Recently, The Prime Minister of India visited Vienna, Austria.
Significance of the PM Visit to Austria
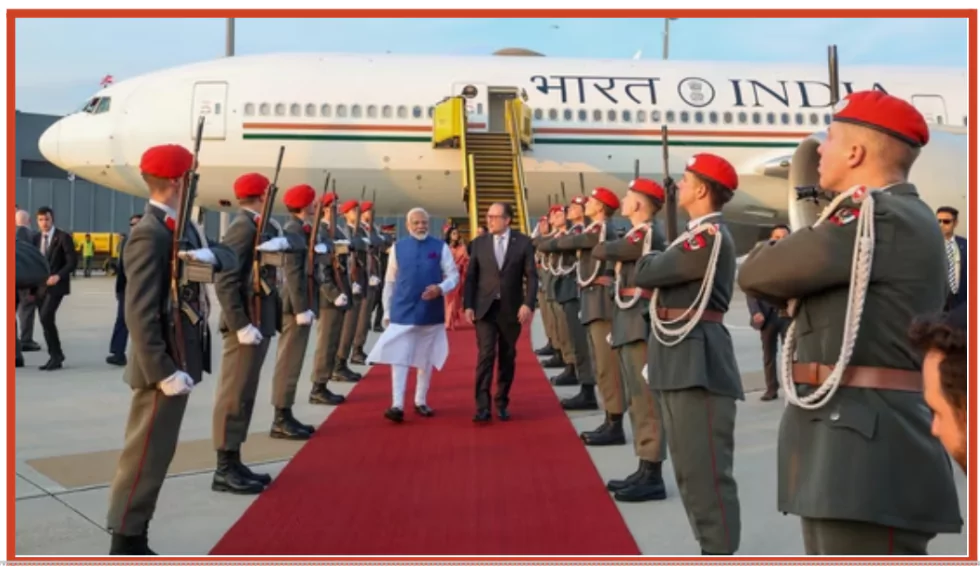

- Narendra Modi’s visit to Vienna is the first by an Indian Prime Minister since 1983, when Indira Gandhi traveled to Austria.
- This visit highlights Austria’s non-NATO status amidst tensions with Russia and Western allies.
-
Messages Conveyed
-
- During his visit, Modi emphasized India’s concern over civilian casualties in conflicts, including recent events in Ukraine.
- He reiterated that war cannot solve problems and underscored the need for peace talks.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key outcomes of visit
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: The bilateral relation between Austria and India was established in 1949.infrastructure, renewable energy, e-commerce, fintech, enterprise tech
- Narendra Modi’s recent visit to Austria and his discussion with Karl Nehammer on various matters such as war and its consequences strengthened the bond between two countries again.
- Economic and Technological Collaboration: The discussion emphasised on “future-oriented bilateral sustainable economic and technology partnership” between India and Austria.
- It could open new doors for advancement of technology in both the countries.
- Stance on Russia-Ukraine war: Two two countries have maintained a balanced position on the Russia-Ukraine war.
- Austria and India both support EU sanctions against Russia. At the same time, continue to engage in commercial ties with Russia, including gas imports.
Austria’s Neutrality and Historical Background
- During World War II, Vienna was under Nazi occupation.
- It was later divided into four sectors by the US, UK, France, and Soviet Union.
 The Allies occupied Austria for a decade after the war ended.
The Allies occupied Austria for a decade after the war ended. - About Austria
- Austria is strategically located between Western Europe and the Eastern bloc.
- Vienna is the capital of Austria.
- It gained independence in 1955 through the Austrian State Treaty.
- The treaty, ratified by four occupying powers, mandated Austria’s neutrality, akin to Switzerland’s stance.
- The country’s constitution prohibits joining military alliances or hosting foreign military bases.
India’s Role in Austria’s Independence
- Austrian Appeal for Sovereignty: In 1952-53, Austria sought Jawaharlal Nehru’s assistance to achieve independence from Allied occupation.
