![]() 22 Jul 2024
22 Jul 2024
Post-1848, the widespread surge of nationalism paved the way for the unification of Germany and Italy, marking a significant chapter in their histories as sovereign nation-states. In Europe France, Germany and Italy Became the epicentre for dissipation of Nationalist Ideas.
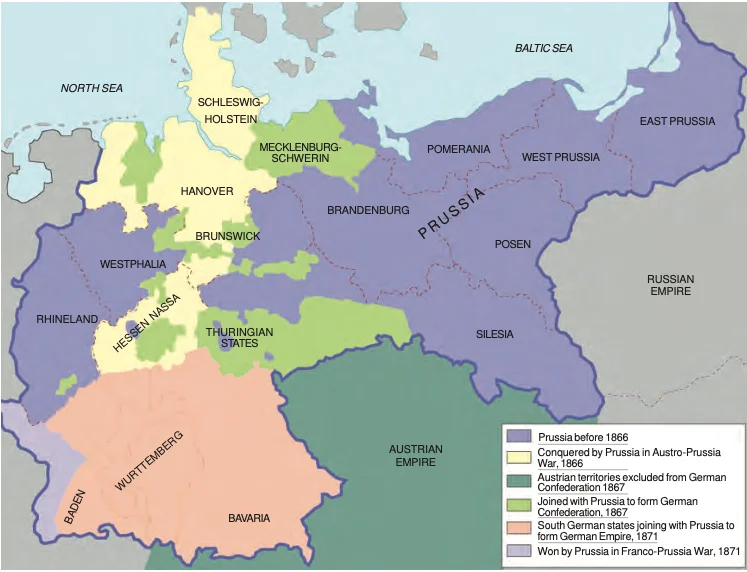
Suppression of Liberal Nationalism: This liberal initiative to nation-building was, however, repressed by the combined forces of the monarchy and the military, supported by the large landowners called Junkers of Prussia.
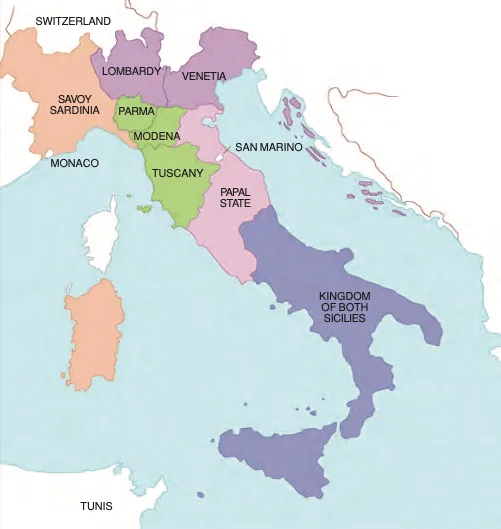
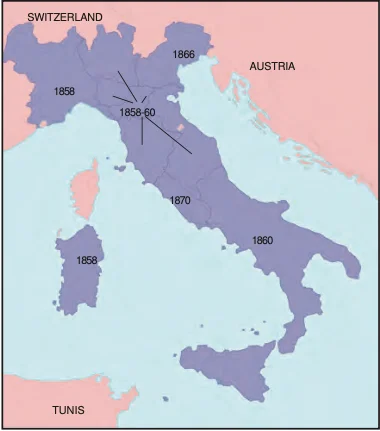
Divided Italy: In the mid-19th century, Italy was territorially fragmented into seven distinct states. (Refer to Figure)
National Allegories: In the 18th and 19th centuries, artists skillfully personified countries, portraying them as distinct individuals, while nations were represented with grace and strength through female allegorical figures.
Shrinaking Nationalism: Nationalism began to decline in influence during the last quarter of the 19th century, marking a shift in global ideologies.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Nationalism became a strong influence in 19th century Europe, bringing together countries such as Germany and Italy and also escalating conflicts in the Balkans. Although it first promoted a feeling of togetherness and autonomy, its harmful capabilities were revealed during World War I. The concept of the nation-state, while under scrutiny, continued to be a key political goal.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>