Indirect evidence of normal regular and dark matter in the ring of an old galaxy named JWST-ER1g has been observed by the James Webb Space Telescope, as reported in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The Dark Universe
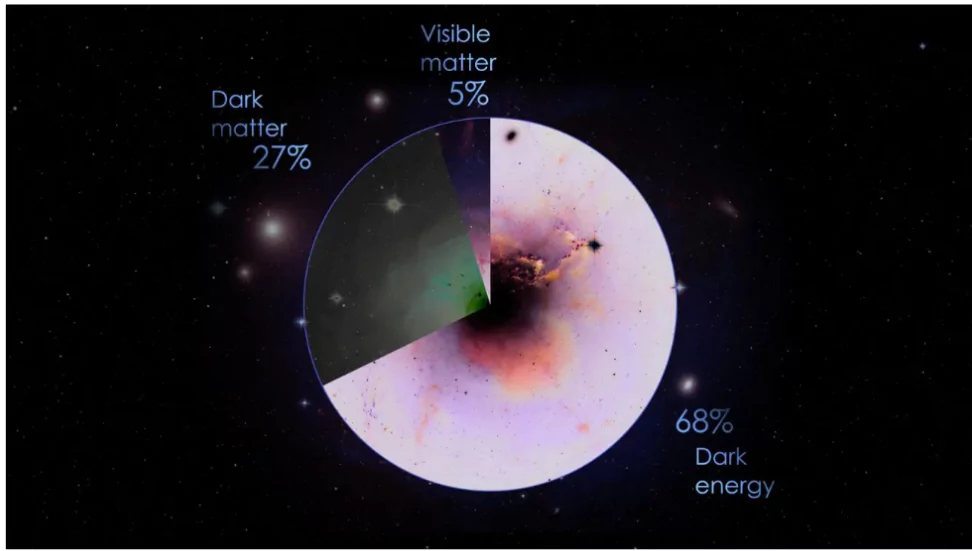
- The universe: It is made up of three components: normal or visible matter (5%), dark matter (27%), and dark energy (68%).
- Need to understand the Dark Universe: To fully understand the general theory of relativity, we need to figure out what dark matter and dark energy are.
- Dark Matter:
- Dark matter takes up space and holds mass like normal matter, but it doesn’t reflect, absorb, or radiate light (not detected yet)
- Discovered: A Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky in the 1930s coined the term while studying the Coma galaxy cluster, but it was in the 1970s that the existence of Dark Matter was confirmed by U.S. astronomer Vera Rubinby by studying how individual galaxies rotated.
- Her team found that individual galaxies may contain invisible mass made of dark matter.
- Present Knowledge: Dark matter exists in a vast, web-like structure that winds through the whole universe, like a gravitational scaffold that attracts most of the cosmos’ normal matter is the popular perception in the scientific community today.
- It is determined that dark matter isn’t composed of known particles of matter and the search for what makes up dark matter continues.
- Dark Energy:
- Dark energy may compose roughly 68% of the universe.
- Establishing the existence of Dark Energy is important to explain why the universe is expanding at an accelerated pace than it did before.
- A form of repulsive gravitational effect: Dark Energy is thought to be a mysterious form of gravity-defying energy which blew out from the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago.
- It creates a sort of negative pressure that stretches the fabric of spacetime and allows celestial objects like stars and galaxies to drift apart in contrast to the Newtonian idea of gravity, as an attractive force
- Present knowledge: In places with lots of visible matter, gravity has more of an effect than dark energy. But when space is empty of matter, dark energy dominates.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Indirect Evidences of Dark Universe
- Observation through simulations: A study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society by U.S. researchers, reported being able to explain the observed behaviour of real galaxies and the motions of their stars and gases in simulations that assumed the galaxies contain dark matter.
- Exclusion Area: Scientists have also found a certain mass range where there is no presence of Dark Matter particles. The research was published as the first results of the Broadband Search for Dark Photon Dark Matter (BREAD) experiment.
- 3D map of Universe: The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) in Arizona, in the U.S., is attempting to make the largest 3D map of the universe.
- This mountain-top telescope is fit with 5,000 small robots that help it look 11 billion years into the past with greater precision than before.
- Till now data from DESI has agreed at a basic level with the ΛCDM model of the universe (our best mathematical model to explain the Big Bang and the universe today) ‘CDM’ is short for ‘cold dark matter’.
- Changing nature: Some studies have found that dark energy might be changing with time, which is at odds with assumptions of the ΛCDM model.
- Λ (lambda) is the cosmological constant: it represents the energy density of space and is closely associated with dark energy. It appears in equations of the general theory of relativity.
General Theory of Relativity
The Theory of General relativity aims to understand how gravity affects the fabric of space-time.
- Propounded by: The theory is given by physicist Albert Einstein published in 1915. He expanded the theory of special relativity that he had published 10 years earlier.
- Special relativity argued that space and time are inextricably connected, but that theory didn’t acknowledge the existence of gravity.
- What is general relativity?
- General relativity is a physical theory about space and time according to which spacetime is a 4-dimensional object that has to obey an equation, called the Einstein equation, which explains how matter curves spacetime.
- Gravity: General relativity explains gravity, ie. how particularly massive objects warp the fabric of space-time, a distortion that manifests as gravity. The gravitational field comes out of the description of general relativity as a result of the curved spacetime.
|
![]() 17 Jun 2024
17 Jun 2024
