India and Japan are planning to establish a Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) for carbon trading and carbon credit adjustment.
Memorandum of Cooperation
- A Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) is being prepared for this mechanism.
- The MoC will involve emission-reduction credits being shared between the two countries.
-
Contribution to Climate Goals
-
Economic and Financial Implications
-
- The mechanism is expected to attract investments in low-carbon and clean technologies, boosting job creation.
- There will be financial implications, but the specifics are not detailed.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
Authorization and Implementation
-
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) of India is authorized to sign the MoC with Japan.
- Japan will support the transfer of technology, finance, and capacity building for new technologies under the JCM.
About Carbon Credit
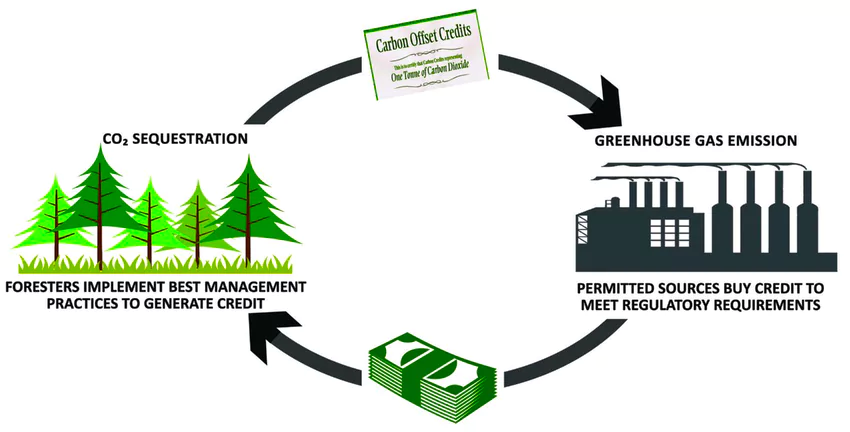
- Carbon credits are Permits that allow the owner to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases (GHGs).
- Measurement: One credit allows for the emission of one ton of carbon dioxide or its equivalent in other GHGs.
- Alternative Name: Also known as carbon offsets.
 Carbon credit pricing in India
Carbon credit pricing in India-
- India does not set a specific price for carbon credit.
- Its value is determined by different factors such as fuel costs, emission trading schemes, taxes, and the quality of projects.
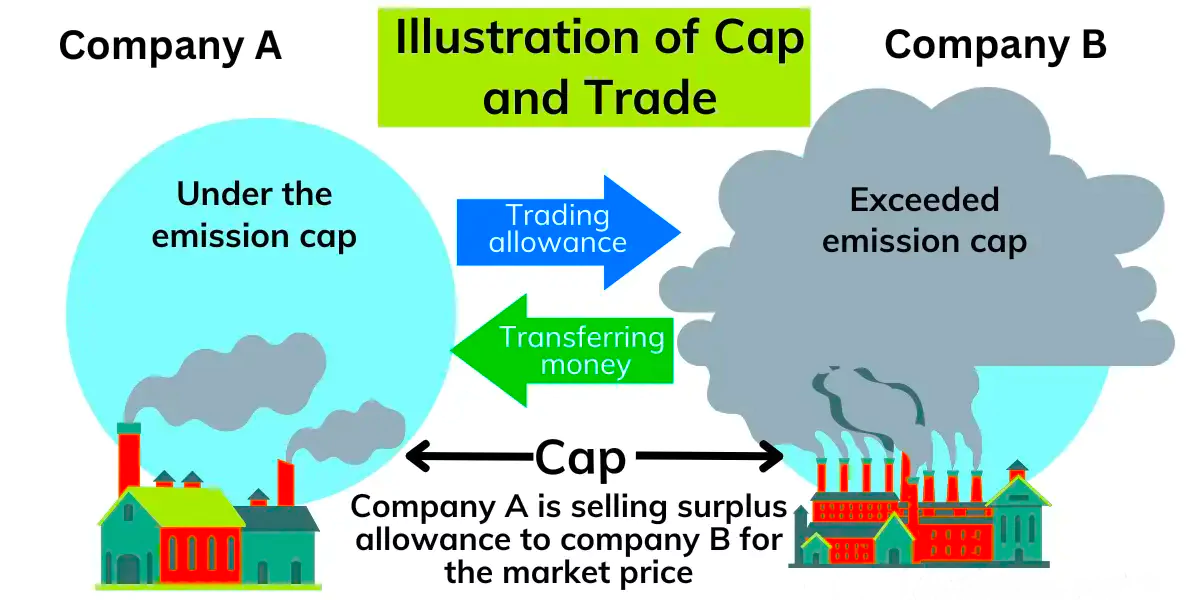
- Function of Carbon Credits
- Cap-and-Trade System: Carbon credits are part of a cap-and-trade program.
