Context
Recently Mumbai (13 May) and Delhi (10 May), separated by 1,500 km, experienced dust storms with extremely high wind speeds.
Billboard Collapse Tragedy, Fatalities in Delhi and Mumbai Amid Powerful Storms
- Casualties: While 2 people were killed in Delhi and 23 were injured, 14 people were killed in Mumbai, when a billboard collapsed.
- Source: Both the events occurred due to powerful storm systems that were fuelled by fierce external winds.
- Annually, around 2 billion tonnes of sand and dust traverse extensive distances across the Earth’s atmosphere, creating a global phenomenon with profound implications.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
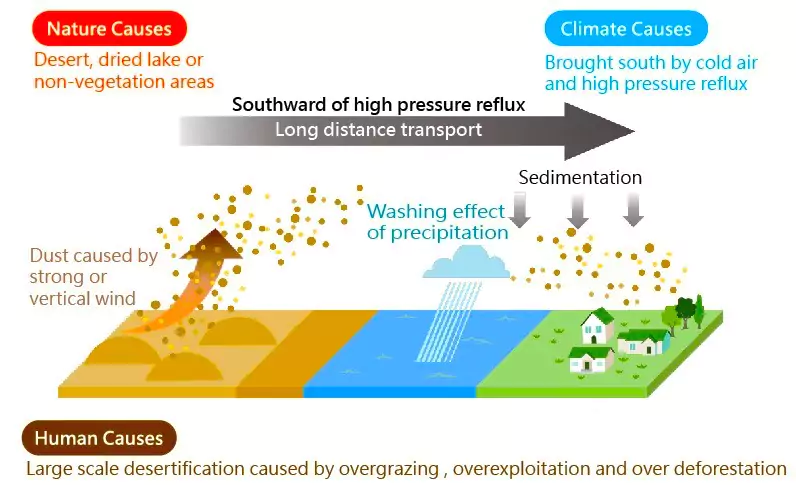
About Dust Storms
- Dust storms are meteorological events where extremely high winds lift up dust and soil from the ground, and transport them over long distances. These kinds of dust storms are quite common in arid and semi-arid regions.
- These events are similar to thunderstorms, except they occur when the base of the cloud is at a higher level from the ground and there’s little moisture in the air.
- Prerequisite factor: Heating of the land is a necessary factor for the formation of any storm. Usually, heating of 4-5 days is needed for convection to form which develops into a storm.
- Driving Factor: Once the storm forms, it is sometimes piloted by cold and dry downdraft winds that are downward facing and energetic, also aided by gravity. These winds can get very strong when they travel over hot surfaces caused by heating during summers.
- Roadblock in achieving SDG targets: Sand and dust storms present a huge and wide-spread challenge to achieving 11 of the 17 sustainable development goals.
Cause of Dust Storm Formation
- Natural Factors accentuated by Climate Change:
- Increased Western Disturbances: Western disturbances, originating from the Mediterranean region, move across Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, impacting India’s weather. These disturbances can lead to intense dust storms.
- Example: In 2022, unusual dust storms in North India were attributed to increased western disturbances.
- Heating of Northwestern India: High temperatures in northwestern India create favorable conditions for dust storms by causing the air to become dry and parched.
- Delhi’s peak wind gust during a dust storm reached 92.7 km/hr, significantly higher than the normal 40-50 km/hr.
- Rapid Warming of the Arctic Region: The Arctic region’s rapid warming influences global weather patterns, contributing to the intensity of dust storms in India.
- The 2018 dust storms in North India were linked to the rapid warming of the Arctic region.
- Geographical Factors: Proximity to the Arabian Sea and neighboring arid regions, along with local topography, play a crucial role in dust storm formation.
- Mumbai’s location near the Arabian Sea and its sweltering summer climate make it prone to strong winds laden with sand and dust.
- Tunneling Effect: Winds flowing through valleys between high built-up areas, such as the Western Ghats surrounding Mumbai, can intensify, creating a tunneling effect.
- The tunneling effect can increase wind speeds by up to 40% during dust storms.
