative AI models, is valued at nearly $90bn; Microsoft, its partner, has become the world’s most valuable company, with a market capitalization of $3.2trn.
Arising Concerns with Generative AI
- Threat to Privacy & Security: Through cognitive behavioral manipulation, critically dangerous incidents have surfaced, with voice-activation toys and gadgets that encourage dangerous behaviors in children and/or posing a grave threat to one’s privacy and security.
- Remote and real-time biometric identification systems (such as facial recognition) have further jeopardized the right to privacy and massively endangered individuals on several occasions in recent times.
 Vulnerability of Organisations: Most organizations cite undetectable phishing attacks (37%), an increase in the volume of attacks (33%), and growing privacy concerns (39%) as the biggest challenges.
Vulnerability of Organisations: Most organizations cite undetectable phishing attacks (37%), an increase in the volume of attacks (33%), and growing privacy concerns (39%) as the biggest challenges.- Increase in Criminal Cases: With rise in use of Generative AI, criminal cases are also rising.
- Last year, an incident of a frantic mother who had received an ominous call from “kidnappers” who had ‘kidnapped’ her daughter, raised an alarm in the U.S. Senate about the detrimental impact of artificial intelligence.
- Loopholes in Regulations: While stringent ethical and legislative frameworks are underway to combat growing cyber crimes due to AI, loopholes and a lack of industrial understanding/comprehension in regulating generative AI persist.
- Ethical Concerns: Generative AI raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding the misuse of synthetic media, deep fakes, and potential infringement of intellectual property rights.
- With the advent of advanced machine learning capabilities like large language models, neural translation, information understanding, and reinforcement learning, it is now possible to generate synthetic media that can be very difficult to distinguish from real media, posing serious ethical implications.
- Example: In November 2023, a deep fake video of actress Rashmika Mandanna was circulated widely on social media platforms.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Gendered Impact: Effects of automation are “highly gendered”, with more than double the share of women potentially affected by automation, due to their overrepresentation in clerical work, especially in high- and middle-income countries.
- Digital Divide: Generative AI technology is dependent on access and cost of broadband connectivity, as well as electricity.
- In 2022, one-third of the global population (around 2.7 billion people), still did not have access to the internet.
- Dataset Bias and Generalization: Generative models heavily rely on the training data they are exposed to. If the training data is biased or limited, the generated outputs would also be biased.
- Quality and Coherence: While generative models have made significant progress, they may still struggle with producing outputs that consistently exhibit high quality, coherence, and contextual relevance.
- Generative models may also produce low-quality and less accurate information specifically in the context of complex engineering and medical diagnosis.
Initiatives Taken to Combat Challenges of Artificial Intelligence

- The Bletchley Declaration:
- It has been signed at the AI Safety Summit, 2023 and is the first global pact to counter AI risks, and reflects a high-level political consensus and commitment among the major AI players in the world.
- The countries that signed the agreement include China, the European Union, France, Germany, India, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI): In 2020, India joined with 15 other countries to form the GPAI to establish frameworks for the responsible utilization of emerging technologies.
- Global AI Ethics and Governance Observatory: It is an initiative of UNESCO that aims to provide a global resource for policymakers, regulators, academics, the private sector and civil society to find solutions to the most pressing challenges posed by Artificial Intelligence.
- It showcases information about the readiness of countries to adopt AI ethically and responsibly.
- It also hosts the AI Ethics and Governance Lab, which gathers contributions, impactful research, toolkits and good practices.
- Ethical Principles: UNESCO produced the first-ever global standard on AI ethics – the ‘Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence’ in November 2021. This framework was adopted by all 193 Member States.
- The protection of human rights and dignity is the cornerstone of the Recommendation, based on the advancement of fundamental principles such as transparency and fairness, always remembering the importance of human oversight of AI systems.
|
- Initiatives by Private Players: Amazon, Microsoft, Meta, Google and OpenAI have signed a voluntary agreement to emphasize safety, security and trust when developing AI technologies.
-
- In India, Nasscom has come out with a framework listing out the obligations of all stakeholders in the development of AI.
India’s Initiatives for Developing AI:
- NITI Aayog Contribution: NITI Aayog has come with the ‘National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence’ Discussion Paper that focuses on establishing the International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) in the country through private sector collaboration.
- AIRAWAT: NITI Aayog is to set up India’s first AI-specific cloud computing infrastructure called AIRAWAT.
- Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform: It is a Cloud computing platform, aiming to make India a pioneer amongst emerging economies with regards to AI.
- The National AI Portal of India: It was launched in 2020. It is a one-stop digital platform for artificial intelligence-related developments.
- The Responsible AI for Youth programme, launched along with the portal, aims to empower young students with the skills and knowledge to create meaningful social impact solutions using AI.
- The FutureSkills PRIME Programme: It was launched by MeitY in partnership with NASSCOM, is a business-to-consumer framework for re-skilling/up-skilling IT professionals in emerging technologies including AI.
|
Way Forward
- Safe Digital Space: There is a need to build a more robust defense against the evolving threats in this AI-driven digital landscape by adapting ever-evolving technology.
- The Cyber Dome Project of Kerala Police aims at combating cyber threats and enhancing cybersecurity. This Public-Private Partnership leverages advanced technology, intelligence, and community engagement to prevent cybercrimes, aid investigations, and raise public awareness about online safety.
- Foster Digital Awareness: There is a need to accommodate digital awareness to efficiently navigate the digital landscape, identify credibility and verify the sources for authentication.
- AI For All: It is India’s AI strategy, which focuses on leveraging AI for inclusive development, representing India’s ‘AI for Social Good’ vision.
- It was formulated by NITI Aayog in 2018 and covers five core areas– agriculture, education, health, smart cities/infrastructure and transport.
- Robust Global Initiatives: With such multifaceted cyberattacks on the rise, robust initiatives have become necessary. It becomes imperative now to develop solutions through collaborative avenues to safeguard confidential information, identities, and even human rights.
- Policy-led Efforts: At the institutional level, stern policy-led efforts are pivotal to counter the increasing cyber challenges via solutions such as enhancing the stance for watermarking to identify AI-generated content.
- This could reduce cyber threats from AI-generated content, warning consumers to take appropriate actions.
- Collaborative Approach: To harbor a sense of security, enabling individuals and organizations to further empower communities to safeguard their personal interests and identities, there is a need to adopt collaborative approach.
- For a truly holistic approach to cybersecurity in an AI-driven world, the crucial role of non-governmental organizations and other outreach organizations is desired.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
![]() 14 May 2024
14 May 2024


 Vulnerability of Organisations: Most organizations cite undetectable phishing attacks (37%), an increase in the volume of attacks (33%), and growing privacy concerns (39%) as the biggest challenges.
Vulnerability of Organisations: Most organizations cite undetectable phishing attacks (37%), an increase in the volume of attacks (33%), and growing privacy concerns (39%) as the biggest challenges.