- Pollution Limit: Companies receive credits to emit GHGs up to a certain limit, which is gradually reduced.
- Credit Trading: Companies can sell unused credits to others that need them.
Difference between compliance-based and voluntary carbon credit trading?
| Feature |
Compliance-Based Trading |
Voluntary Trading |
| Emissions of carbon per unit output |
Set by a governing body (government) |
No pre-set limits |
| Participation |
Mandatory for included companies/industries |
Optional – companies choose to participate |
| Reason for Trading |
Companies must buy credits to stay under their limit and avoid penalties |
Companies buy credits to offset emissions due to sustainability goals |
Benefits of Carbon Credits
-
Environmental Benefits
- Emission Reduction: Carbon credits limit the amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) companies can emit, helping to reduce overall emissions.
- Incentive for Innovation: Encourages companies to create and use new technologies to lower their emissions.
- Climate Action Projects: Supports verified projects that lead to measurable reductions in emissions.
-
Economic Benefits
- Financial Incentives: Companies that cut their emissions can sell their unused credits to make money.
- Cost-Effective Compliance: Provides a flexible way for companies to meet emission limits by buying extra credits if needed.
- Market Creation: Creates a market for carbon trading, opening up economic opportunities for businesses.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Carbon credit Laws in India
- Amendment to the Act: The (Indian) Energy Conservation Act, 2001 was amended through Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022 (“Act”).
- Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022 (“Act”) came into effect in 2023.
- This act allows the ministry of power and central government authority to create and manage carbon trading schemes and issue Carbon Credit Certificates.
- Carbon Credit Certificates
- Under section 14AA Act, the government can issue carbon credit certificates to entities that follow carbon credit trading schemes.
- These certificates can be sold to
- The organizations that emit more levels of Carbon than authorized;
- The Government of India to fulfill its commitments;
- Other nations that need help to fulfill their commitments.
- Challenges
- Lack of clarity: There is low clarity on carbon trading schemes as to which authority will issue Carbon Trading Certificates.
- Other issues: There are other various issues such as set-up and regulation of a trading platform.
Impact of India-Japan Carbon Credit Mechanism on Indian Economy
India’s decision to enter a joint crediting mechanism (JCM) with Japan can have several positive impacts on the Indian economy. Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits:
- Boosting Green Technologies and Investments:
- The JCM will encourage investments in India for low-carbon technologies, such as renewable energy systems, energy-efficient appliances, and waste management solutions.
- This will create a market for these technologies, leading to their wider adoption and innovation in the clean energy sector.
- Job Creation and Skill Development:
- Implementing JCM projects will require skilled personnel in areas like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and waste management. This will create new employment opportunities in these sectors.
- The JCM may also involve capacity building programs, further enhancing the skills of the Indian workforce in these green fields.
- Fulfilling India’s Climate Goals:
- The JCM allows India to earn carbon credits for emission reduction projects.
- These credits can be used to meet India’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC), its commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions under the Paris Agreement.
- Access to Japanese Expertise and Finance:
- Japan is expected to facilitate the transfer of technology, finance, and expertise related to clean technologies.
- This can accelerate India’s transition to a greener economy by providing access to advanced solutions and financial resources.
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties:
-
- The JCM fosters collaboration between India and Japan on climate action.
- This cooperation can strengthen the relationship between the two countries and pave the way for further partnerships in the future.
Overall, India’s participation in the JCM with Japan holds promise for the Indian economy by promoting green technologies, creating jobs, and supporting India’s climate goals.
Challenges of Carbon Credits
-
Environmental Challenges
- Questionable Effectiveness: Some believe carbon credits may not significantly lower emissions, as companies can buy credits instead of reducing their own emissions.
- Double Counting: There’s a risk of the same emission reductions being claimed by more than one party.
-
Economic Challenges
- Market Volatility: The price of carbon credits can vary widely, causing uncertainty for companies planning long-term investments.
- High Costs: Setting up and maintaining carbon credit systems and projects can be expensive, deterring smaller companies and developing countries.
-
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
- Complex Regulations: Companies may find it hard to navigate the complex rules and standards for carbon credits.
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistent global frameworks make trading credits across different markets difficult.
- Fraud and Corruption: The carbon credit market can be vulnerable to fraud, like issuing fake credits or misrepresenting emission reductions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
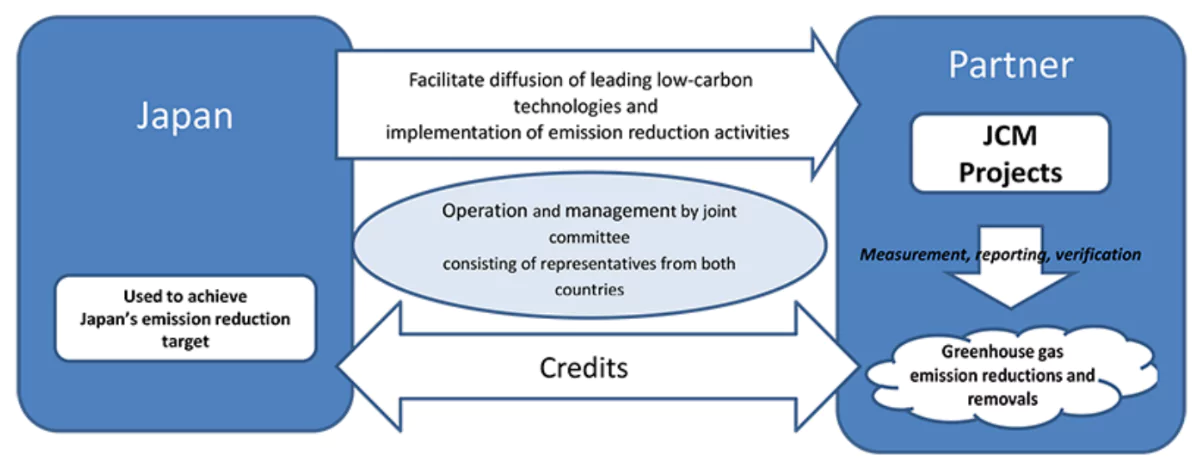
Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
-
Purpose of the JCM
- The JCM is designed to work with developing countries to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Shared Contribution: The emission reductions achieved are recognized as contributions by both the partner countries and Japan.
-
Mechanism Objectives
- Technology and Infrastructure Diffusion: The JCM aims to spread advanced decarbonizing technologies and infrastructure through investments by Japanese companies.
- GHG Reduction and Sustainable Development: These efforts help reduce or remove GHG emissions and promote sustainable development in partner countries.
- Achieving NDCs: The JCM supports the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) of both Japan and partner countries by quantifying Japan’s contributions and earning credits.
|
![]() 22 Jul 2024
22 Jul 2024

 Carbon credit pricing in India
Carbon credit pricing in India