![]() June 4, 2024
June 4, 2024
![]() 1256
1256
![]() 0
0
Genetics, the study of heredity and variation, has significantly advanced from Gregor Mendel’s foundational work on inheritance laws to modern DNA technology. Mendel’s laws of inheritance laid the groundwork for understanding the chromosomal and molecular basis of genetics. Key concepts such as the DNA double helix, the role of RNA, the Central Dogma of molecular biology, and DNA profiling have deepened our understanding of genetic information flow and its practical applications in fields like medicine, forensics, and evolutionary biology.
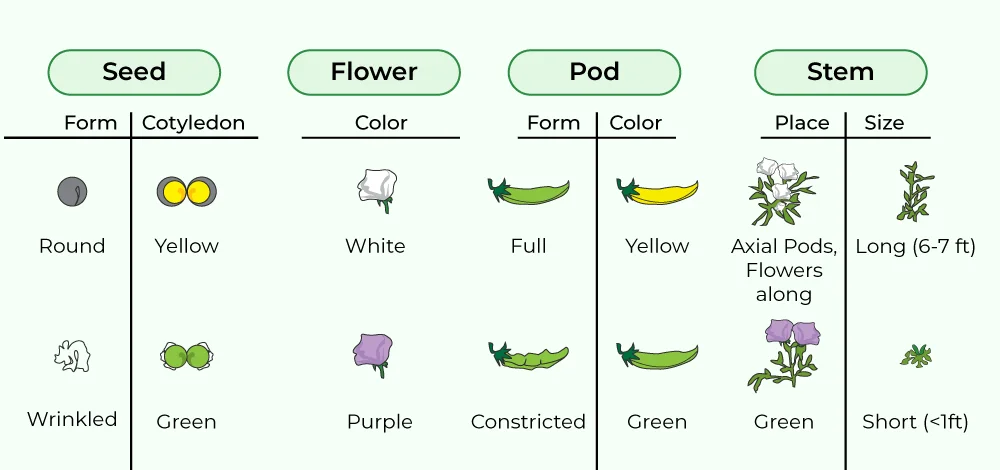
About: Mendel is known as the father of genetics. He worked on the pea plants and proposed the fundamental laws of inheritance. These are:
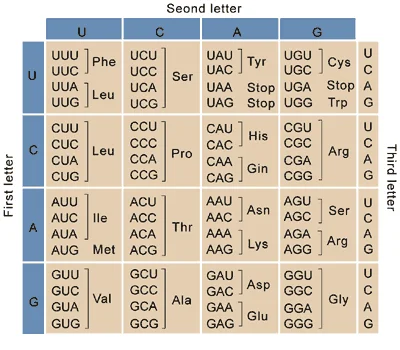
Central Dogma states that the genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to Protein.

| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
From Mendel’s foundational laws to the intricacies of the genetic code, genetics has unlocked the secrets of inheritance and protein synthesis. The Central Dogma elucidates the flow of genetic information, guiding our understanding of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, paving the way for transformative discoveries in medicine and biotechnology.
| Related Articles | |
| Genetic Inheritance: Evolution, Traits & Role of Reproduction | Recombinant DNA: Definition, Application, Tools & Process |
| Recombinant Proteins | Genetic Profiling of Captive Elephants |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments