Aphelion
|
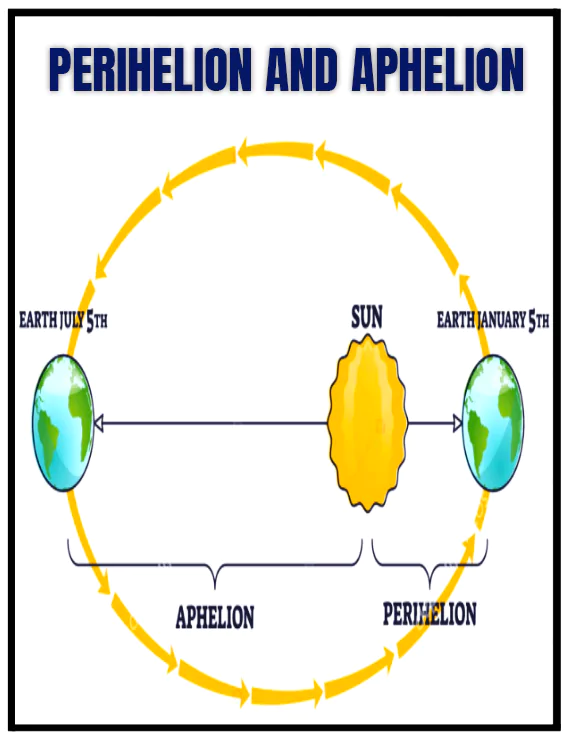
Context: On July 5, Earth reaches its farthest from the sun for the entire year, a moment astronomers call Aphelion.Aphelion
- About: Aphelion is the point in Earth’s orbit where it is farthest from the Sun. The Earth receives less radiation from the sun, as heat, than at any other time of the year.
- Occurrence: Aphelion occurs every year in July.
- The sun is at its smallest in the sky.
Aphelion and Earth’s Elliptical Orbit
- Johannes Kepler: It was 17th-century German mathematician Johannes Kepler who revealed that all planets orbit in an ellipse in his first law of planetary motion.
- Elliptical Orbit of the Earth: Earth’s orbit around the Sun is not a perfect circle; it is elliptical (oval-shaped).
- Aphelion and Perihelion: This elliptical shape means that there are points in the orbit where Earth is closer to the Sun (perihelion) and points where it is farther from the Sun (aphelion).
- At aphelion, Earth is about 152.1 million km (94.5 million miles) from the Sun.
- In early January, Earth reaches perihelion, the point where it is closest to the Sun, at about 147.1 million km (91.4 million miles).
Gravitational Influences:
- The elliptical nature of planetary orbits is due to gravitational forces.
- Planets exert gravitational influences on each other, causing their orbits to be elongated rather than circular.
- Jupiter, the most massive planet in the solar system, has the greatest influence on the orbits of other planets.
Measuring Eccentricity:
- The degree to which an orbit deviates from a perfect circle is called its eccentricity.
- Higher eccentricity indicates a more elliptical orbit.
- For example, Mars has an eccentricity of 0.094, Pluto has 0.244, and Earth has a low eccentricity of 0.017.
Aphelion and Earth’s Temperatures:
- A common misconception is that Earth’s varying distance from the Sun causes the seasons.
- Earth receives 7% less sunlight at aphelion compared to perihelion, leading to slightly milder summers and winters in the Northern Hemisphere.
- However, the effect of Earth’s distance from the Sun is offset by the planet’s axial tilt, which causes the seasons.
Hypothetical Scenarios:
- No Aphelion: If Earth’s orbit were a perfect circle, the lengths of the seasons would be exactly the same.
- Currently, spring and summer are a few days longer than fall and winter in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Increased Eccentricity: If Earth’s orbit became more eccentric, it would lead to extreme seasons, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Summers would be unbearably hot, and winters intolerably cold, potentially leading to crop failures and making advanced civilization difficult.
Conclusion: Earth’s current orbital characteristics and distance from the Sun create a stable environment conducive to life. |
Mt Etna
|
Context:
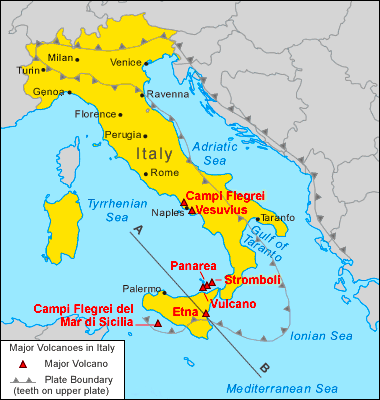
Recently, Mount Etna in Sicily (Italy) has erupted along with the smaller Stromboli volcano. This has raised alert levels on the Mediterranean island of Sicily.
Mt Etna:
- About: Mount Etna is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania.
- Location: It is located above the convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is Europe’s most active volcano and one of the largest in the world.
- Recorded Activity: Its recorded volcanic activity dates back to 1500 B.C. Since then, it has erupted more than 200 times.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: In June 2013, it was added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Volcanoes:
- About : Volcanoes are openings, or vents where lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.
- Place of Formation: They can be formed on land and in the ocean.
- Method of Formation: Volcanoes are, in part, a result of their own eruptions but also the general formation of our planet, as tectonic plates move.
- Mountain ranges like the Andes in South America and the Rockies in North America, as well as volcanoes, formed through the movement and collision of tectonic plates.
- Types of Volcanoes: Their type is determined by how the lava from an eruption flows and how that flow affects the volcano, and, as a result, how it affects its surrounding environment. There are four main types of volcanoes:
- Cinder cones: It is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent.
- Composite or stratovolcanoes: A stratovolcano is shaped like a steep cone and formed by layers of hardened lava and tephra.
- The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and solidifies before spreading far, due to high viscosity.
- Shield volcanoes: Shield volcanoes form from the eruption of low-viscosity lava, which flows far and spreads into thin layers compared to the thicker lava from stratovolcanoes.
- Over time, repeated eruptions build broad, gently sloping shields characteristic of these volcanoes.
- Lava domes: It is a circular, mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano.
- Manner of volcanoes eruption:
- Volcanoes erupt when pressure from molten rock (magma) beneath the Earth’s surface forces its way through cracks and vents, spewing out lava, ash, and gasses.
- This explosive release occurs when the pressure becomes too intense for the Earth’s crust to contain.
- Ring of Fire: Some of the most active volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which includes New Zealand, Southeast Asia, Japan and the western coast of the Americas.
- About 90% of all earthquakes worldwide strike within this region.
- Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions:
Scientists are capable of predicting some of the volcanic eruptions hours, or sometimes several days, in advance.
- Seismographic Data: Monitoring earthquakes and tremors as potential precursors to volcanic activity.
- Ground Deformation: Observing changes in the ground’s shape due to magma movement.
- Gas Emissions: Measuring volcanic gas emissions as a sign of increasing activity.
- Gravity and Magnetic Field Changes: Tracking alterations in gravity and magnetic fields near volcanoes, indicating potential eruption risks.
|
Aluminium, Steel utensils now need ISI mark
|
Context: In a move aimed at enhancing kitchen safety, quality, and efficiency, the Indian government has introduced a Quality Control Order (QCO) for all stainless steel and aluminium utensils.
Key Requirements of the Quality Control Order (QCO):
- ISI Mark Requirement: All utensils made of stainless steel or aluminium must now bear the ISI mark, signifying compliance with Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) regulations.
- Non-Compliance Penalties: Failure to adhere to QCO norms will result in punishable offences, under guidelines set by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- New Standards by Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): According to the consumer affairs ministry, the BIS has established updated standards for essential kitchen items to ensure high quality and safety.
- Standards: Manufacturers are required to meet stringent BIS standards concerning material composition, uniformity, and practical design.
- Testing Protocols: Stainless steel utensils must undergo various tests, including staining tests, mechanical shock tests, and thermal shock tests, to ensure their quality and durability.
- Purpose of the Standards: These standards are designed to uphold cultural diversity in cooking practices while enhancing product performance and consumer safety.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Utensils:
- Durability: Stainless steel utensils are widely favoured in kitchens globally due to their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal.
- Material Composition: Stainless steel is renowned for its resistance to rust, durability, and strength, derived from a blend of steel, chromium, and additional metals such as nickel, molybdenum, and manganese.
|
Global Conclave on Plastic Recycling and Sustainability (GCPRS)
|
The four-day Global Conclave on Plastic Recycling and Sustainability (GCPRS) is currently underway at the Bharat Mandapam, Pragati Maidan in Delhi.
About Global Conclave on Plastic Recycling and Sustainability (GCPRS)
- Organisers: It’s organised by industry bodies All India Plastics Manufacturers’ Association (AIPMA) and the Chemicals and Petrochemicals Manufacturers’ Association (CPMA)
- Focus: Event focuses on the rising use of plastic, its impact on the environment and also on the steps needed for solutions.
- AIM: GCPRS aims to provide a platform for dialogues and discussions to develop solutions and the Indian industry is actively working to improve plastic circularity and ensure the effective implementation of regulatory requirements through cooperation with the government.
Plastic Pollution Crisis:
- The imbalance between the volumes of plastic that are produced and used, as well as the world’s ability to manage those volumes when they become waste, is the root cause of plastic pollution.
- Global consumption of plastic is accelerating: Over half of the plastic production ever manufactured has been produced since 2000 and we are set to double our current global annual production by 2050.
- Only about an estimated 9% of the plastics ever produced have been recycled and 12% have been incinerated.
- The remainder is either still in use or has either been disposed of in landfills or released into the environment, including the oceans
|
![]() 6 Jul 2024
6 Jul 2024