- Support at the UN: India was one of the few nations supporting Austria’s plea at the UN in 1952, advocating an end to Allied occupation and restoration of sovereignty.
- Nehru’s Diplomatic Influence: Nehru’s respected stature among Western nations and the Soviets made him a pivotal figure in Austria’s negotiations for independence.
- Mediation Role: Nehru played a crucial role as a diplomatic mediator during Austria’s treaty discussions, introducing a new dynamic to the negotiations.
- Historic Visit: In June 1955, shortly after Austria gained independence, Nehru made the first state visit to Austria by a foreign leader.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
India-Austria Relations: Historical Highlights
- Longstanding ties: India and Austria established diplomatic relations in 1949, and this year marks the 75th anniversary.
- High-level visits: Regular visits by heads of state and government officials from both countries have helped strengthen bilateral relations.
- For example, President K.R. Narayanan visited Austria in 1999, and Austrian President Heinz Fischer reciprocated in 2005.
-
India’s Cultural Relation with Austria:
- Indo – austrian culture dates back to the 16th century when Balthasar Springer travelled from Tyro to India in 1505 with the third Portuguese fleet.
- Indology in Austria: This tradition started between 1825-1920.
- It is a period known for its distinguished philologists and archaeologists.
- Vienna was established as a centre for indology
- The Chair for Indology became an independent Department with new premises after 1955.
- Today, it is known as the Institute for South Asian, Tibetan and Buddhist Studies at the University of Vienna.
- Sanskrit teaching: In 1845, Sanskrit teaching started at at Vienna University
- Cultural Performances: Indian artists and Austrian artists have performed in each other’s countries .
- For example: Recent, Indian artists are
- Kuchipudi dancers “ Raja and Radha Reddy”,
- Martial arts performers – Monish Nayak Kathak Dance Group, Pt. Bholanath Mishra Indian vocal music, Rajasthani folk dance group
-
India’s Relation with Austria in Space Sector
- Austria’s first two satellites were launched by India’s PSLV-C20 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- The two satellites were developed in collaboration with
- The Institute ofCommunication Networks and Satellite Communications (IKS) at the Technical University of Graz (TUG)
- Institute for Astronomy of the University of Vienna
- The Space Flight Lab (SFL) at the University of Toronto Institute Of Aerospace Studies
- (UTIAS).
-
Austria-India Association
- This association was founded by Prof. Arnold Keyserling
- It was the first registered Austria – India Association
- Objective: It aimed to popularise Indian dance and music in Austria.
- Notable Performances: Ravi Shankar, Ali Akbar Khan, and Bismillah Khan
- Current Activities
- It organises lectures and exhibitions on Indian folk art and paintings.
- Hosts Odissi and Bharatanatyam dance workshops and film festivals in Austria.
Significance of Austria for India’s Economy
- Strong potential for economic partnership: Indian Prime Minister Modi and Austrian Chancellor Nehammer discussed a “future-oriented bilateral sustainable economic and technology partnership.”
- This suggests that Austria sees India as a valuable partner for collaboration in various sectors like infrastructure, renewable energy, e-commerce, and fintech.
- Opportunities for Indian businesses: A potential economic partnership with Austria could open doors for Indian businesses in areas like e-commerce, fintech, and enterprise technology.
- These are growing sectors in India, and Austria’s expertise could be valuable for Indian companies looking to expand or improve their offerings.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Austrian State Treaty
- Independence Restoration: Signed on May 15, 1955 in Vienna.
- The Austrian State Treaty restored Austria’s independence after World War II.
- Parties Involved: Signed between the Allied powers of World War II and the Austrian government.
- Prohibitions: The treaty prohibited Austria from forming a union with Germany.
- It also banned any Nazi or fascist government in Austria.
- Neutrality Commitment: Austria pledged perpetual neutrality, committing to not participate in any wars or military alliances.
|
![]() 12 Jul 2024
12 Jul 2024

 The Allies occupied Austria for a decade after the war ended.
The Allies occupied Austria for a decade after the war ended.