The Multidimensional Vulnerability Index (MVI), a new data-driven “vulnerability” index that would help small island states and developing nations gain access to low-interest financing was officially launched by The UN General Assembly.
- The Index will act as a complement to GDP and other development metrics.
- Voluntary: The use of the index is voluntary, but the UN has called out on its organs and multilateral development banks to consider using the new tool to complement existing policies.
About Multidimensional Vulnerability Index
- Multidimensional Vulnerability Index focuses on vulnerabilities that could put someone at risk of falling into poverty by considering dimensions and indicators crucial to measure the extent of vulnerabilities.
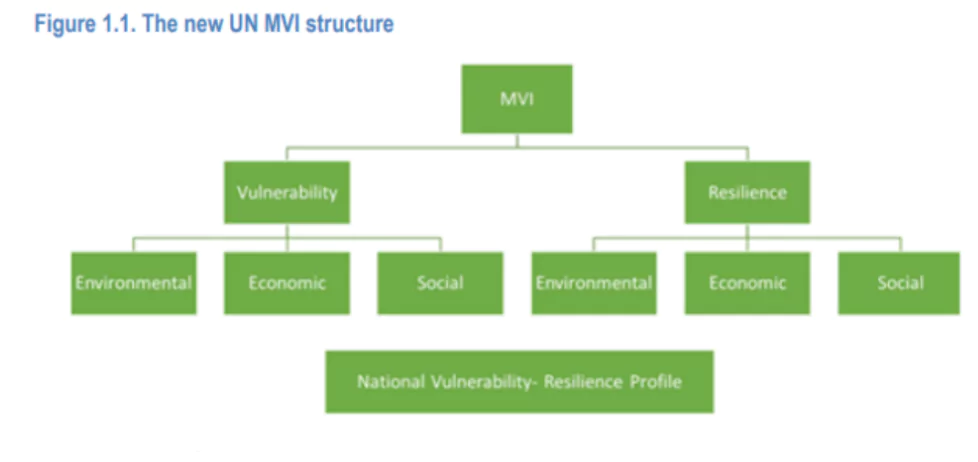
- Dimensions and Indicators: The vulnerability is assessed in three critical dimensions ie. Education, Health and Disaster, and Living Standards measured by 12 indicators.
- Factors: It include import dependency, exposure to extreme weather events and pandemics, impacts of regional violence, refugees, demographic pressure, water and arable land resources and mortality of children under five
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Origin: A call for the development of a globally accepted vulnerability assessment was first made in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development which was repeated by SIDS in 1994, in the Programme of Action for the Sustainable Development of SIDS.
- Aim: MVI will capture exogenous vulnerabilities and lack of resilience to exogenous shocks of all developing countries
- It will incorporate indicators linked to a state’s structural vulnerabilities and lack of economic, environmental and social resilience.
- How The MVI will be used:
- To facilitate action to address vulnerability and build in-country resilience through the development of evidence-based policies and partnerships
- To facilitate evidence-based, targeted and effective support and smarter resource allocations
- To complement performance-based allocation models, allowing the use of a vulnerability component
- To support and guide the design of innovative financing mechanisms
- To serve as a tool for monitoring, evaluation and measuring vulnerability and targeted policies in that regard
- To support and guide the formulation of country vulnerability resilience profiles
![]() 17 Aug 2024
17 Aug 2024

