7th Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

|
Context: Recently, the 7th Rashtriya Poshan Maah was inaugurated with a strong emphasis on enhancing nutrition awareness.
About Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The Rashtriya Poshan Maah is being celebrated during the month of September every year.
- It is celebrated under POSHAN Abhiyaan (PM’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment), which was launched in 2018.
About POSHAN Abhiyaan:
- Overview: It is a flagship programme to improve nutritional outcomes for children under 6 years of age, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD).
- Mission Poshan 2.0 (Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0): It has been launched as an integrated nutrition support program to strengthen nutritional content, delivery, outreach and outcomes.
- It focuses on developing practices that nurture health, wellness and immunity to disease and malnutrition.
|
AgriSURE Fund & Krishi Nivesh Portal

|
Context: Union Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare and Rural Development Minister launched AgriSURE Fund & Krishi Nivesh Portal recently at PUSA, New Delhi.
About Agri Fund for Start-Ups & Rural Enterprises (AgriSURE):
- Launched: To support start-ups and agripreneurs through investments in sector-specific, sector-agnostic, and debt Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs), as well as direct equity support to start-ups working in Agriculture and allied sectors.
- Aim: To foster innovation and sustainability in India’s agricultural sector through the establishment of a Rs 750 crore Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF).
- The fund will offer both equity and debt support, specifically targeting high-risk, high- impact activities in the agriculture value chain.
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- NABVENTURES, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NABARD, will act as the Fund manager of AgriSURE.
About Krishi Nivesh Portal:
- Aim: To boost the agriculture investment in the country.
- Developed: As an Integrated, centralized one stop Portal for all Agri- investors to avail benefits from various Government schemes.
|
eShram Portal

|
Context: In a short span of three years since its launch, eShram has registered more than 30 crore unorganised workers.
About eShram Portal:
- e-Shram Portal: It is a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW), seeded with Aadhaar.
- Launch: The Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) launched the eShram portal in August 2021.
- Purpose: It will have comprehensive details of worker for optimum realization of their employability and extend the benefits of the social security schemes to them.
- Unorganised Worker: Any worker who is a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker working in the unorganised sector and not a member of ESIC or EPFO, is called an unorganised worker.
- Significance: It is the first-ever national database of unorganised workers including migrant workers, construction workers, gig and platform workers, etc.
|
Semiconductor Chip Manufacturing
|
Context: The Union Cabinet has recently cleared a semiconductor assembly and testing plant being set up by Kaynes Semicon at a cost of Rs 3,300 crore.
Chip Manufacturing in India:
- Chip Hub: India has ambitions to become a major chip hub on the lines of the United States, Taiwan and South Korea.
- Previous Projects:
- Country has approved a fabrication plant worth $11 billion being set up by Tata Electronics in partnership with Taiwan’s Powerchip.
- Three different chip assembly plants being set up by the Tatas, US-based Micron Technology, and Murugappa Group’s CG Power in partnership with Japan’s Renesas.
- Subsidy: Approved under India’s ambitious Rs 76,000 crore chip manufacturing incentive scheme.
About Semiconductors:
- Semiconductor: it is a material that exhibits properties of both insulators and conductors.
- Composition: Typically made of silicon.
- Doping Process: The conductivity and other properties of semiconductors can be modified by introducing impurities.
- Common Uses: Integral to a wide range of products including Computers, Smartphones, Appliances, Gaming hardwares, Medical equipments etc.
|
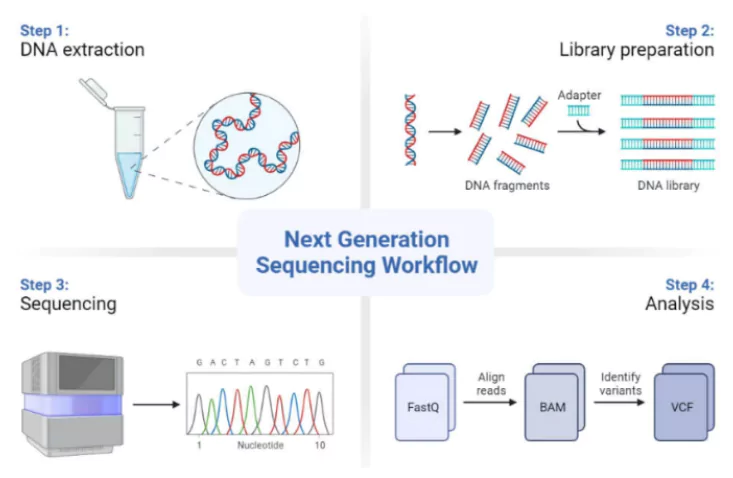
Next-Generation Sequencing
|
Context: National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB) using next generation sequencing for genetic print of indigenous cattle.
About Genetic Sequencing:
- Genetic Sequencing: It is the process of determining the order of the four chemical building blocks, or nucleotides, that makeup an organism’s DNA.
- Methods of Genetic Sequencing: Includes Sanger sequencing, Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), and Single Molecule Real-Time (SMRT) sequencing.
About Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS):
- NGS: It is a technology for determining the sequence of DNA or RNA to study genetic variation associated with diseases or other biological phenomena.
- Also known as high-throughput sequencing.
- Significance: Allow for sequencing of DNA and RNA much more quickly and cheaply than the previously used Sanger sequencing
- Advantages of NGS:
- It offers single-nucleotide resolution, making it possible to detect related genes, allelic gene variants etc.
- Higher dynamic range of signal.
- Requires less DNA/RNA as input.
- Offers higher reproducibility.
|
Project Bhediya

|
Context: The Uttar Pradesh government launched ‘Operation Bhediya’ to capture the pack of wolves that has killed several people.
About Operation Bhediya:
- Objective: To catch wolves that are targeting children and villagers in Uttar Pradesh’s Bahraich.
- Innovative Effort: The forest department is using “teddy dolls” soaked in children’s urine as a false bait to capture these predators.
About Indian Wolf (Canis Lupus Pallipes):
- Description: Intermediate in size, positioned between the Tibetan and Arabian wolf.
- Habitat: Found in areas with scrub, grasslands, and semi-arid pastoral agro-ecosystems.
- Distribution: Widely distributed from the Indian subcontinent to Israel.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Least Concern
- Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972: Schedule I
- CITES : Appendix 1
|
![]() 3 Sep 2024
3 Sep 2024