An AI based National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS) was launched by the Union Government to help farmers to connect with agriculture scientists and experts on controlling pests.
- The System is proposed for key pests of selected crops i.e. Rice, Cotton, Maize, Mango and Chilies benefitting about 14 crore farmers in the country
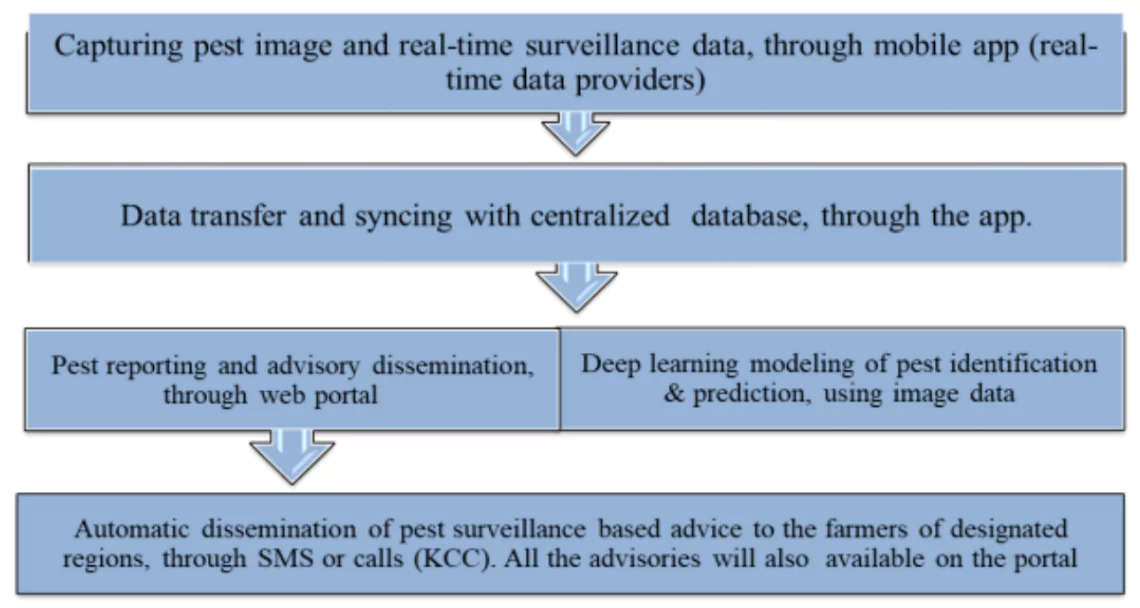
About National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS)
- Implementing Agencies: The project is a collaborative Initiative by the Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage and ICAR-National Research Centre for Integrated Pest Management
- Modal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, GOI
- Aim: To reduce the dependence of farmers on pesticide retailers and inculcate a scientific approach among them towards pest management by analyzing the latest data on pests using AI tools
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Crop
|
Pest
|
| Rice |
Brown planthopper, Rice leaffolders, Rice seed midge |
| Cotton |
Fruit borer (Helicoverpa armigera), Pink bollworm, Spotted bollworms |
| Maize |
Spotted stem borer, pink stem borer [Sesamia inferens Walker], shoot fly [Atherigona spp.] and fall armyworm [Spodoptera frugiperda |
| Mango |
Mango hoppers, mealy bug, stem borer, fruit fly, mango nut weevil |
| Chillies |
Gram pod borer, Tobacco caterpillar, Spider mites, Root-knot nematodes, Thrips. |
| Wheat |
Fall armyworm, Russian wheat aphid, Aphids |
- Significance:
- Timely Access: The system will provide easy and timely access to expert support for pest identification and pest surveillance based pest management advice to farmers
- Minimize Risk: The system will assist in avoiding and better preparation for epidemics which will help minimize crop loss due to pests with the real data submission by Government,resources & lead farmers.Developing a National Repository: A repository of national pest scenario will be available to various public agencies, working in the field of plant protection to identify the pest hotspots and formulate plant protection policies.
- Automate process: The NPSS platform will leverage digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (Al) and smart phones, to automate the process of providing expert support on pest identification and management.
- Field based Mode: NPSS will connect scientists with the fields as Farmers will be the point source of information by taking photos of the infested crops or the insect using the NPSS platform and these will reach scientists and experts.
- Address Pesticide Overuse Problem: NPSS will help the farmers to use the correct quantity of correct pesticide at the correct time by giving timely advisories.
- Precision Diagnosis: The Technology will help in accurate diagnosis and accurate treatment building confidence among farmers and increasing production
Economic Cost of Pest Attacks
- Global estimates: As per FAO, Pests account for 20-40% of yield losses worldwide, costing the global economy a combined $290 billion
- Yield losses of up to 70% can occur across many major food crops, with weeds contributing for the highest losses at 30%, followed by animal pests and pathogens at 23% and 17%, respectively in the absence of crop protection.
- Climate Change: Some figures assert that every 1 degree increase in global temperatures will increase pest-linked yield losses by 10-25%.
- India: The crop yield losses due to insect pests, diseases, nematodes, weeds and rodents range from 15-25 percent in India, amounting to 0.9 to 1.4 lakh crore rupees a year
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
India’s Plant Quarantine System:
- Implementing Agency: The Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare looks after issues related to plant quarantine.
- Legal Provision: Plant Quarantine regulatory measures are operative through the ‘Destructive Insects & Pests Act, 1914 (Act2 of 1914)’
- Import Regulation: The import of agricultural commodities is presently regulated through the Plant Quarantine (Regulation of Import in to India) Order, 2003
- For import of new commodities, Pest Risk Analysis is mandatory and should be submitted to the Plant Protection Adviser to the Govt. of India.
- Objective: It is to inspect imported agricultural commodities for preventing the introduction of exotic pests and diseases inimical to Indian fauna and flora.
|
![]() 16 Aug 2024
16 Aug 2024
