In 2024, heightened concerns over disinformation AI-driven digital and cyber threats, including those targeting major events like the 33rd Summer Olympic Games in France and incidents like the Microsoft CrowdStrike outage, underscored the increased focus on managing sophisticated security risks.
- The concerns essentially stemmed from new threats posed by Artificial Intelligence (AI) including Generative AI and Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- About: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science dedicated to creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, learning, reasoning, and understanding natural language. For Example: ChatGPT
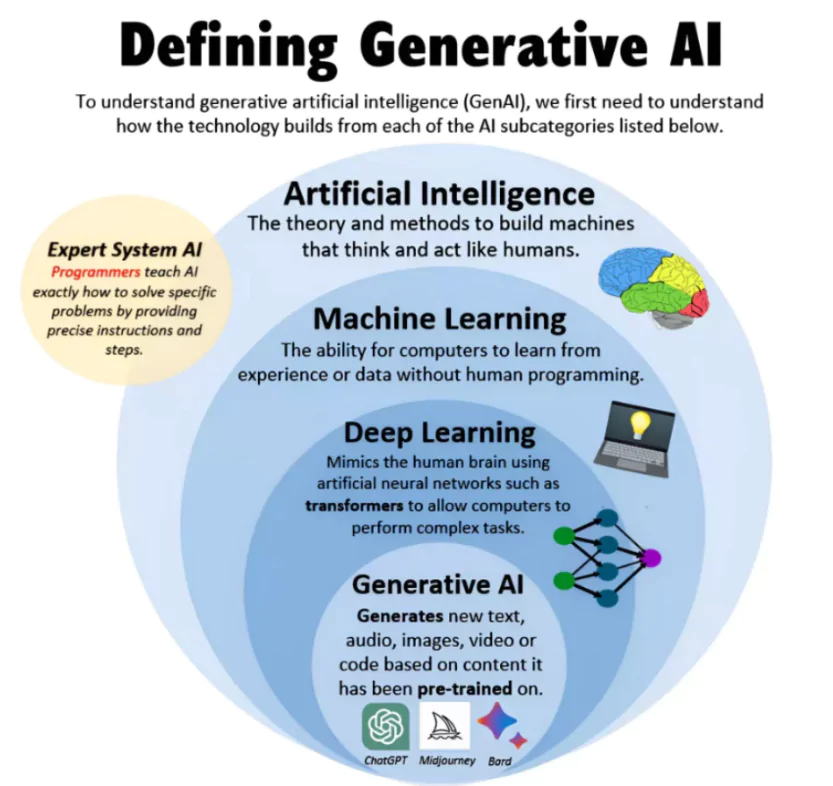 Includes: AI encompasses various subfields and techniques, including:
Includes: AI encompasses various subfields and techniques, including:
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and improve performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Techniques that enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Computer Vision: Methods for enabling machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual input from the world.
- Robotics: The design and use of robots that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously.
- Expert Systems: AI programs that mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert in specific domains.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Generative AI and Artificial General Intelligence
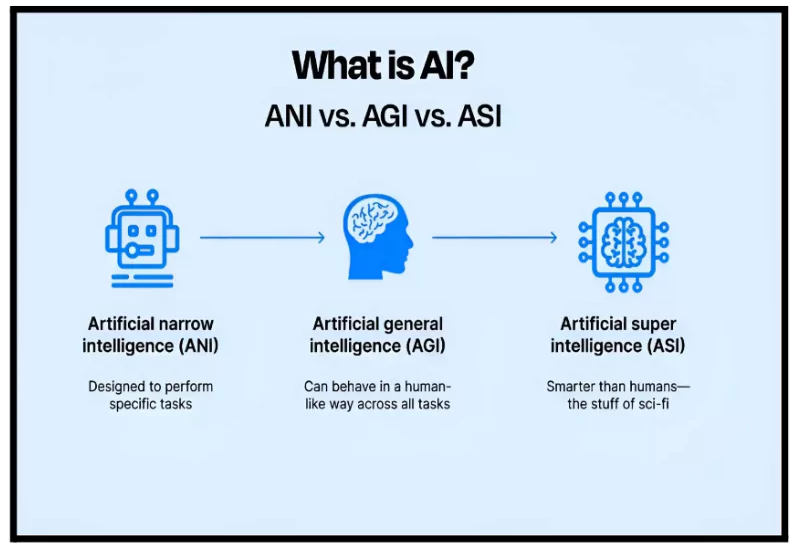
- Generative Artificial Intelligence: Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) model that can be used to generate new text, images, video, audio, code, or synthetic data in response to a user’s prompt or request.
- Generative AI relies on sophisticated machine learning models called deep learning models that simulate the learning and decision-making processes of the human brain.
- Artificial General Intelligence: Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that matches or surpasses human capabilities across a wide range of cognitive tasks.
- AGI envisions a broader, more generalised form of intelligence, not confined to any particular task (like humans).
- Examples of Artificial General Intelligence include: Self Driving Cars, Virtual Personal Assistants etc.
