According to a paper published in the journal Nature Communications, an earthquake around 2,500 years ago could have caused the Ganga river to abruptly change course.
- Researchers believe that this event led to the river abandoning its former channel in what is now Bangladesh and creating a new path.
Key Findings Of Paper
- Change in Course: This study is the “first confirmed instance” of an earthquake driving avulsion in deltas, especially for an immense river such as the Ganga.
- Avulsions: Many river-course changes, this is called ‘avulsions’
- The Satellite images showed former main channel of the river, about 100 kilometres south of Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh.
- This is a low-lying area about 1.5 kilometres wide that can be found intermittently for some 100 kilometres almost parallel to the current river course.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Seismites:
- It refers to deformation of existing sediment.
- It was first proposed to interpret earthquake-deformed beds composed of Soft-sediment deformation structures (SSDS)
|
-
-
- Exploring this area in 2018, the researchers spotted features created as a result of earthquakes, called seismites.
- Similar to other rivers running through major deltas, the Ganga too is known to regularly change its course.
- The quake could have had one of two possible sources:
-
- One is a subduction zone to the south and east, where a huge plate of oceanic crust is shoving itself under Bangladesh, Myanmar and northeastern India,
- The other possibility is that the seismic shock came from giant faults at the foot of the Himalayas to the north, which are gradually rising because the Indian subcontinent is slowly colliding with the rest of Asia, they said.
- Rivers can take years or decades to change their course, but an earthquake can cause an avulsion almost instantaneously
Risks Of Another Such Event In Future
- A 2016 study suggested that an earthquake of comparable magnitude could strike the region again, affecting some 140 million people.
Earthquake
- An earthquake is shaking the earth. It is a natural event caused due to release of energy, which generates waves that travel in all directions.
- The release of energy occurs along a fault
- A fault is a sharp break in the crustal rocks.
- Rocks along a fault tend to move in opposite directions.
- As the overlying rock strata press them, the friction locks them together.
- However, their tendency to move apart at some point of time overcomes the friction.
- As a result, the blocks get deformed and eventually, they slide past one another abruptly.
- This causes a release of energy, and the energy waves travel in all directions.
Key Terms Related to Earthquakes
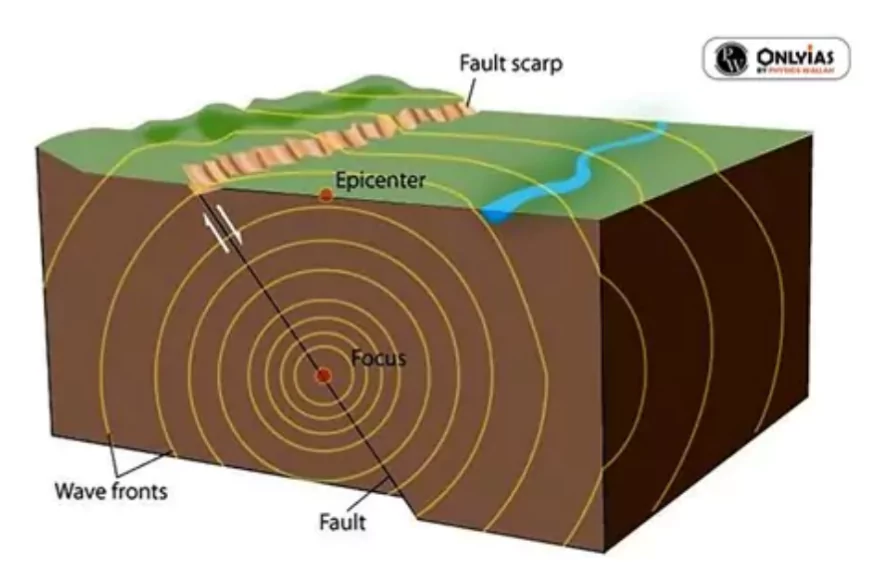
- Focus/Hypocentre: The point inside the earth where the earthquake originates.
- Epicentre: The point on the earth’s surface directly above the focus. It’s the first point to feel the waves
|
- Large earthquakes impact large areas and can have long-lasting economic, social and political effects
Immediate Consequences
- Flooding: An abrupt change could lead to immediate flooding in areas along the new course, causing widespread damage and loss of life.
- Emergency Response: The need for emergency response and disaster relief would be immediate and extensive, requiring significant resources and coordination.
Economic Impact
- Agriculture: Many regions rely on the Ganga for irrigation. A course change could disrupt water supply, leading to crop failures and loss of livelihood for farmers.
- Infrastructure Damage: Bridges, dams, and other infrastructure along the original course would become obsolete or require significant modification & Floods would lead to damage
Environmental Impact
- Ecosystem Disruption: Ganga supports a wide range of flora and fauna. An abrupt course change could destroy habitats, threaten endangered species, and disrupt the ecological balance.
- Water Quality: New course could introduce pollutant.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Social Impact
- Displacement : This sudden change in course would lead to mass displacement of people.
- Health: Changes in water availability and quality could affect public health, particularly in regions where clean water is already scarce
Geopolitical Impact
- Interstate Relations: Ganga flows through multiple states in India. A change in its course could lead to conflicts over water rights and resource allocation.
![]() 21 Jun 2024
21 Jun 2024