- Cyclonic Circulation: Cyclonic circulations, swirls of winds in the lower atmosphere, can induce storm systems and cause dust storms.
- A cyclonic circulation over south-interior Karnataka and a trough between it and northwest Madhya Pradesh might have influenced dust storms in Mumbai.
- Presence of an Anticyclone: Anticyclones over the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal, with their clockwise winds, bring northerly winds that favor dust storm conditions. They bring more moisture or dust, depending on their position, contributing to weather phenomena like dust storms across India.
- Climate-Related Amplifiers: High temperatures, minimal precipitation, and arid conditions drive the likelihood and intensity of dust storms.
- Climate change leads to intensified wind patterns and prolonged droughts, exacerbating the frequency and severity of dust storms.
- Anthropogenic Factors:
- Unsustainable Agricultural Practices: Agricultural activities such as tillage, land clearing, and abandoned croplands contribute significantly to dust emissions.
- The Aral Sea’s shrinkage due to water diversion for agriculture has transformed it into the Aralkum Desert, a new source of dust storms.
- Land Use Changes: Deforestation and urbanization destabilize surfaces, enhancing dust emissions. Urban expansion and deforestation in arid regions contribute to increased dust storm activity.
Reasons for IMD’s Inability to Accurately Forecast Dust Storms:
- Localized and Brief Nature of Dust Storms
- IMD lacks sufficient number of Doppler Radars (essential for tracking meteorological condition)
- Various meteorological factors like western disturbances, cyclonic circulations, and anticyclones influence dust storm making it complex to model accurately.
|
Impacts of Dust Storms
- Socioeconomic Impacts
- Health Consequences: Dust storms can negatively impact respiratory health, cardiovascular health, cause allergies, and exacerbate conditions like asthma.
- Economic Consequences: These storms cause considerable economic damage by harming infrastructure, reducing agricultural productivity, disrupting transportation, and increasing healthcare costs.
- India, China and Pakistan lost 1,584 gigawatt-hours (gWh), 679 gWh and 555 gHw of energy loss, respectively, due to sand and dust storms in 2019, amounting to over $107 million for India per year.
- Social Disruption: Dust storms can disrupt daily life, leading to social unrest, migration, and displacement of populations.
- Environmental Impacts:
- Soil Degradation: Dust storms remove the nutrient-rich topsoil, diminishing soil quality and fertility. This erosion reduces the land’s ability to sustain vegetation, impacting agriculture and contributing to desertification.
- Ecosystem Disruption: These storms can bury vegetation, disrupt natural habitats, and affect wildlife. Invasive species can also be transported by the storms which may outcompete native species, leading to biodiversity loss and ecological imbalance.
Ways to Mitigate Impacts Dust Storms
- Soil Conservation Practices: Implement techniques such as contour plowing, windbreaks, and cover cropping to reduce soil erosion and maintain soil fertility.
- Afforestation and Reforestation: Plant trees and restore forests to stabilize soil, reduce wind speeds, and create barriers against dust storms.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Adopt no-till farming, crop rotation, and organic farming to improve soil health and reduce dust emissions from agricultural lands.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: Design urban landscapes with green belts and buffer zones to act as barriers against dust storms. Use dust-resistant materials in construction.
- Early Warning Systems: Enhance forecasting capabilities and establish early warning systems to alert communities about impending dust storms, allowing for timely preparations.
- Health Protection Measures: Promote the use of masks and air purifiers, and establish medical facilities equipped to handle respiratory issues during dust storm events.
- Infrastructure Development: Building infrastructure like windbreaks, barriers, or green belts to reduce the speed and impact of wind carrying dust and sand.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD):
- The UNCCD is the only legally binding framework set up to address desertification and the effects of drought.
- There are currently 197 Parties to the Convention, including 196 country Parties and the European Union.
- The Convention specifically focuses on drylands, including arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid regions, which are home to some of the most fragile ecosystems and vulnerable populations.
|
![]() 18 May 2024
18 May 2024