Cyber Security
- About: Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks and unauthorised access.
- It involves technologies, processes, and measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
- Key areas include network security, information security, application security, and incident response.
|
Challenges and Cyber Security Threats Due to Artificial Intelligence in 2024
- Emerging Threats
- Cybersecurity Concerns: Rising disinformation and cyber threats contribute to a challenging security environment.
- Generative AI-Driven Disinformation
- Generative AI: The affordability and accessibility of generative AI have lowered the barrier for disinformation campaigns. This technology enables the creation of deep fakes,digitally manipulated videos, audio, or images that can convincingly spread false narratives.
- This has been notably seen in geopolitical conflicts where AI-generated misinformation has undermined public trust and social stability.
- Ukraine Case Study: In the ongoing Ukraine conflict, both factions have used AI to disseminate false information, exacerbating tensions and hindering peace efforts.
- Enhanced Cyber Attack:
- Critical Infrastructure Vulnerabilities: AI-enhanced cyberattacks have targeted essential systems like power grids and communication networks, exposing significant weaknesses in national security.
- Microsoft CrowdStrike Outage: A software glitch in Microsoft Windows caused global disruptions, offering a glimpse into potential cyberattack impacts.
- Historical Cyberattacks: Past attacks like WannaCry, Shamoon, Petya, and Stuxnet underscore the severe consequences of cyber threats.
- Digital Vulnerability:
- Increased Cybercrime: Surge in cyber fraud, phishing, spamming, skimming etc affecting individuals and businesses.
- Insufficient Protection: Many private institutions and businesses lag in cyber defences, highlighting the need for better security measures.
- Data Privacy Risks: AI’s capability to analyse large datasets has heightened concerns about data privacy, leading to a rise in identity theft and fraud through targeted cyberattacks.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Steps Taken by the Indian Government for Ensuring Cyber Security
- NITI Aayog Contribution: NITI Aayog has come with the ‘National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence’ Discussion Paper that focuses on establishing the International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) in the country through private sector collaboration.
- Establishment of AIRAWAT: NITI Aayog is to set up India’s first AI-specific cloud computing infrastructure called AIRAWAT.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Objective: Provides a comprehensive framework for law enforcement agencies to tackle cyber crimes.
- Components: Includes the National Cyber Crime Threat Analytics Unit and the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal to enhance state coordination.
- YUVAai: It is a platform to enhance the skills of school students from classes 8 to 12 on using AI to tackle critical problems and become future-ready.
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- Role: Central agency for managing cybersecurity incidents and disseminating alerts.
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Purpose: Aims to raise awareness about cyber crimes and improve safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and IT staff in government departments.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: Key Functions:
- Detection: Identifies malicious software affecting systems.
- Removal: Provides tools and support to eliminate botnets and malware.
- Prevention: Assists in maintaining system hygiene and security.
- AI for All: AI for All is a self learning platform designed to teach AI to people from all walks of life. India’s effort towards AI journey focuses on social empowerment and inclusion at the core.
International Efforts for Ensuring Cyber Security
- Bletchley Park Declaration: The Bletchley Park Declaration is the first global agreement on addressing frontier AI risks, reflecting a broad political consensus among leading AI stakeholders.
- The declaration calls for international cooperation and announces a regular AI Safety Summit for ongoing dialogue and collaboration.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: International treaty for harmonising laws and enhancing international cooperation on cybercrime; in force since July 1, 2004. India is not a signatory.
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI):
- Mission: Ensure AI aligns with human rights, diversity, and innovation while promoting sustainable economic growth.
- Secretariat: Based at the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
- Membership: A global alliance of 29 countries, including the US, UK, Germany, Israel, Singapore, Australia, Belgium, France, and the EU.
- India’s Role: Founding member since June 2020.
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Specialised UN agency focused on telecommunications and cyber security standards and development.
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF): Platform for multi-stakeholder dialogue on internet governance, first convened in October–November 2006.
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN): Non-profit organisation overseeing domain name systems and ensuring stable and secure operation of the internet; headquartered in Los Angeles, U.S.A.
|
Way Forward for Addressing Digital Threats
- Strengthen Cybersecurity Measures: There is a need to establish a precise legal framework mechanism for the use of AI, such as regulations on data protection, transparency in AI-driven advertising and standards for the ethical use of AI.
- Coordinated Efforts: Emphasis on coordinated action and budgetary support to tackle digital threats and protect democratic societies.
- Regulatory Gaps: Current regulations often fall short in addressing the nuances of AI-driven cyber threats, highlighting the need for new legislation to safeguard personal data.
- Public Awareness Initiatives: Educating the public about AI-related risks and cyber threats is essential. Awareness campaigns can help individuals recognize and defend against sophisticated misinformation and cyber fraud.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 13 Aug 2024
13 Aug 2024

 Includes: AI encompasses various subfields and techniques, including:
Includes: AI encompasses various subfields and techniques, including:

